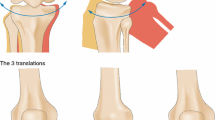
Abstract
Purpose
Higher patient’s expectations and dissatisfaction following total knee arthroplasty are well-documented phenomena. Despite the implications of different patients’ related factors both modifiable and nonmodifiable, in the last decade a lot of emphasis has been focused on surgical technique, implant alignment and stability both as a cause and a potential solution of several problems.
Methods
Different alignment and balancing techniques have been recently described and the introduction of new technologies such as computer and robotic-assisted surgery have been the basis for their optimization. In this paper, the surgical technique of the ROSA Knee System will be described focusing on the potential alignment options and the ligament balancing technique. The current literature available about the system will also be analyzed.
Results
The ROSA® robotic system have been recently introduced in the market and presents specific and peculiar features to optimize ligament balancing and an individualized alignment of the implant in a three dimensional prospective.
Discussion
The system is showing a favourable gap balancing technique and the possibility to create an individualized alignment. Preliminary results have now been shown in the literature both on the accuracy of the system and on clinical outcomes.
Conclusions
Preliminary results are promising both in terms of accuracy of the system and of clinical outcomes.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hampp E, Chughtai M, Scholl L et al (2019) Robotic-arm assisted total knee arthroplasty demonstrated greater accuracy and precision to plan compared with manual techniques. J Knee Surg 32:239–250. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0038-1641729
Vaidya NV, Deshpande AN, Panjwani T et al (2022) Robotic-assisted TKA leads to a better prosthesis alignment and a better joint line restoration as compared to conventional TKA: a prospective randomized controlled trial. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 30:621–626. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00167-020-06353-2
Zhang J, Ndou WS, Ng N et al (2022) Robotic-arm assisted total knee arthroplasty is associated with improved accuracy and patient reported outcomes: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 30:2677–2695. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00167-021-06464-4
Kort N, Stirling P, Pilot P, Müller JH (2022) Robot-assisted knee arthroplasty improves component positioning and alignment, but results are inconclusive on whether it improves clinical scores or reduces complications and revisions: a systematic overview of meta-analyses. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 30:2639–2653. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00167-021-06472-4
Oussedik S, Abdel MP, Victor J, Pagnano MW, Haddad FS (2020) Alignment in total knee arthroplasty. Bone Joint J 102-B(3):276–279. https://doi.org/10.1302/0301-620X.102B3.BJJ-2019-1729
Mercuri JJ, Pepper AM, Werner JA, Vigdorchik JM (2019) Gap balancing, measured resection, and kinematic alignment: how, when, and why? JBJS Rev 7:e2–e2. https://doi.org/10.2106/JBJS.RVW.18.00026
Agarwal N, To K, McDonnell S, Khan W (2020) Clinical and radiological outcomes in robotic-assisted total knee arthroplasty: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Arthroplasty 35:3393-3409.e2. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arth.2020.03.005
Chen AF, Kazarian GS, Jessop GW, Makhdom A (2018) Robotic technology in orthopaedic surgery. J Bone Joint Surg 100:1984–1992. https://doi.org/10.2106/JBJS.17.01397
Kayani B, Konan S, Ayuob A et al (2019) Robotic technology in total knee arthroplasty: a systematic review. EFORT Open Reviews 4:611–617. https://doi.org/10.1302/2058-5241.4.190022
Batailler C, Hannouche D, Benazzo F, Parratte S (2021) Concepts and techniques of a new robotically assisted technique for total knee arthroplasty: the ROSA knee system. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 141:2049–2058. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00402-021-04048-y
Parratte S, Price AJ, Jeys LM et al (2019) Accuracy of a new robotically assisted technique for total knee arthroplasty: a cadaveric study. J Arthroplasty 34:2799–2803. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arth.2019.06.040
Vermue H, Batailler C, Monk P et al (2022) The evolution of robotic systems for total knee arthroplasty, each system must be assessed for its own value: a systematic review of clinical evidence and meta-analysis. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00402-022-04632-w
