Abstract
Background
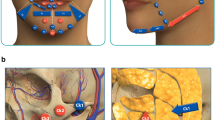
Creating the ideal aesthetic eyebrow shape and position is an important goal in facial rejuvenation. One challenge of an eyebrow lift is to find a predictable procedure that balances the advantages and disadvantages of the available strategies. The gliding brow lifting (GBL) is a technique that provides minimal incisions, an effective and stable eyebrow lift, and offers the advantage of precise reshaping of the eyebrow.
Methods
In a retrospective review, 124 patients, who underwent GBL technique from November 2015 through April 2016, were evaluated. With minimal incisions and tumescent infiltration, the subcutaneous plane of the forehead, eyebrows and temporal face is undermined releasing the skin from the underlying frontalis muscle, orbicularis oculi muscle, corrugator muscle and temporal parietal fascia. Fixation of the repositioned and reshaped eyebrow is achieved with the use of a hemostatic net for temporary cutaneous fixation.
Results
The average follow-up period was 17 months. Adequate brow repositioning and/or reshaping was achieved in 118 patients. Six patients had bilateral or unilateral recurrence of ptosis. Of these patients with recurrence, four patients had the same procedure re-performed within 1 month postoperatively with successful repositioning and/or reshaping of their brow. There was no incidence of hematoma, seroma, infection, permanent sensory changes, motor dysfunction, skin flap necrosis or alopecia.
Conclusion
The “gliding brow lifting” (GBL), which combines subcutaneous frontal undermining with minimal incisions, elevation and reshaping of eyebrow and use of a temporary cutaneous fixation with hemostatic net (Net), allows effective, long-lasting results with low rates of complications and satisfactory results.
Level of Evidence IV
This journal requires that authors assign a level of evidence to each article. For a full description of these Evidence-Based Medicine ratings, please refer to the Table of Contents or the online Instructions to Authors www.springer.com/00266.














Similar content being viewed by others
References
Friedman O (2005) Changes associated with the aging face. Facial Plast Surg Clin N Am 13:371–380
De La Plaza R, Valiente E, Arroyo JM (1991) Supraperiosteal lifting of the upper two-thirds of the face. Br J Plast Surg 44(5):325–332
Knize DM (1998) Reassessment of the coronal incision and subgaleal dissection for foreheadplasty. Plast Reconstr Surg 102(2):478–489
Tessier P (1989) Subperiosteal face-lift. Ann Chir Plast Esthet 34(3):193–197
Psillakis JM, Rumley TO, Camargos A (1988) Subperiosteal approach as an improved concept for correction of the aging face. Plast Reconstr Surg 82(3):383–394
Wojtanowski MH (1993) Subcutaneous forehead lift: a technical alternative for upper facial rejuvenation. Can J Plast Surg 1(3):116–122
Elkwood A, Matarasso A, Rankin M, Elkowitz M, Godek CP (2001) National plastic surgery survey: brow lifting techniques and complications. Plast Reconstr Surg 108(7):2143–2152
Byun S, Mukovozov I, Farrokhyar F, Thoma A (2013) Complications of browlift techniques: a systematic review. Aesthet Surg J 33(2):189–200
Castañares S (1964) Forehead wrinkles, glabellar frown and ptosis of the eyebrows. Plast Reconstr Surg 34:406–413
Vinas JC, Caviglia C, Cortinas JL (1976) Forehead rhytidoplasty and brow lifting. Plast Reconstr Surg 57(4):445–454
Matarasso A, Terino EO (1994) Forehead-brow rhytidoplasty: reassessing the goals. Plast Reconstr Surg. 93(7):1378–1389 (discussion 1390-1)
Vasconez LO, Core GB, Gamboa-Bobadilla M, Guzman G, Askren C, Yamamoto Y (1994) Endoscopic techniques in coronal brow lifting. Plast Reconstr Surg 94(6):788–793
