Abstract
Purpose
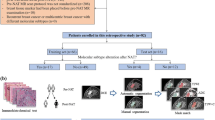
The aim of the study was to evaluate the volumetric integration patterns of standard MRI and 11C-methionine positron emission tomography (PET) images in the surgery planning of gliomas and their relationship to the histological grade.
Methods
We studied 23 patients with suspected or previously treated glioma who underwent preoperative 11C-methionine PET because MRI was imprecise in defining the surgical target contour. Images were transferred to the treatment planning system, coregistered and fused (BrainLAB). Tumour delineation was performed by 11C-methionine PET thresholding (vPET) and manual segmentation over MRI (vMRI). A 3-D volumetric study was conducted to evaluate the contribution of each modality to tumour target volume. All cases were surgically treated and histological classification was performed according to WHO grades. Additionally, several biopsy samples were taken according to the results derived either from PET or from MRI and analysed separately.
Results
Fifteen patients had high-grade tumours [ten glioblastoma multiforme (GBM) and five anaplastic), whereas eight patients had low-grade tumours. Biopsies from areas with high 11C-methionine uptake without correspondence in MRI showed tumour proliferation, including infiltrative zones, distinguishing them from dysplasia and radionecrosis. Two main PET/MRI integration patterns emerged after analysis of volumetric data: pattern vMRI-in-vPET (11/23) and pattern vPET-in-vMRI (9/23). Besides, a possible third pattern with differences in both directions (vMRI-diff-vPET) could also be observed (3/23). There was a statistically significant association between the tumour classification and integration patterns described above (p < 0.001, κ = 0.72). GBM was associated with pattern vMRI-in-vPET (9/10), low-grade with pattern vPET-in-vMRI (7/8) and anaplastic with pattern vMRI-diff-vPET (3/5).
Conclusion
The metabolically active tumour volume observed in 11C-methionine PET differs from the volume of MRI by showing areas of infiltrative tumour and distinguishing from non-tumour lesions. Differences in 11C-methionine PET/MRI integration patterns can be assigned to tumour grades according to the WHO classification. This finding may improve tumour delineation and therapy planning for gliomas.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Louis DN, Ohgaki H, Wiestler OD, Cavenee WK. WHO classification of tumours of the central nervous system. Lyon: IARC; 2007.
Salzman KL. Astrocytic tumors, infiltrating neoplasm. In: Osborn AG, Salzman KL, Barkovich AJ, editors. Diagnostic imaging: brain. 2nd ed. Salt Lake City: Amirsys; 2010. p. 14–7.
Lacroix M, Abi-Said D, Fourney DR, Gokaslan ZL, Shi W, DeMonte F, et al. A multivariate analysis of 416 patients with glioblastoma multiforme: prognosis, extent of resection, and survival. J Neurosurg 2001;95:190–8.
Smith JS, Chang EF, Lamborn KR, Chang SM, Prados MD, Cha S, et al. Role of extent of resection in the long-term outcome of low-grade hemispheric gliomas. J Clin Oncol 2008;26:1338–45.
Stupp R, Tonn JC, Brada M, Pentheroudakis G, ESMO Guidelines Working Group. High-grade malignant glioma: ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann Oncol 2010;21:v190–3.
Soffietti R, Baumert BG, Bello L, von Deimling A, Duffau H, Frénay M, et al. Guidelines on management of low-grade gliomas: report of an EFNS-EANO Task Force. Eur J Neurol 2010;17:1124–33.
Sanai N, Berger MS. Glioma extent of resection and its impact on patient outcome. Neurosurgery 2008;62:753–64. discussion 264-6.
Stupp R, Mason WP, van den Bent MJ, Weller M, Fisher B, Taphoorn MJ, et al. Radiotherapy plus concomitant and adjuvant temozolomide for glioblastoma. N Engl J Med 2005;352:987–96.
Kelly PJ, Daumas-Duport C, Kispert DB, Kall BA, Scheithauer BW, Illig JJ. Imaging-based stereotaxic serial biopsies in untreated intracranial glial neoplasms. J Neurosurg 1987;66:865–74.
Watanabe M, Tanaka R, Takeda N. Magnetic resonance imaging and histopathology of cerebral gliomas. Neuroradiology 1992;34:463–9.
Grosu AL, Weber WA, Riedel E, Jeremic B, Nieder C, Franz M, et al. L-(methyl-11C) methionine positron emission tomography for target delineation in resected high-grade gliomas before radiotherapy. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 2005;63:64–74.
Plotkin M, Blechschmidt C, Auf G, Nyuyki F, Geworski L, Denecke T, et al. Comparison of F-18 FET-PET with F-18 FDG-PET for biopsy planning of non-contrast-enhancing gliomas. Eur Radiol 2010;20:2496–502.
Jacobs AH, Li H, Winkeler A, Hilker R, Knoess C, Rüger A, et al. PET-based molecular imaging in neuroscience. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 2003;30:1051–65.
Chung JK, Kim YK, Kim SK, Lee YJ, Paek S, Yeo JS, et al. Usefulness of 11C-methionine PET in the evaluation of brain lesions that are hypo- or isometabolic on 18F-FDG PET. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 2002;29:176–82.
Van Laere K, Ceyssens S, Van Calenbergh F, de Groot T, Menten J, Flamen P, et al. Direct comparison of 18F-FDG and 11C-methionine PET in suspected recurrence of glioma: sensitivity, inter-observer variability and prognostic value. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 2005;32:39–51.
