Abstract
Background
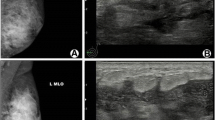
Granulomatous mastitis (GM) is not among the well-known diseases in the field of aesthetic breast surgery (ABS). The clinical presentation of GM resembles infectious diseases or malignancies, but the management of these diseases is quite different. In this study, we aimed to present the management of GM in patients who underwent ABS.
Methods
In this study, patients with GM (n = 65) and patients who underwent ABS (n = 531) were evaluated. A total of six GM patients with a history of ABS were included in the study between January 1, 2010, and January 1, 2019. The data were collected retrospectively. The quantitative variables are shown as medians (minimum–maximum), and categorical variables are shown as numbers and percentages (%).
Results
Median duration of disease onset after the ABS was 16 (8–38) months. After the diagnosis of GM was obtained, all patients received steroid treatment. Median steroid treatment duration was 10 (8–20) weeks. Methotrexate was administered in two patients due to persistent breast mass and steroid side effect. Surgical excision was performed in three patients with wide excision. No patient needed further surgery such as mastectomy. Median follow-up period was 37.5 (18–70) months.
Conclusion
This is the first study to declare GM in patients who underwent ABS. Atypical clinical presentation such as breast abscess, mass or fistula after ABS should alert the surgeon about GM. Unlike other mastitis, the primary treatment of this rare disease is steroid and immunosuppressive treatment. Insufficient knowledge about GM can lead to unnecessary surgeries or breast loss.
Level of Evidence IV
This journal requires that authors assign a level of evidence to each article. For a full description of these Evidence-Based Medicine ratings, please refer to the Table of Contents or the online Instructions to Authors www.springer.com/00266.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Fischer JP, Cleveland EC, Shang EK, Nelson JA, Serletti JM (2014) Complications following reduction mammaplasty: a review of 3538 cases from the 2005–2010 NSQIP data sets. Aesthet Surg J 34:66–73
Spear SL, Dayan JH, Clemens MW (2009) Augmentation mastopexy. Clin Plast Surg 36:105–115
Gurleyik G, Aktekin A, Aker F, Karagulle H, Saglam A (2012) Medical and surgical treatment of idiopathic granulomatous lobular mastitis: a benign inflammatory disease mimicking invasive carcinoma. J Breast Cancer 15:119–123
de Vita R, Buccheri EM, Villanucci A, Ragusa LA (2019) Breast asymmetry, classification, and algorithm of treatment: our experience. Aesthet Plast Surg 43(6):1439–1450
Nava MB, Rancati A, Angrigiani C, Angrigiani C, Catanuto G, Rocco N (2017) How to prevent complications in breast augmentation. Gland Surg 6:210–217
Hidalgo DA, Spector JA (2013) Mastopexy. Plast Reconstr Surg 132:642–656
Wirthmann AE, Welsch L, Wellenbrock SV, Kasper L, Schlosshauer T, Bozkurt A, Hüttinger S, Rieger UM (2018) Reduction mammoplasty in adolescents and elderly: a ten year case series analyzing age related outcome with focus on safety and complications. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg 71:377–383
Reisman NR (2016) Medicolegal issues in breast reduction. Clin Plast Surg 43:441–444
Atak T, Sagiroglu J, Eren T, Ozemir IA, Alimoglu O (2015) Strategies to treat idiopathic granulomatous mastitis: retrospective analysis of 40 patients. Breast Dis 35:19–24
Altintoprak F, Kivilcim T, Ozkan OV (2014) Aetiology of idiopathic granulomatous mastitis. World J Clin Cases 16:852–858
Cohen WA, Homel P, Patel NP (2016) Does time affect patient satisfaction and health-related quality of life after reduction mammoplasty? Eplasty 21(16):e7
