Abstract
Background
Keloid and hypertrophic scars are the most common types of pathological scars. They can cause itching, pain, erythema, and psychological stress due to cosmetic problems, decreasing the quality of life for affected individuals. The neodymium-doped yttrium aluminum garnet (Nd:YAG) multipurpose laser is used to treat pathological scars, and studies have shown that the Nd:YAG laser can markedly improve scarring.
Aims
We performed a meta-analysis to evaluate the efficacy of the Nd:YAG laser in the treatment of keloid and hypertrophic scars.
Methods
A literature search of PubMed, Web of Science, Scopus, Cochrane, Embase, CNKI, and Wanfang was performed between January 1st, 2010, and July 14th, 2021. The Vancouver Scar Scale (VSS) was used to evaluate treatment outcomes. We used the R version 4.0.0 software for statistical analysis.
Results
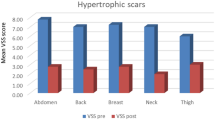
The Nd:YAG laser improved the condition of keloid and hypertrophic scars and reduced VSS score (mean difference [MD]: 2.96, 95% confidence interval [CI]: 2.08–3.84, p < 0.01). There was no obvious difference in the results between regions. A subgroup analysis by scar type revealed that the curative effect of the Nd:YAG laser on keloid scars (MD: 2.02, 95% CI: 0.58–4.63, p = 0.10) was less marked compared with that on hypertrophic scars (MD: 3.05, 95% CI: 1.58–4.52, p < 0.01). With the combined use of the Nd:YAG laser and other treatment methods, a more significant change in VSS score was noted (MD: 4.28, 95% CI: 2.07–6.49).
Conclusions
This meta-analysis showed that the Nd:YAG laser can improve the condition of keloid and hypertrophic scars and effectively reduce VSS score. Moreover, the curative effect of this approach on keloid scars is less marked compared with that on hypertrophic scars.
Level of evidence III
This journal requires that authors assign a level of evidence to each article. For a full description of these Evidence-Based Medicine ratings, please refer to the Table of Contents or the online Instructions to Authors www.springer.com/00266






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hedayatyanfard K, Haddadi NS, Ziai SA, Karim H, Niazi F, Steckelings UM et al (2020) The renin-angiotensin system in cutaneous hypertrophic scar and keloid formation. Exp Dermatol 29(9):902–909. https://doi.org/10.1111/exd.14154
Lee HJ, Jang YJ (2018) Recent understandings of biology, prophylaxis and treatment strategies for hypertrophic scars and keloids. Int J Mol Sci 19(3):711. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19030711
Ogawa R, Akita S, Akaishi S, Aramaki-Hattori N, Dohi T, Hayashi T et al (2019) Diagnosis and treatment of keloids and hypertrophic scars-japan scar workshop consensus document 2018. Burns Trauma. 7:39. https://doi.org/10.1186/s41038-019-0175-y
Nischwitz SP, Rauch K, Luze H, Hofmann E, Draschl A, Kotzbeck P et al (2020) Evidence-based therapy in hypertrophic scars: an update of a systematic review. Wound Repair Regen. https://doi.org/10.1111/wrr.12839
Panchaprateep R, Munavalli G (2015) Low-fluence 585 nm Q-switched Nd:YAG laser: a novel laser treatment for post-acne erythema. Lasers Surg Med 47(2):148–155. https://doi.org/10.1002/lsm.22321
Abergel RP, Dwyer RM, Meeker CA, Uitto J, Lask G, Kelly AP (1984) Laser treatment of keloids: a clinical trial and an in vitro study with Nd:YAG laser. Lasers Surg Med 4(3):291–295. https://doi.org/10.1002/lsm.1900040310
Tawfic SO, El-Tawdy A, Shalaby S, Foad A, Shaker O, Sayed SS et al (2020) Evaluation of fractional co2 versus long pulsed ND:YAG lasers in treatment of hypertrophic scars and keloids: a randomized clinical trial. Lasers Surg Med. https://doi.org/10.1002/lsm.23249
