Abstract
Background
Oncoplastic breast surgery is more likely to achieve superior aesthetic outcomes compared to lumpectomy alone. Oncoplastic reduction mammoplasty (ORM) is a volume displacement oncoplastic technique that combines lumpectomy and reduction mammoplasty. Data on aesthetic and quality-of-life (QoL) outcomes after ORM are scarce in the literature. Based on a literature review, this present study reports outcomes on the largest group of ORM patients to date.
Methods
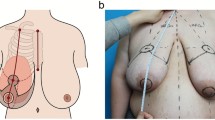
A retrospective review was conducted of all patients who underwent ORM between 2011 and 2018 at a tertiary care centre. Patients were excluded if no pedicle information was available or did not undergo post-operative radiotherapy. All patients with available post-operative photographs were aesthetically evaluated by four blinded, independent investigators blinded based on breast symmetry, nipple symmetry, and overall appearance. The BREAST-Q (breast conserving module) was used to assess QoL outcomes.
Results
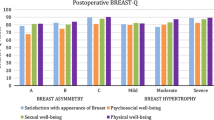
Two-hundred-and-sixteen consecutive patients (223 breasts) were included. Macromastia (cup size D or higher) was present in 173 patients (80.1%). Inferior pedicle ORM was utilized in 179 (80.3%) breasts. Eighty-eight patients (40.7%) were aesthetically evaluated, of whom 69 patients (78.4%) had “good”, “very good”, or “excellent” grades in all aesthetic categories. Seventy-five patients (85.2%) had “good” or better grades in overall appearance. Preoperative ptosis grade, cup size, presence of post-operative complications, and breast specimen weight had no significant correlations with aesthetic grades. Inferior pedicle ORM was associated with a higher “satisfaction with breast” Q-score (p=0.017) compared to other pedicle approaches.
Conclusion
Inferior pedicle ORM achieves objectively excellent aesthetic outcomes and high patient satisfaction with the reconstruction.
Level of Evidence IV
This journal requires that authors assign a level of evidence to each article. For a full description of these Evidence-Based Medicine ratings, please refer to the Table of Contents or the online Instructions to Authors www.springer.com/00266.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jonczyk MM, Jean J, Graham R et al (2019) Surgical trends in breast cancer: a rise in novel operative treatment options over a 12 year analysis. Breast Cancer Res Tr 173:267–274
Mansell J, Weiler-Mithoff E, Stallard S et al (2017) Oncoplastic breast conservation surgery is oncologically safe when compared to wide local excision and mastectomy. Breast 32:179–185
Barnea Y, Inbal A, Barsuk D et al (2014) Oncoplastic reduction using the vertical scar superior-medial pedicle pattern technique for immediate partial breast reconstruction. Can J Surg 57:E134–E140
Chan SWW, Chueng PSY, Lam SH (2010) Cosmetic outcome and percentage of breast volume excision in oncoplastic breast conserving surgery. World J Surg 34:1447–1452
Losken A, Dugal CS, Styblo TM et al (2014) A meta-analysis comparing breast conservation therapy alone to the oncoplastic technique. Ann Plas Surg 72:145–149
D’Aniello C, Grimaldi L, Barbato A et al (1999) Cosmetic results in 242 patients treated by conservative surgery for breast cancer. Scand J Plast Reconstr Surg Hand Surg 34:419–422
Clough KB, Cuminet J, Fitoussi A et al (1998) Cosmetic sequelae after conservative treatment for breast cancer: classification and results of surgical correction. Ann Plast Surg 41:471–481
Munhoz AM, Montag E, Arruda E et al (2008) Assessment of immediate conservative breast surgery reconstruction: a classification system of defects revisited and an algorithm for selecting the appropriate technique. Plast Reconstr Surg 121:716–727
Santos G, Urban C, Edelweiss MI et al (2015) Long-term comparison of aesthetical outcomes after oncoplastic surgery and lumpectomy in breast cancer patients. Ann Surg Oncol 22:2500–2508
Chang EI, Peled AW, Foster RD et al (2012) Evaluating the feasibility of extended partial mastectomy and immediate reduction mammoplasty reconstruction as an alternative to mastectomy. Ann Surg 255:1151–1157
Clough KB, Lewis JS, Couturaud B et al (2003) Oncoplastic techniques allow extensive resections for breast-conserving therapy of breast carcinomas. Ann Surg 237:26–34
Peled AW, Sbitany H, Foster RD et al (2014) Oncoplastic mammoplasty as a strategy for reducing reconstructive complications associated with postmastectomy radiation therapy. Breast J 20:302–307
Clough KB, Kaufman GJ, Nos C et al (2010) Improving breast cancer surgery: a classification and quadrant per quadrant atlas for oncoplastic surgery. Ann Surg Oncol 17:1375–1391
Scomacao I, Al-Hilli Z, Schwarz G (2020) The role of oncoplastic surgery for breast cancer. Curr Treat Options Oncol 21:1–11