Collins K, Agius PA, Fraval A, Petterwood J (2022) Initial experience with the NAVIO robotic-assisted total knee replacement—coronal alignment accuracy and the learning curve. J Knee Surg 35:1295–1300. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0040-1722693
Knapp PW, Nett MP, Scuderi GR (2022) Optimizing total knee arthroplasty with ROSA® robotic technology. Surg Technol Int 40:289–296. https://doi.org/10.52198/22.STI.40.OS1522
Rossi SMP, Ivone A, Ghiara M et al (2021) A ligament tensor-guided extramedullary alignment technique for distal femoral cut in total knee replacement: results at a minimum 3 years follow-up. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 141:2295–2302. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00402-021-04115-4
Vanlommel L, Neven E, Anderson MB et al (2021) The initial learning curve for the ROSA® Knee System can be achieved in 6–11 cases for operative time and has similar 90-day complication rates with improved implant alignment compared to manual instrumentation in total knee arthroplasty. J Exp Ortop 8:119. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40634-021-00438-8
Bolam SM, Tay ML, Zaidi F et al (2022) Introduction of ROSA robotic-arm system for total knee arthroplasty is associated with a minimal learning curve for operative time. J Exp Ortop 9:86. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40634-022-00524-5
Haffar A, Krueger CA (2022) Goh, Lonner GS Total knee arthroplasty with robotic surgical assistance results in less physician stress and strain than conventional methods. J Arthroplasty 37(6S):S193–S200. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arth.2021.11.021. (Epub 2022 Feb 17)
Charette RS, Sarpong NO, Weiner TR, Shah RP, Cooper HJ (2022) Registration of bony landmarks and soft tissue laxity during robotic total knee arthroplasty is highly reproducible. Surg Technol Int 41:sti41/1633. https://doi.org/10.52198/22.STI.41.OS1633
Rossi SMP, Sangaletti R, Perticarini L et al (2022) High accuracy of a new robotically assisted technique for total knee arthroplasty: an in vivo study. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00167-021-06800-8
Shin C, Crovetti C, Huo E, Lionberger D (2022) Unsatisfactory accuracy of recent robotic assisting system ROSA for total knee arthroplasty. J EXP ORTOP 9:82. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40634-022-00522-7
Mancino F, Rossi SMP, Sangaletti R et al (2022) A new robotically assisted technique can improve outcomes of total knee arthroplasty comparing to an imageless navigation system. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00402-022-04560-9
Batailler C, Anderson MB, Flecher X, Ollivier M, Parratte S (2022) Is sequential bilateral robotic total knee arthroplasty a safe procedure? A matched comparative pilot study. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00402-022-04455-9
Parratte S, Van Overschelde P, Bandi M et al (2022) An anatomo-functional implant positioning technique with robotic assistance for primary TKA allows the restoration of the native knee alignment and a natural functional ligament pattern, with a faster recovery at 6 months compared to an adjusted mechanical technique. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00167-022-06995-4
Kenanidis E, Paparoidamis G, Milonakis N et al (2022) Comparative outcomes between a new robotically assisted and a manual technique for total knee arthroplasty in patients with osteoarthritis: a prospective matched comparative cohort study. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00590-022-03274-3
Acknowledgements
None
Funding
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
SMPR and FB designed and were responsible for the manuscript. Both authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
None.
Consent to participate
None. No need for IRB approval for the current study.
Conflict of interest
Francesco Benazzo is Consultant for Zimmer Biomet and Limacorporate. Grants from Limacorporate; Royalties from Zimmer Biomet and Limacorporate. Stefano Marco Paolo Rossi have no disclosures. Prof. Francesco Benazzo declares a teaching contract with the manufacturer (Zimmer Biomet). No other conflict of interest to be declared by any of the authors for the current study.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Rossi, S.M.P., Benazzo, F. Individualized alignment and ligament balancing technique with the ROSA® robotic system for total knee arthroplasty. International Orthopaedics (SICOT) 47, 755–762 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00264-022-05671-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00264-022-05671-z