Cho SB, Lee JH, Lee SH, Lee SJ, Bang D, Oh SH (2010) Efficacy and safety of 1064-nm Q-switched Nd:YAG laser with low fluence for keloids and hypertrophic scars. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol 24(9):1070–1074. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1468-3083.2010.03593.x
Koike S, Akaishi S, Nagashima Y, Dohi T, Hyakusoku H, Ogawa R (2014) Nd:YAG laser treatment for keloids and hypertrophic scars: an analysis of 102 cases. Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open 2(12):e272. https://doi.org/10.1097/GOX.0000000000000231
Hultman CS, Edkins RE, Wu C, Calvert CT, Cairns BA (2013) Prospective, before-after cohort study to assess the efficacy of laser therapy on hypertrophic burn scars. Ann Plast Surg 70(5):521–526. https://doi.org/10.1097/SAP.0b013e31827eac5e
Alster TS, Lewis AB, Rosenbach A (1998) Laser scar revision: comparison of CO2 laser vaporization with and without simultaneous pulsed dye laser treatment. Dermatolo Surg: Off Publ Am Soc Dermatol Surg 24(12):1299–1302. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1524-4725.1998.tb00003.x
Brewin MP, Lister TS (2014) Prevention or treatment of hypertrophic burn scarring: a review of when and how to treat with the pulsed dye laser. Burns: J Int Soc Burn Injuries. 40(5):797–804. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.burns.2013.12.017
Choi YJ, Kim JY, Nam JH, Lee GY, Kim WS (2019) Clinical outcome of 1064-nm picosecond neodymium-doped yttrium aluminium garnet laser for the treatment of hypertrophic scars. J Cosmet Laser Ther 21(2):91–98. https://doi.org/10.1080/14764172.2018.1469768
Akaishi S, Koike S, Dohi T, Kobe K, Hyakusoku H, Ogawa R (2012) Nd:YAG laser treatment of keloids and hypertrophic scars. Eplasty. 12:1
Tian WC (2016) Savior of post-blepharoepicanthoplasty scarring: Novel use of a low-fluence 1064-nm Q-switched Nd:YAG laser. J Cosmet Laser Ther 18(2):69–71. https://doi.org/10.3109/14764172.2015.1063661
Al-MohamadyAel S, Ibrahim SM, Muhammad MM (2016) Pulsed dye laser versus long-pulsed Nd:YAG laser in the treatment of hypertrophic scars and keloid: a comparative randomized split-scar trial. J Cosmet Laser Ther 18(4):208–212. https://doi.org/10.3109/14764172.2015.1114648
Sj L, Jw L, Sh K, Is S, Hs J (2019) Comparison of the scar prevention effect between a carbon dioxide fractional laser and a continuous ablative carbon dioxide laser with a 595-nm ND:YAG laser. Aesthetic Plast Surg 43(1):213–220. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00266-018-1210-2
Elrefaie AM, Salem RM, Faheem MH (2020) High-resolution ultrasound for keloids and hypertrophic scar assessment. Lasers Med Sci 35(2):379–385. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10103-019-02830-4
Gold MH, McGuire M, Mustoe TA, Pusic A, Sachdev M, Waibel J et al (2014) Updated international clinical recommendations on scar management: part 2–algorithms for scar prevention and treatment. Dermatolo Surg: Off Publ Am Soc Dermatol Surg 40(8):825–831. https://doi.org/10.1111/dsu.0000000000000050
Rubin IK, Farinelli WA, Doukas A, Anderson RR (2012) Optimal wavelengths for vein-selective photothermolysis. Lasers Surg Med 44(2):152–157. https://doi.org/10.1002/lsm.21161
Wattanakrai P, Mornchan R, Eimpunth S (2010) Low-fluence Q-switched neodymium-doped yttrium aluminum garnet (1,064 nm) laser for the treatment of facial melasma in Asians. Dermatolo Surg: Off Publ Am Soc Dermatol Surg 36(1):76–87. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1524-4725.2009.01383.x
Jih MH, Kimyai-Asadi A (2008) Fractional photothermolysis: a review and update. Semin Cutan Med Surg 27(1):63–71. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sder.2008.01.002