Ramirez OM (1994) Endoscopic full facelift. Aesthet Plast Surg 18(4):363–371
Isse NG (1994) Endoscopic facial rejuvenation: endoforehead, the functional lift. Case reports. Aesthet Plast Surg 18(1):21–29
Chiu ES, Baker DC (2003) Endoscopic brow lift: a retrospective review of 628 consecutive cases over 5 years. Plast Reconstr Surg 112(2):628–633
Graziosi AC, Beer SMC (1998) Browlifting with thread: the technique without undermining using minimum incisions. Aesthet Plast Surg 22(2):120–125
Erol OO, Sozer O, Velidedeoglu HV (2002) Brow suspension: a minimally invasive technique in facial rejuvenation. Plast Reconstr Surg 109:2521
Abraham RF, DeFatta RJ, Williams EF III (2009) Thread-lift for facial rejuvenation: assessment of long-term results. Arch Facial Plast Surg 11(3):178–183
Paul MD (1996) Subperiosteal transblepharoplasty forehead lift. Aesthet Plast Surg 20(2):129–134
Niechajev I (1996) Transpalpebral browpexy. Plast Reconstr Surg 113(7):2172–2180
Cohen BD, Reiffel AJ, Spinelli HM (2011) Browpexy through the upper lid (BUL): a new technique of lifting the brow with a standard blepharoplasty incision. Aesthet Surg J 31(2):163–169
Viterbo F, Auersvald A (2017) Gliding brow lifting (GBL). Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open 5(9):186–187
Guyuron B, Davies B (1988) Subcutaneous anterior hairline forehead rhytidectomy. Aesthet Plast Surg 12(2):77–83
Powell B, Younes A, Friedman O (2011) Evaluation of the midforehead brow-lift operation. Arch Facial Plast Surg 13(5):337–342
Abramo AC (1995) Forehead rhytidoplasty: endoscopic approach. Aesthet Plast Surg 19(5):463–467
Pontes R (2011) Universo da ritidoplastia. Ed. Revinter, Rio de Janeiro
Auersvald A, Auersvald LA, Biondo-Simões MLP (2012) Hemostatic net: an alternative for the prevention of hematoma in rhytidoplasty. Rev Bras Cir Plast 27:22–30
Auersvald A, Auersvald LA (2014) Hemostatic net in rhytidoplasty: an efficient and safe method for preventing hematoma in 405 consecutive patients. Aesthet Plast Surg 38(1):1–9
Luz DF, Wolfenson M, Figueiredo J, Didier JC (2005) Full-face undermining using progressive dilators. Aesthet Plast Surg 29(2):95–99
Berkowitz RL, Jacobs DI, Gorman PJ (2005) Brow fixation with the endotine forehead device in endoscopic brow lift. Plast Reconstr Surg 116(6):1761–1767
Graham DW, Heller J, Kurkjian TJ, Schaub TS, Rohrich RJ (2011) Brow lift in facial rejuvenation: a systematic literature review of open versus endoscopic techniques. Plast Reconstr Surg 128(4):335e–341e
Kim JC, Crawford Downs J, Azuola ME, Devon Graham H III (2004) Time scale for periosteal readhesion after brow lift. Laryngoscope 114(1):50–55
Brodner DC, Downs JC, Graham HD III (2002) Periosteal readhesion after brow-lift in New Zealand white rabbits. Arch Facial Plast Surg 4(4):248–251
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that Dr. Fausto Viterbo receives royalties from Faga Medical, the company that produces the dissectors used to perform this technique. The other authors, Dr. André Auersvald and Dr. T. Gerald O’Daniel have no conflict of interest.
Ethical Approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of Fausto Viterbo Plastic Surgery Clinic and with the 1964 Helsinki Declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed Consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary material 1 (MP4 86618 kb)
Supplementary material 2 (MP4 90380 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Viterbo, F., Auersvald, A. & O’Daniel, T.G. Gliding Brow Lift (GBL): A New Concept. Aesth Plast Surg 43, 1536–1546 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00266-019-01486-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00266-019-01486-3