Abstract
Objective
Real-time sonoelastography (SE) is a new ultrasound-based imaging technique that provides information on tissue elasticity and stiffness. We determined the efficacy of SE for assessing Achilles tendon abnormalities in patients with ankylosing spondylitis (AS).
Materials and methods
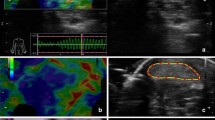
Forty-one consecutive AS patients and 32 asymptomatic healthy subjects were enrolled. Achillodynia was scored on a 0- to 100-mm visual analog scale. A high-resolution ultrasound machine equipped with an elastography-compatible linear probe was used to perform bilateral B-mode ultrasound, Doppler ultrasound, and SE examinations of Achilles tendons. Tendons were divided into proximal, middle, and distal segments. B-mode examinations included tendon thicknesses, echotextures, and enthesopathic findings. SE using color-coded images was performed in the same areas. Normal consistent tendon structures were coded as blue or green, and moderately (yellow) or severely (red) softened areas were considered pathological.
Results
The distal third of the Achilles tendons was the most commonly affected part in the AS patients compared with healthy subjects (p = 0.001), whose middle third was more commonly affected. Achillodynia intensity tended to be higher in patients with pathological B-mode or SE examination findings (p = 0.09 and p = 0.07 respectively). Softening detected by SE in the distal third was associated with enthesopathy findings such as calcaneal bone erosions (Fisher’s X 2, p = 0.07) and tendinous enlargement (Fisher’s X 2, p = 0.001). B-mode and SE findings had moderate to good correlation in the assessment of Achilles tendon abnormalities.
Conclusions
Sonoelastography may be useful for the evaluation of tendon abnormalities in patients with AS; in addition; it may be useful for the evaluation of other inflammatory rheumatic conditions.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Garra BS. Elastography: current status, future prospects, and making it work for you. Ultrasound Q. 2011;27(3):177–86. doi:10.1097/RUQ.0b013e31822a2138.
Klauser AS, Faschingbauer R, Jaschke WR. Is sonoelastography of value in assessing tendons? Semin Musculoskelet Radiol. 2010;14(3):323–33. doi:10.1055/s-0030-1254521.
Li Y, Snedeker JG. Elastography: modality-specific approaches, clinical applications, and research horizons. Skeletal Radiol. 2011;40(4):389–97. doi:10.1007/s00256-010-0918-0.
Ophir J, Cespedes I, Ponnekanti H, Yazdi Y, Li X. Elastography: a quantitative method for imaging the elasticity of biological tissues. Ultrason Imaging. 1991;13(2):111–34.
Bojunga J, Herrmann E, Meyer G, Weber S, Zeuzem S, Friedrich-Rust M. Real-time elastography for the differentiation of benign and malignant thyroid nodules: a meta-analysis. Thyroid : Official Journal of the American Thyroid Association. 2010;20(10):1145–50. doi:10.1089/thy.2010.0079.
Alam F, Naito K, Horiguchi J, Fukuda H, Tachikake T, Ito K. Accuracy of sonographic elastography in the differential diagnosis of enlarged cervical lymph nodes: comparison with conventional B-mode sonography. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2008;191(2):604–10. doi:10.2214/AJR.07.3401.
Gong X, Xu Q, Xu Z, Xiong P, Yan W, Chen Y. Real-time elastography for the differentiation of benign and malignant breast lesions: a meta-analysis. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2011;130(1):11–8. doi:10.1007/s10549-011-1745-2.
Ying L, Hou Y, Zheng HM, Lin X, Xie ZL, Hu YP. Real-time elastography for the differentiation of benign and malignant superficial lymph nodes: a meta-analysis. Eur J Radiol. 2012;81(10):2576–84. doi:10.1016/j.ejrad.2011.10.026.
Carstensen EL, Parker KJ, Lerner RM. Elastography in the management of liver disease. Ultrasound Med Biol. 2008;34(10):1535–46. doi:10.1016/j.ultrasmedbio.2008.03.002.
McNally EG. The development and clinical applications of musculoskeletal ultrasound. Skeletal Radiol. 2011;40(9):1223–31. doi:10.1007/s00256-011-1220-5.
Dong Q, Fessell DP. Achilles tendon ultrasound technique. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2009;193(3):W173. doi:10.2214/AJR.09.3111.
Drakonaki EE, Allen GM, Wilson DJ. Real-time ultrasound elastography of the normal Achilles tendon: reproducibility and pattern description. Clin Radiol. 2009;64(12):1196–202. doi:10.1016/j.crad.2009.08.006.
Francois RJ, Braun J, Khan MA. Entheses and enthesitis: a histopathologic review and relevance to spondyloarthritides. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2001;13(4):255–64.
van der Linden S, Valkenburg HA, Cats A. Evaluation of diagnostic criteria for ankylosing spondylitis. A proposal for modification of the New York criteria. Arthritis Rheum. 1984;27(4):361–8.
Archambault JM, Wiley JP, Bray RC, Verhoef M, Wiseman DA, Elliott PD. Can sonography predict the outcome in patients with achillodynia? J Clin Ultrasound JCU. 1998;26(7):335–9.
De Zordo T, Fink C, Feuchtner GM, Smekal V, Reindl M, Klauser AS. Real-time sonoelastography findings in healthy Achilles tendons. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2009;193(2):W134–8. doi:10.2214/AJR.08.1843.
De Zordo T, Chhem R, Smekal V, Feuchtner G, Reindl M, Fink C, et al. Real-time sonoelastography: findings in patients with symptomatic Achilles tendons and comparison to healthy volunteers. Ultraschall Med. 2010;31(4):394–400. doi:10.1055/s-0028-1109809.
Tan S, Kudas S, Ozcan AS, Ipek A, Karaoglanoglu M, Arslan H, et al. Real-time sonoelastography of the Achilles tendon: pattern description in healthy subjects and patients with surgically repaired complete ruptures. Skeletal Radiol. 2011;41(9):1067–72. doi:10.1007/s00256-011-1339-4.
Sconfienza LM, Silvestri E, Cimmino MA. Sonoelastography in the evaluation of painful Achilles tendon in amateur athletes. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2010;28(3):373–8.
Havre RF, Elde E, Gilja OH, Odegaard S, Eide GE, Matre K, et al. Freehand real-time elastography: impact of scanning parameters on image quality and in vitro intra- and interobserver validations. Ultrasound Med Biol. 2008;34(10):1638–50. doi:10.1016/j.ultrasmedbio.2008.03.009.
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Turan, A., Tufan, A., Mercan, R. et al. Real-time sonoelastography of Achilles tendon in patients with ankylosing spondylitis. Skeletal Radiol 42, 1113–1118 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00256-013-1637-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00256-013-1637-0