Honigman RJ, Phillips KA, Castle DJ (2004) A review of psychosocial outcomes for patients seeking cosmetic surgery. Plast Reconst Surg 113:1229–1237
Klassen AF, Pusic AL, Scott A, Klok J, Cano SJ (2009) Satisfaction and quality of life in women who undergo breast surgery: a qualitative study. BMC Womens Health 9:11
Purohit S (2008) Reduction mammoplasty. Indian J Plast Surg 41(Suppl 01):64–79
Kessler E, Wolloch Y (1972) Granulomatous mastitis: a lesion clinically simulating carcinoma. Am J Clin Pathol 58:642–646
Atalay C, Kızıltan G, Ozaslan C, Pak I (2011) Idiopathic granulomatous mastitis. J Breast Health 7:203–206
Aydın HO, Baykal A, Konan A, Kaynaroglu V (2019) Idiopathic granulomatous mastitis: factors influencing recovery and recurrence. Eur Res J 5:768–775
Pluguez-Turull CW, Nanyes JE, Quintero CJ, Alizai H, Mais DD, Kist KA, Dornbluth NC (2018) Idiopathic granulomatous mastitis: manifestations at multimodality imaging and pitfalls. Radiographics 38:330–356
Özşen M, Tolunay Ş, Gökgöz MŞ (2018) Granulomatous lobular mastitis: clinicopathologic presentation of 90 cases. Age 34:215–219
Hoda SA (2014) Inflammatory and reactive tumors. In: Hoda SA, Brogi E, Koerner FC, Rosen PP (eds) Rosen’s breast pathology, 4th edn. Lippincott Williams and Wilkins, Philadelphia, pp 37–77
Lester SC, Hicks DG (2016) Inflammatory lesions: granulomatous lobuler mastitis. In: Lester SC, Hicks DG (eds) Diagnostic pathology: breast, 2nd edn. Elsevier, Salt Lake City, UT, pp 596–601
Wolfrum A, Kümmel S, Theuerkauf I, Pelz E, Reinisch M (2018) Granulomatous mastitis: a therapeutic and diagnostic challenge. Breast Care (Basel) 13:413–418
Illman JE, Terra SB, Clapp AJ, Hunt KN, Fazzio RT, Shah SS, Glazebrook KN (2018) Granulomatous diseases of the breast and axilla: radiological findings with pathological correlation. Insights Imaging 9:59–71
Bakaris S, Yuksel M, Ciragil P, Guven MA, Ezberci F, Bulbuloglu E (2006) Granulomatous mastitis including breast tuberculosis and idiopathic lobular granulomatous mastitis. Can J Surg 49:427–430
Vural S, Ertop P, Ceyhan K, Şanli H (2017) An unusual cause of oligoarthritis and erythema nodosum: idiopathic granulomatous mastitis. Arch Rheumatol 32:71–75
Wong T, Lo LW, Fung PY, Lai HYM, She HLH, Ng WKC, Kwok KMK, Lee CM (2016) Magnetic resonance imaging of breast augmentation: a pictorial review. Insights Imaging 7:399–410
Margolis NE, Morley C, Lotfi P, Shaylor SD, Palestrant S, Moy L, Melsaether AN (2014) Update on imaging of the postsurgical breast. Radiographics 34:642–660
Velidedeoglu M, Kilic F, Mete B, Yemisen M, Celik V, Gazioglu E, Ferahman M, Ozaras R, Yilmaz MH, Aydogan F (2016) Bilateral idiopathic granulomatous mastitis. Asian J Surg 39:12–20
Garcia-Rodiguez JA, Pattullo A (2013) Idiopathic granulomatous mastitis: a mimicking disease in a pregnant woman: a case report. BMC Res Notes 14:95
Néel A, Hello M, Cottereau A, Graveleau J, De Faucal P, Costedoat-Chalumeau N, Rondeau-Lutz M, Lavigne C, Chiche L, Hachulla E, Seiberras S, Cabane J, Tournemaine N, Hamidou M (2013) Long-term outcome in idiopathic granulomatous mastitis: a western multicentre study. QJM 106:433–441
Funding
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Authors have no commercial associations or sources of support that might pose a conflict of interest.
Ethical Approval
This study was approved by the Human Ethics Committee of the University (protocol number: 2019/202).
Informed Consent
Written informed consent was obtained from all the patients.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Berkesoglu, M., Dag, A., Tuncel, F. et al. Management of Granulomatous Mastitis Following Aesthetic Breast Surgery. Aesth Plast Surg 45, 875–881 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00266-020-01992-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00266-020-01992-9