Abstract
Background
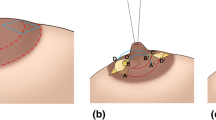
Various operative methods exist for nipple reconstruction. Selection of an appropriate skin flap and core strut material is imperative in achieving a satisfactory outcome in nipple reconstruction. Long-term maintenance of nipple projection requires further investigation by surgeons. We propose a new technique that uses a semilunar flap and omega-shaped acellular dermal matrix (ADM).
Methods
Total 53 nipples were reconstructed by this method. An omega-shaped ADM strut was inserted into the barrel made by a semilunar flap. The footplates of omega-shaped ADM struts were spread out under the subcutaneous tissue of the donor site of the semilunar flap to support the dome of the omega strut.
Results
The mean maintenance rate of nipple projection was 95.12 ± 6.30% at 3 weeks, 80.60 ± 8.93% at 3 months, and 71.70 ± 8.67% at 6 months postoperatively when compared to the projection observed in the immediate postoperative period. Thirty-five patients (66.0%) showed a maintenance rate over 70% at 6 months post operation, with most patients (94.3%) demonstrating a maintenance rate greater than 60%.
Conclusions
Our study with the omega-shaped ADM strut showed superior maintenance rates of projection when compared to other studies on that used AlloDerm® as a core strut for nipple reconstruction. Omega-shaped struts, when made with cross-linked thick ADM, supported the skin flap quite well. We propose that our method combining the semilunar flap with an omega-shaped ADM may be a good option for nipple reconstruction.
Level of Evidence IV
"This journal requires that authors assign a level of evidence to each article. For a full description of these Evidence-Based Medicine ratings, please refer to the Table of Contents or the online Instructions to Authors www.springer.com/00266."







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Momoh AO, Colakoglu S, de Blacam C et al (2012) The impact of nipple reconstruction on patient satisfaction in breast reconstruction. Ann Plast Surg 69:389–393
Farhadi J, Maksvytyte GK, Schaefer DJ et al (2006) Reconstruction of the nipple-areola complex: an update. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg 59:40–53
Little JW III, Munasifi T, McCulloch DT (1983) One-stage reconstruction of a projecting nipple: the quadrapod flap. Plast Reconstr Surg 71:126–133
Cohen IK, Ward JA, Chandrasekhar B (1986) The pinwheel flap nipple and barrier areola graft reconstruction. Plast Reconstr Surg 77:995–999
Serafin D, Georgiade N (1982) Nipple-areola reconstruction after mastectomy. Ann Plast Surg 8:29–34
Losken A, Mackay GJ, Bostwick J III (2001) Nipple reconstruction using the C-V flap technique: a long-term evaluation. Plast Reconstr Surg 108:361–369
Anton MA, Eskenazi LB, Hartrampf CR Jr (1991) Nipple reconstruction with local flaps: star and wrap flaps. Perspect Plast Surg 5:68–78
Little JW III (1984) Nipple-areola reconstruction. Clin Plast Surg 11:351–364
Valdatta L, Montemurro P, Tamborini F et al (2009) Our experience of nipple reconstruction using the C-V flap technique 1 year evaluation. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg 62:1293–1298
Bernard RW, Beran SJ (2003) Autologous fat graft in nipple reconstruction. Plast Reconstr Surg 112:964–968
Temiz G, Yesiloglu N, Sirinoglu H, Sarici M (2015) A new modification of C-V flap technique in nipple reconstruction: rolled triangular dermal-fat flaps. Aesthetic Plast Surg 39:173–175
Collis N, Garrido A (2000) Maintenance of nipple projection using auricular cartilage. Plast Reconstr Surg 105:2276–2277
Guerra AB, Khoobehi K, Metzinger SE, Allen RJ (2003) New technique for nipple areola reconstruction: arrow flap and rib cartilage graft for long-lasting nipple projection. Ann Plast Surg 50:31–37
Nahabedian MY (2005) Secondary nipple reconstruction using local flaps and AlloDerm. Plast Reconstr Surg 115:2056–2061
Garramone CE, Lam B (2007) Use of AlloDerm in primary nipple reconstruction to improve long-term nipple projection. Plast Reconstr Surg 119:1663–1668
Seaman BJ, Akbari SR, Davison SP (2012) A novel technique for nipple-areola complex reconstruction: the acellular dermal matrix onlay graft. Plast Reconstr Surg 129:580e–581e
Chen WF, Barounis D, Kalimuthu R (2010) A novel cost-saving approach to the use of acellular dermal matrix (AlloDerm) in postmastectomy breast and nipple reconstructions. Plast Reconstr Surg 125:479–481
Lee JW, Hwang E (2018) Semilunar flap for minimizing the scar length in nipple reconstruction. Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open 6:e1947
Sisti A, Grimaldi L, Tassinari J et al (2016) Nipple-areola complex reconstruction techniques: a literature review. Eur J Surg Oncol 42(4):441–465
Haslik W, Nedomansky J, Hacker S et al (2015) Objective and subjective evaluation of donor-site morbidity after nipple sharing for nipple areola reconstruction. J Plastic Reconstr Aesthetic Surg 68:168–174
Yanaga H (2003) Nipple-areola reconstruction with a dermal-fat flap: technical improvement from rolled auricular cartilage to artificial bone. Plast Reconstr Surg 112(7):1863–1869
Park GY, Yoon ES, Cho HE et al (2016) Acellular dermal matrix as a core strut for projection in nipple reconstruction: approaches for three different methods of breast reconstruction. Arch Plast Surg 43(5):424–429
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they do not have any conflict of interest.
Ethical Approval
The study was performed after approval by the CHA University Bundang CHA Medical Center Internal Review Board (CHAMC 2020-02-016).
Informed Consent
Informed consent is not required for this type of retrospective study.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hwang, E., Yang, J.Y., Ha, H.J. et al. Nipple Reconstruction Using the Semilunar Flap and Omega-shaped Acellular Dermal Matrix Strut. Aesth Plast Surg 46, 152–160 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00266-021-02438-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00266-021-02438-6