Audretsch W, Rezai M, Kolotas C et al (1998) Tumor-specific immediate reconstruction in breast cancer patients. Semin Plast Surg 11:71–100
Kronowitz SJ, Kuerer HM, Buchholz TA et al (2008) A management algorithm and practical oncoplastic surgical techniques for repairing partial mastectomy defects. Plast Reconstr Surg 122:1631–1647
Duraes EFR, Durand P, Morisada M et al (2022) A novel validated breast aesthetic scale – VBRAS. Plast Reconstr Surg 149:1297–1308
Klassen AF, Dominici L, Fuzesi S et al (2020) Development and validation of the BREAST-Q breast conserving therapy module. Ann Surg Onc 27:2238–2247
Kronowitz SJ, Hunt KK, Kuerer HM et al (2007) Practical guidelines for repair of partial mastectomy defects using the breast reduction technique in patients undergoing breast conservation therapy. Plast Reconstr Surg 120:1755–1768
Matory WE Jr, Wertheimer M, Fitzgerald TJ et al (1990) Aesthetic results following partial mastectomy and radiation therapy. Plast Reconstr Surg 85:739–746
Piper ML, Esserman LJ, Sbitany H et al (2016) Outcomes following oncoplastic reduction mammoplasty: a systematic review. Ann Plast Surg 76:S222–S226
Emiroglu M, Sert I, Karaali C et al (2016) The effectiveness of simultaneous oncoplastic breast surgery in patients with locally advanced breast cancer. Breast Cancer 23:463–470
Munhoz AM, Montag E, Arruda EG et al (2006) Critical analysis of reduction mammaplasty techniques in combination with conservative breast surgery for early breast cancer treatment. Plast Reconstr Surg 117:1091–1103
Gray JR, McCormick B, Cox L et al (1991) Primary breast irradiation in large-breasted or heavy women: analysis of cosmetic outcome. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 21:347–354
Atisha DM, Alderman AK, Kuhn LE et al (2008) The impact of obesity on patient satisfaction with breast reconstruction. Plast Reconstr Surg 121:1893–1899
Emiroglu M, Sert I, Inal A (2015) The role of oncoplastic breast surgery in breast cancer treatment. J Breast Health 11:1–9
Davison SP, Mesbahi AN, Ducic I et al (2007) The versatility of the superomedial pedicle with various skin reduction patterns. Plast Reconstr Surg 120:1466–1476
Habibi M, Broderick KP, Sebai ME et al (2018) Oncoplastic breast reconstruction: should all patients be considered. Surg Oncol Clin N Am 27:167–180
Hall-Findlay EJ, Shestak KC (2015) Breast reduction. Plast Reconstr Surg 136:531e–544e
Weber WP, Haug M, Kurzeder C et al (2018) Oncoplastic breast consortium consensus conference on nipple-sparing mastectomy. Breast Cancer Res Treat 172:523–537
Mundy LR, Homa K, Klassen AF et al (2017) Breast cancer and reconstruction: normative data for interpreting the BREAST-Q. Plast Reconstr Surg 139:1046e–1055e
Howes BH, Watson DI, Xu C et al (2016) Quality of life following total mastectomy with and without reconstruction versus breast-conserving surgery for breast cancer: a case-controlled cohort study. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg 69:1184–1191
Di Micco R, O’Connell RL, Barry PA et al (2017) Standard wide local excision or bilateral reduction mammoplasty in large-breasted women with small tumours: surgical and patient-reported outcomes. Eur J Surg Oncol 43:636–641
Gardfjell A, Dahlbäck C, Åhsberg K (2019) Patient satisfaction after unilateral oncoplastic volume displacement surgery for breast cancer, evaluated with the BREAST-QTM. World J Surg Oncol 17:96
Agrawal A (2019) Oncoplastic breast surgery and radiotherapy-Adverse aesthetic outcomes, proposed classification of aesthetic components, and causality attribution. Breast J 25:207–218
Yi A, Kim HH, Shin HJ et al (2009) Radiation-induced complications after breast cancer radiation therapy: a pictorial review of multimodality imaging findings. Korean J Radiol 10:496–507
Kronowitz SJ, Feledy JA, Hunt KK et al (2006) Determining the optimal approach to breast reconstruction after partial mastectomy. Plast Reconstr Surg 117:1–11
Mattingly AE, Ma Z, Smith PD et al (2017) Early postoperative complications after oncoplastic reduction. South Med J 110:660–666
Acknowledgements
None.
Funding
No funding was received for this stud.y
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose pertaining to this study.
Ethical approval
Ethical approval of the review methodology was granted by the Institutional Review Board (IRB). This study was conducted in accordance with the Helsinki Declaration.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Xia, T.Y., Scomacao, I., Duraes, E. et al. Aesthetic, Quality-of-Life, and Clinical Outcomes after Inferior Pedicle Oncoplastic Reduction Mammoplasty. Aesth Plast Surg 47, 905–911 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00266-023-03257-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00266-023-03257-7