Abstract
Objective
To retrospectively evaluate the efficacy and safety of microwave ablation (MWA) combined with osteoplasty in lung cancer patients with painful extraspinal bone metastases.
Materials and methods
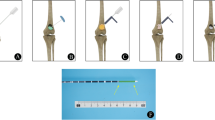
From January 2011 to July 2014, 26 lung cancer patients with 33 painful extraspinal bone metastases underwent percutaneous MWA combined with osteoplasty. Effectiveness was evaluated by visual analog scale (VAS) and daily morphine dose with a follow-up of 6-months. Complications were also recorded.
Results
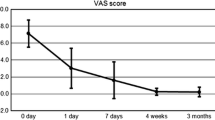
Mean VAS score and morphine dose pre-procedure were 7.4 ± 1.6 (range, 5–10) and 47.7 ± 30.1 mg (range, 20–120 mg), respectively. Technical success and pain relief were achieved in all patients. Mean VAS scores and daily morphine doses post-procedure were as follows: 48 h, 1.7 ± 1.2 (p < 0.001) and 29.6 ± 16.1 mg (p = 0.003); 7 days, 1.9 ± 1.7 (p < 0.001) and 16.1 ± 12.0 mg (p < 0.001); 1 month, 1.5 ± 0.9 (p < 0.001) and 10.8 ± 10.9 (p < 0.001); 3 months, 0.9 ± 0.7 (p < 0.001) and 8.4 ± 9.2 mg (p < 0.001); and 6 months, 1.2 ± 0.8 (p < 0.001) and 9.2 ± 12.3 mg (p < 0.001). Complications were observed in eight patients (28 %); among these, major complications were reported in two (7.7 %) patients, one with local infection and the other with a bone fracture. The minor complication rate was 23.1 % (6/26).
Conclusion
MWA combination with osteoplasty appeared to be an effective and safe treatment for lung cancer patients with painful extraspinal bone metastases.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Berrettoni BA, Carter JR. Mechanisms of cancer metastasis to bone. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1986;68(2):308–12.
Coleman RE. Clinical features of metastatic bone disease and risk of skeletal morbidity. Clin Cancer Res. 2006;12(20):6243s–9.
Jemal A, Thun MJ, Ries LA, et al. Annual report to the nation on the status of cancer, 1975–2005, featuring trends in lung cancer, tobacco use, and tobacco control. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2008;100:1672–94.
Harris K, Chow E, Zhang L, et al. Patients’ and health care professionals’ evaluation of health-related quality of life issues in bone metastases. Eur J Cancer. 2009;45:2510–8.
Dorrepaal KL, Aaronson NK, van Dam FS. Pain experience and pain management amongst hospitalized cancer patients: a clinical study. Cancer. 1989;63:593–8.
van der Linden YM, Dijkstra SP, Vonk EJ, et al. Prediction of survival in patients with metastases in the spinal column: results based on a randomized trial of radiotherapy. Cancer. 2005;103:320–8.
Smith HS. Painful osseous metastases. Pain Physician. 2011;14:373–403.
Gösling T, Becker-Schiebe M. Surgical treatment of skeletal metastases. Unfallchirurg. 2015;118(4):347–63.
Johnstone C, Lutz ST. External beam radiotherapy and bone metastases. Ann Palliat Med. 2014;3(2):114–22.
Pusceddu C, Sotgia B, Fele RM, et al. Treatment of bone metastases with microwave thermal ablation. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2013;24(2):229–33.
Simon CJ, Dupuy DE, Mayo-Smith WW. Microwave ablation: principles and applications. Radiographics. 2005;25 Suppl 1:S69–83.
Kurup AN, Callstrom MR. Ablation of musculoskeletal metastases: pain palliation, fracture risk reduction, and oligometastatic disease. Tech Vasc Interv Radiol. 2013;16(4):253–61.
Lam MK, Huisman M, Nijenhuis RJ, et al. Quality of MR thermometry during palliative MR-guided high-intensity focused ultrasound (MR-HIFU) treatment of bone metastases. J Ther Ultrasound. 2015;3:5.
Dupuy DE, Liu D, Hartfeil D, et al. Percutaneous radiofrequency ablation of painful osseous metastases: a multicenter American College of Radiology imaging network trial. Cancer. 2010;116(4):989–97.