Eichenfield DZ, Ortiz AE (2020) Efficacy and safety of the 532-nm KTP and long-pulsed 1064-nm neodymium-doped yttrium aluminum garnet laser for treatment of vascular malformations. Dermatolo Surg: Off Publ Am Soc Dermatol Surg 46(12):1535–1539. https://doi.org/10.1097/dss.0000000000002386
Murthy AS, Dawson A, Gupta D, Spring S, Cordoro KM (2017) Utility and tolerability of the long-pulsed 1064-nm neodymium:yttrium-aluminum-garnet (LP Nd:YAG) laser for treatment of symptomatic or disfiguring vascular malformations in children and adolescents. J Am Acad Dermatol 77(3):473–479. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaad.2017.04.014
Monib KME, Hussein MS (2020) Nd:YAG laser vs IPL in inflammatory and noninflammatory acne lesion treatment. J Cosmet Dermatol 19(9):2325–2332. https://doi.org/10.1111/jocd.13278
Zoccali G, Piccolo D, Allegra P, Giuliani M (2010) Melasma treated with intense pulsed light. Aesthetic Plast Surg 34(4):486–493. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00266-010-9485-y
Tawfic SO, El-Tawdy A, Shalaby S, Foad A, Shaker O, Sayed SS et al (2020) Evaluation of fractional CO(2) versus long pulsed Nd:YAG lasers in treatment of hypertrophic scars and keloids: a randomized clinical trial. Lasers Surg Med 52(10):959–965. https://doi.org/10.1002/lsm.23249
Ogawa R, Dohi T, Tosa M, Aoki M, Akaishi S (2021) The latest strategy for keloid and hypertrophic scar prevention and treatment: the nippon medical school (NMS) protocol. J Nippon Med School Nippon Ika Daigaku zasshi. 88(1):2–9. https://doi.org/10.1272/jnms.JNMS.2021_88-106
Rossi A, Lu R, Frey MK, Kubota T, Smith LA, Perez M (2013) The use of the 300 microsecond 1064 nm Nd:YAG laser in the treatment of keloids. J Drugs Dermatol: JDD. 12(11):1256–1262
Chen XE, Liu J, Bin Jameel AA, Valeska M, Zhang JA, Xu Y et al (2017) Combined effects of long-pulsed neodymium-yttrium-aluminum-garnet laser, diprospan and 5-fluorouracil in the treatment of keloid scars. Exp Ther Med 13(6):3607–3612. https://doi.org/10.3892/etm.2017.4438
Tsai CH, Kao HK, Akaishi S, An-Jou Lin J, Ogawa R (2020) Combination of 1064-nm neodymium-doped yttrium aluminum garnet laser and steroid tape decreases the total treatment time of hypertrophic scars: an analysis of 40 cases of cesarean-section scars. Dermatol Surg: Off Publ Am Soc Dermatol Surg 46(8):1062–1067. https://doi.org/10.1097/dss.0000000000002235
Annabathula A, Sekar CS, Srinivas CR (2017) Fractional carbon dioxide, long pulse Nd:YAG and pulsed dye laser in the management of keloids. J Cutan Aesthet Surg 10(2):76–80. https://doi.org/10.4103/jcas.jcas_136_16
Jinping D, Bo C, Yilin C (2016) Research progress of laser treatment for pathological scar. J Tissue Eng Reconstr Surg. 12(2):141–3
Acknowledgments
The present study was supported by the National Natural Foundation of China (Grant No. 81971842) and the Jilin Scientific and Technological Development Program (20190701039GH; 20200201371JC; 20200201580JC).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Human and Animal Rights
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Informed Consent
For this type of study, informed consent is not required.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pan, L., Qin, H., Li, C. et al. Efficacy of the Neodymium-Doped Yttrium Aluminum Garnet Laser in the Treatment of Keloid and Hypertrophic Scars: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Aesth Plast Surg 46, 1997–2005 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00266-021-02716-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00266-021-02716-3