Abstract
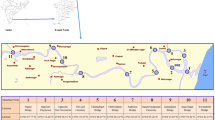
Ten sites along the Tecate River, Mexico were sampled to evaluate the cadmium, lead, nickel and chromium concentrations in sediments. The result shows contamination for cadmium in most of the sites, where two sites were class 4 (polluted to strongly polluted) according to geoaccumulation index proposed by Muller. Two sites were found polluted for all the heavy metals analyzed (Cr, Cd, Pb and Ni), indicating the effect of anthropogenic activities. A correlation between Ni and Cd concentration had been found indicating a common source. These metals are usually used in electroplating industry. The results of this study can be used for decision makers to prioritize measures to control the pollution for these metals.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
APHA (1995) Standard methods for examination of water and wastewater. American Health Public Association
Audry S, Schafer J, Blanc G, Jouanneau JM (2004) Fifty-year sedimentary record of heavy metal pollution (Cd, Zn, Cu, Pb) in the Lot River reservoirs (France). Environ Pollut 132(3):413–426
Axtmann E, Luoma S (1991) Large scale distribution of metal contamination in the fine-grained sediments of the Clark Fork River, USA. Appl Geochem 6:75–88
Bermejo Santos JC, Beltran R, Gomez Araiza JL (2003) Spatial variations of heavy metals contamination in sediments from Odiel River (Southwest Spain). Environ Int 29(1):69–77
Binning K, Baird D (2001) Survey of heavy metals in the sediments of the Swartkops River Estuary, Port Elizabeth South Africa. Water SA 27(4):461–466
Chang JS, Yu KC, Tsai LJ, Ho ST (1998) Spatial distribution of heavy metals in bottom sediment of Yenshui river, Taiwan. Water Sci Technol 38(11):159–167
Davies CA, Tomlinson K, Stephenson T (1991) Heavy metals in River Tees estuary sediments. Environ Technol. 12:961–972
Harrison RM, Wilson SJ (1985) The chemical composition of highway drainage waters III. Runoff water metal speciation characteristics. Sci Total Environ 43:89–102
Instituto Nacional de Estadística, geografía e Informática (INEGI) (2001) “Sistemas de información empresarial mexicano, SIEM”. (Systems of Mexican business information) http://www.inegi.gob.mx. Cited 21 September 2006
Irion G (1991) Minerals in rivers. In: Degens E, Kempe F, Richey J (eds) Biogeochemistry of major world rivers, SCOPE 42. Wiley, New York, pp 356
Makepeace DK, Smith DW, Stanley SJ (1995) Urban stormwater quality: summary of contamination data. Crit Rev Environ Sci Technol 25(2):93–139
Meyer SF, Gersberg R (1997) Heavy metals and acid-volatile sulfide in sediments of the Tijuana Estuary. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 59:113–119
Muller G (1979) Schwermetalle in den Sedimenten des Rheins Veranderungen seit 1971. Umschau 79(24):778–783
Munendra S, Müller G, Sinhg B (2002). Heavy metals in freshly deposited stream sediments of rivers associated with urbanization of the Ganga plain, India. Water, Air Soil Pollut 141:35–54
Placchi CA (1998) Land use and water quality in the upper reaches of the Tijuana River. Master thesis. San Diego State University
Ponce VM 2004, Feasibility of pumping scheme to provide water for Tecate River park, http://ponce.sdsu.edu/tecate_rio_parque_report_september2004.html. Accessed 12 May 2005
Rowell DL (1994) Soil science, methods & applications. Logman Essex, England
Sakai H, Kojima Y, Saito K (1986) Distribution of heavy metals in water and sieved sediments in the Toyohira river. Water Res 20:559–567
Sondi Y, Juracic M, Prohic ME, Pradvdic V (1994) Particulates and the environmental capacity for trace metals. A small river as a model for land-sea transfer system The Rasa River Estuary. Sci Total Environ 155:173–185
Thorne LT, Nickless G (1981) The relation between heavy metals and particle size fractions within the Severn estuary (UK) inter-tidal sediments. Sci Total Environ 19:207–213
Wang F, Cheng J, Forsling W (1997) Modeling sorption of trace metals on natural sediments by surface complexation model. Environ Sci Technol 31:448–453
Weis DA, Callaway JC, Gersberg RM (2001) Vertical accreation rates and heavy metal chronologies in wetland sediments of the Tijuana Estuary. Estuaries 24(6):840–850
Acknowledgments
This research has been conducted with the support of Universidad Autonoma de Baja California. The authors would like to thank Mario Del Valle for correcting the draft of this paper and the anonymous reviewers for their useful comments.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wakida, F.T., Lara-Ruiz, D., Temores-Peña, J. et al. Heavy metals in sediments of the Tecate River, Mexico. Environ Geol 54, 637–642 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00254-007-0831-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00254-007-0831-6