Prieto E, Martí-Climent JM, Domínguez-Prado I, Garrastachu P, Díez-Valle R, Tejada S, et al. Voxel-based analysis of dual-time-point FDG PET images for brain tumor identification and delineation. J Nucl Med 2011;52:865–72.
Kracht LW, Miletic H, Busch S, Jacobs AH, Voges J, Hoevels M, et al. Delineation of brain tumor extent with [11C]L-methionine positron emission tomography: local comparison with stereotactic histopathology. Clin Cancer Res 2004;10:7163–70.
Miwa K, Shinoda J, Yano H, Okumura A, Iwama T, Nakashima T, et al. Discrepancy between lesion distributions on methionine PET and MR images in patients with glioblastoma multiforme: insight from a PET and MR fusion image study. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 2004;75:1457–62.
Smits A, Baumert BG. The clinical value of PET with amino acid tracers for gliomas WHO grade II. Int J Mol Imaging 2011;2011:372509.
Mosskin M, Ericson K, Hindmarsh T, von Holst H, Collins VP, Bergström M, et al. Positron emission tomography compared with magnetic resonance imaging and computed tomography in supratentorial gliomas using multiple stereotactic biopsies as reference. Acta Radiol 1989;30:225–32.
Pirotte B, Goldman S, Dewitte O, Massager N, Wikler D, Lefranc F, et al. Integrated positron emission tomography and magnetic resonance imaging-guided resection of brain tumors: a report of 103 consecutive procedures. J Neurosurg 2006;104:238–53.
Roessler K, Gatterbauer B, Becherer A, Paul M, Kletter K, Prayer D, et al. Surgical target selection in cerebral glioma surgery: linking methionine (MET) PET image fusion and neuronavigation. Minim Invasive Neurosurg 2007;50:273–80.
Tanaka Y, Nariai T, Momose T, Aoyagi M, Maehara T, Tomori T, et al. Glioma surgery using a multimodal navigation system with integrated metabolic images. J Neurosurg 2009;110:163–72.
Levivier M, Massager N, Wikler D, Lorenzoni J, Ruiz S, Devriendt D, et al. Use of stereotactic PET images in dosimetry planning of radiosurgery for brain tumors: clinical experience and proposed classification. J Nucl Med 2004;45:1146–54.
Pirotte BJ, Levivier M, Goldman S, Massager N, Wikler D, Dewitte O, et al. Positron emission tomography-guided volumetric resection of supratentorial high-grade gliomas: a survival analysis in 66 consecutive patients. Neurosurgery 2009;64:471–81.
Quincoces G, Peñuelas I, Valero M, Serra P, Collantes M, Martí-Climent J, et al. Simple automated system for simultaneous production of 11C-labeled tracers by solid supported methylation. Appl Radiat Isot 2006;64:808–11.
Grosu AL, Lachner R, Wiedenmann N, Stärk S, Thamm R, Kneschaurek P, et al. Validation of a method for automatic image fusion (BrainLAB System) of CT data and 11C-methionine-PET data for stereotactic radiotherapy using a LINAC: first clinical experience. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 2003;56:1450–63.
Abramson JH. WINPEPI (PEPI-for-Windows): computer programs for epidemiologists. Epidemiol Perspect Innov 2004;1:6.
Grosu AL, Nestle U, Weber WA. How to use functional imaging information for radiotherapy planning. Eur J Cancer 2009;45 Suppl 1:461–3.
Pirotte B, Goldman S, Massager N, David P, Wikler D, Vandesteene A, et al. Comparison of 18F-FDG and 11C-methionine for PET-guided stereotactic brain biopsy of gliomas. J Nucl Med 2004;45:1293–8.
Galldiks N, Ullrich R, Schroeter M, Fink GR, Jacobs AH, Kracht LW. Volumetry of [(11)C]-methionine PET uptake and MRI contrast enhancement in patients with recurrent glioblastoma multiforme. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 2010;37:84–92.
Herholz K, Hölzer T, Bauer B, Schröder R, Voges J, Ernestus RI, et al. 11C-methionine PET for differential diagnosis of low-grade gliomas. Neurology 1998;50:1316–22.
Kinoshita M, Hashimoto N, Goto T, Yanagisawa T, Okita Y, Kagawa N, et al. Use of fractional anisotropy for determination of the cut-off value in 11C-methionine positron emission tomography for glioma. NeuroImage 2009;45:312–8.
Singhal T, Narayanan TK, Jain V, Mukherjee J, Mantil J. 11C-L-methionine positron emission tomography in the clinical management of cerebral gliomas. Mol Imaging Biol 2008;10:1–18.
Nuutinen J, Sonninen P, Lehikoinen P, Sutinen E, Valavaara R, Eronen E, et al. Radiotherapy treatment planning and long-term follow-up with [(11)C]methionine PET in patients with low-grade astrocytoma. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 2000;48(1):43–52.
Acknowledgement
This work was partially supported by the Research Foundation of the University of Navarra (PIUNA 2010-04) and the Convocatoria de infraestructuras del Fondo de Investigaciones Sanitarias, ISCIII, MSC (IF 08/360)
Conflicts of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(DOC 34.0 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Arbizu, J., Tejada, S., Marti-Climent, J.M. et al. Quantitative volumetric analysis of gliomas with sequential MRI and 11C-methionine PET assessment: patterns of integration in therapy planning. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 39, 771–781 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00259-011-2049-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00259-011-2049-9