Carrafiello G, Laganà D, Ianniello A, et al. Radiofrequency thermal ablation for pain control in patients with single painful bone metastasis from hepatocellular carcinoma. Eur J Radiol. 2009;71(2):363–8.
Masala S, Schillaci O, Bartolucci AD, et al. Metabolic and clinical assessment of efficacy of cryoablation therapy on skeletal masses by 18F-FDG positron emission tomography/computed tomography (PET/CT) and visual analogue scale (VAS): initial experience. Skelet Radiol. 2010;40:159–65.
Carrafiello G, Laganà D, Pellegrino C, et al. Percutaneous imaging-guided ablation therapies in the treatment of symptomatic bone metastases: preliminary experience. Radiol Med. 2009;114:608–25.
Simon CJ, Dupuy DE. Percutaneous minimally invasive therapies in the treatment of bone tumors: thermal ablation. Semin Musculoskelet Radiol. 2006;10(2):137–44.
Basile A, Giuliano G, Scuderi V, et al. Cementoplasty in the management of painful extraspinal bone metastases: our experience. Radiol Med. 2008;113:1018–28.
Xie L, Chen Y, Zhang Y, et al. Status and prospects of percutaneous vertebroplasty combined with 125I seed implantation for the treatment of spinal metastases. World J Surg Oncol. 2015;13(1):119.
Clarecon F, Jean B, Pham HP, et al. Value of percutaneous radiofrequency ablation with or without percutaneous vertebroplasty for pain relief and functional recovery in painful bone metastases. Skelet Radiol. 2013;42:25–36.
Halpin RJ, Bendok BR, Sat KT, et al. Combination treatment of vertebral metastases using image guided percutaneous radiofrequency ablation and vertebroplasty: a case report. Surg Neurol. 2005;63:469–74.
Tian QH, Wu CG, Gu YF, et al. Combination radiofrequency ablation and percutaneous osteoplasty for palliative treatment of painful extraspinal bone metastasis: a single-center experience. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2014;25(7):1094–100.
Wei Z, Ye X, Yang X, et al. Microwave ablation in combination with chemotherapy for the treatment of advanced non-small cell lung cancer. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol. 2015;38(1):135–42.
Yang X, Ye X, Zheng A, et al. Percutaneous microwave ablation of stage I medically inoperable non-small cell lung cancer: clinical evaluation of 47 cases. J Surg Oncol. 2014;110(6):758–63.
Goldberg SN, Grassi CJ, Cardella JF, et al. Image-guided tumor ablation: standardization of terminology and reporting criteria. Radiology. 2005;235(3):728–39.
Mantyh PW, Clohisy DR, Koltzenburg M, et al. Molecular mechanisms of cancer pain. Nat Rev Cancer. 2002;2:201–9.
Mannion RJ, Woolf CJ. Pain mechanisms and management: a central perspective. Clin J Pain. 2000;16(3 Suppl):S144–56.
Goblirsch MJ, Zwolak PP, Clohisy DR. Biology of bone cancer pain. Clin Cancer Res. 2006;12(20Pt):6231s–5.
Alexander ES, Hankins CA, Machan JT, et al. Rib fractures after percutaneous radiofrequency and microwave ablation of lung tumors: incidence and relevance. Radiology. 2013;266(3):971–8.
Lannessi A, Garnon J, Cormier É, et al. Interventional radiology for bone metastases. Bull Cancer. 2013;100(11):1163–73.
Jakanani GC, Jaiveer S, Ashford R, et al. Computed tomography-guided coblation and cementoplasty of a painful acetabular metastasis: an effective palliative treatment. J Palliat Med. 2010;13(1):83–5.
Lane MD, Le HB, Lee S, et al. Combination radiofrequency ablation and cementoplasty for palliative treatment of painful neoplastic bone metastasis: experience with 53 treated lesions in 36 patients. Skelet Radiol. 2011;40:25–32.
Conflict of interest
The study was supported by Shandong Province Medical and Health Science and Technology Development projects (2014WS0346).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Zhigang Wei and Kaixian Zhang contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wei, Z., Zhang, K., Ye, X. et al. Computed tomography-guided percutaneous microwave ablation combined with osteoplasty for palliative treatment of painful extraspinal bone metastases from lung cancer. Skeletal Radiol 44, 1485–1490 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00256-015-2195-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00256-015-2195-4