Abstract
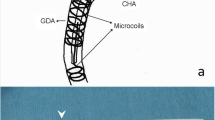
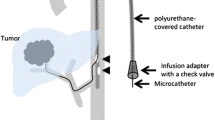
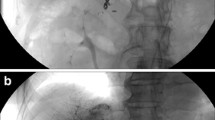
The purpose of this study was to prospectively compare the efficacy and controllability of pushable coil and detachable coil during embolization of gastroduodenal artery (GDA) while performing percutaneous implantation of port-catheter system for hepatic artery infusion chemotherapy. Fifty patients (M:F = 42:8, age: 31–81 years) with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma undergoing port-catheter system implantation were randomized into pushable coil group and detachable coil group. During catheter fixation, GDA was embolized as close to the origin as possible. Success rate, number of coils used, number of coils removed due to malposition after deployment, time to occlusion, uncoiled GDA length, pushability, and complications were compared. Pushability was graded as no tension, slight tension, and difficult to advance. Embolization was successful in 49 patients. One failure resulted from repeated regurgitation of pushable coil into hepatic artery. Number of coils used and removed coils, time to occlusion, and uncoiled GDA length were 1–3 (mean 2.32), 5 coils in 3 patients, 4–20 min (mean 8.00), and 0–15.0 mm (mean 3.36) in pushable coil group, and 1–5 (mean 2.12), 2 coils in 2 patients, 2–15 min (mean 7.40), and 0–10.2 mm (mean 2.92) in detachable coil group, respectively, without significant difference. Pushability was no tension (n = 24) and slight tension (n = 1) in pushable coil group and no tension (n = 16), slight tension (n = 7), and difficult to advance (n = 2) in detachable coil group. One hepatic artery dissection occurred in the failed case during coil removal. Pushable coils and detachable coils had similar efficacy and controllability during GDA embolization, although there was a trend favoring detachable coil.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gianturco C, Anderson JH, Wallace D (1975) Mechanical devices for arterial occlusion. Am J Roentgenol Radium Ther Nucl Med 124:428–435
Dudeck O, Bulla K, Wieners G, et al. (2011) Embolization of the gastroduodenal artery before selective internal radiotherapy: a prospectively randomized trial comparing standard pushable coils with fibered interlock detachable coils. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol. 34:74–80
Seltzer S, Aboulhosn J, Levi DS (2009) Use of interlock fibered detachable coils for occlusion of collaterals, coronary artery fistulae, and patent ductus arteriosus. Catheter Cardiovasc Interv. 74:770–776
Han YM, Song SK, Hwang HP, et al. (2013) Large congenital renal arteriovenous malformation treated with interlock coil embolization. Vasc Med. 18:237–238. doi:10.1177/1358863X13494260
Miyaki D, Aikata H, Honda Y, et al. (2012) Hepatic arterial infusion chemotherapy for advanced hepatocellular carcinoma according to Child-Pugh classification. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 27:1850–1857
Ikeda M, Okusaka T, Furuse J, et al. (2013) A multi-institutional phase II trial of hepatic arterial infusion chemotherapy with cisplatin for advanced hepatocellular carcinoma with portal vein tumor thrombosis. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 72:463–470
Lorenz M, Müller HH (2000) Randomized, multicenter trial of fluorouracil plus leucovorin administered either via hepatic arterial or intravenous infusion versus fluorodeoxyuridine administered via hepatic arterial infusion in patients with nonresectable liver metastases from colorectal carcinoma. J Clin Oncol 18:243–254
Allen-Mersh TG, Earlam S, Fordy C, Abrams K, Houghton J (1994) Quality of life and survival with continuous hepatic-artery floxuridine infusion for colorectal liver metastases. Lancet 344:1255–1260
Shindoh N, Ozaki Y, Kyogoku S, et al. (1999) Stabilization of a percutaneously implanted port catheter system for hepatic artery chemotherapy infusion. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol 22:344–347
Tanaka T, Arai Y, Inaba Y, et al. (2003) Radiologic placement of side-hole catheter with tip fixation for hepatic arterial infusion chemotherapy. J Vasc Interv Radiol 14:63–68
Yamagami T, Iida S, Kato T, et al. (2002) Using n-butyl cyanoacrylate and the fixed-catheter-tip technique in percutaneous implantation of a port-catheter system in patients undergoing repeated hepatic arterial chemotherapy. AJR 179:1611–1617
Yamagami T, Kato T, Hirota T, et al. (2008) Value of micronester coils in port-catheter implantation for continuous hepatic arterial infusion chemotherapy with fixed catheter tip method. Eur Radiol. 18:152–157
Enriquez J, Javadi S, Murthy R, et al. (2013) Gastroduodenal artery recanalization after transcatheter fibered coil embolization for prevention of hepaticoenteric flow: incidence and predisposing technical factors in 142 patients. Acta Radiol. 54:790–794. doi:10.1177/0284185113481696
Acknowledgments
This research is an investigator initiated trial, which was supported by a research Grant from Boston Scientific.
Ethical standards
All procedures comply with the current laws of the country in which the procedures were performed.
Conflict of interest
Sung II Park received the research Grant from Boston Scientific. Shin Jae Lee, Myungsu Lee, Mu Sook Lee, Gyoung Min Kim, Man Deuk Kim, Jong Yun Won, and Do Yun Lee have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Park, S.I., Lee, S.J., Lee, M. et al. Prospective randomized trial comparing pushable coil and detachable coil during percutaneous implantation of port-catheter system for hepatic artery infusion chemotherapy. Abdom Imaging 40, 595–600 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00261-014-0239-1
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00261-014-0239-1