Abstract
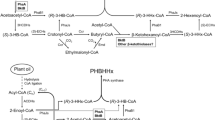
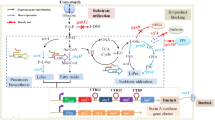
Gluconobacter is a potential strain for single-step production of 2-keto-L-gulonic acid (2-KLG), which is the direct precursor of vitamin C. Three dehydrogenases, namely, sorbitol dehydrogenase (SLDH), sorbose dehydrogenase (SDH), and sorbosone dehydrogenase (SNDH), are involved in the production of 2-KLG from D-sorbitol. In the present study, the potential SNDH/SDH gene cluster in the strain Gluconobacter cerinus CGMCC 1.110 was mined by genome analysis, and its function in transforming L-sorbose to 2-KLG was verified. Proteomic analysis showed that the expression level of SNDH/SDH had a great influence on the titer of 2-KLG, and fermentation results showed that SDH was the rate-limiting enzyme. A systematic metabolic engineering process, which was theoretically suitable for increasing the titer of many products involving membrane-bound dehydrogenase from Gluconobacter, was then performed to improve the 2-KLG titer in G. cerinus CGMCC 1.110 from undetectable to 51.9 g/L in a 5-L bioreactor after fermentation optimization. The strategies used in this study may provide a reference for mining other potential applications of Gluconobacter.
Key points
• The potential SNDH/SDH gene cluster in G. cerinus CGMCC 1.110 was mined.
• A systematic engineering process was performed to improve the titer of 2-KLG.
• The 2-KLG titer was successfully increased from undetectable to 51.9 g/L.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Bhattacharyya S, Jacobs WM, Adkar BV, Yan J, Zhang W, Shakhnovich EI (2018) Accessibility of the Shine-Dalgarno sequence dictates N-terminal codon bias in E. coli. Mol Cell 70(5):894–905 e5. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2018.05.008
Chen Y, Li D, Shan X, Zhou J, Chen J (2022) Characterization of a sorbose oxidase involved in the biosynthesis of 2-keto-L-gulonic acid from Gluconobacter oxydans WSH-004. Process Biochem 116:1–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procbio.2022.02.019
Chen Y, Liu L, Shan XY, Du GC, Zhou JW, Chen J (2019) High-throughput screening of a 2-keto-L-gulonic acid-producing Gluconobacter oxydans strain based on related dehydrogenases. Front Bioeng Biotechnol 7:385. https://doi.org/10.3389/fbioe.2019.00385
Chen Y, Liu L, Yu SQ, Li JH, Zhou JW, Chen J (2021) Identification of gradient promoters of Gluconobacter oxydans and their applications in the biosynthesis of 2-keto-L-gulonic acid. Front Bioeng Biotechnol 9:673844. https://doi.org/10.3389/fbioe.2021.673844
Cheong DE, Ko KC, Han Y, Jeon HG, Sung BH, Kim GJ, Choi JH, Song JJ (2015) Enhancing functional expression of heterologous proteins through random substitution of genetic codes in the 5’ coding region. Biotechnol Bioeng 112(4):822–826. https://doi.org/10.1002/bit.25478
De Muynck C, Pereira CSS, Naessens M, Parmentier S, Soetaert W, Vandamme EJ (2007) The genus Gluconobacter oxydans: comprehensive overview of biochemistry and biotechnological applications. Crit Rev Biotechnol 27(3):147–171. https://doi.org/10.1080/07388550701503584
Gao L, Wu XD, Zhu CL, Jin ZY, Wang W, Xia XL (2020) Metabolic engineering to improve the biomanufacturing efficiency of acetic acid bacteria: advances and prospects. Crit Rev Biotechnol 40(4):522–538. https://doi.org/10.1080/07388551.2020.1743231
Gao LL, Hu YD, Liu J, Du GC, Zhou JW, Chen J (2014) Stepwise metabolic engineering of Gluconobacter oxydans WSH-003 for the direct production of 2-keto-L-gulonic acid from D-sorbitol. Metab Eng 24:30–37. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymben.2014.04.003
Hanke T, Richhardt J, Polen T, Sahm H, Bringer S, Bott M (2012) Influence of oxygen limitation, absence of the cytochrome bc1 complex and low pH on global gene expression in Gluconobacter oxydans 621H using DNA microarray technology. J Biotechnol 157(3):359–372. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbiotec.2011.12.020
Hartl FU, Bracher A, Hayer-Hartl M (2011) Molecular chaperones in protein folding and proteostasis. Nature 475(7356):324–332. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature10317
Hou Y, Hossain GS, Li J, Shin H-D, Du G, Chen J, Liu L (2017) Metabolic engineering of cofactor flavin adenine dinucleotide (FAD) synthesis and regeneration in Escherichia coli for production of α-keto acids. Biotechnol Bioeng 114(9):1928–1936. https://doi.org/10.1002/bit.26336
Hu YD, Wan H, Li JH, Zhou JW (2015) Enhanced production of L-sorbose in an industrial Gluconobacter oxydans strain by identification of a strong promoter based on proteomics analysis. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 42(7):1039–1047. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10295-015-1624-7
Ke X, Yu PH, Hu ZC, Chen L, Sun XQ, Zheng YG (2019) Synergistic improvement of PQQ-dependent D-sorbitol dehydrogenase activity from Gluconobacter oxydans for the biosynthesis of miglitol precursor 6-(N-hydroxyethyl)-amino-6-deoxy-α-L-sorbofuranose. J Biotechnol 300:55–62. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbiotec.2019.05.007
Kiefler I, Bringer S, Bott M (2015) SdhE-dependent formation of a functional Acetobacter pasteurianus succinate dehydrogenase in Gluconobacter oxydans–a first step toward a complete tricarboxylic acid cycle. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 99(21):9147–9160. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-015-6972-8
Kiefler I, Bringer S, Bott M (2017) Metabolic engineering of Gluconobacter oxydans 621H for increased biomass yield. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 101(13):5453–5467. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-017-8308-3
Klamt S, Mahadevan R, Hädicke O (2018) When do two-stage processes outperform one-stage processes? Biotechnol J 13(2):1700539. https://doi.org/10.1002/biot.201700539
Li XY, Lin Y, Chang M, Jin QZ, Wang XG (2015) Efficient production of arachidonic acid by Mortierella alpina through integrating fed-batch culture with a two-stage pH control strategy. Bioresour Technol 181:275–282. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2015.01.009
Liu L, Chen Y, Yu SQ, Chen J, Zhou JW (2021) Simultaneous transformation of five vectors in Gluconobacter oxydans. Plasmid 117:102588. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plasmid.2021.102588
Liu XY, Yu XJ, Zhang T, Wang ZP, Xu JX, Xia J, He AY, Yan YB, Xu JM (2018) Novel two-stage solid-state fermentation for erythritol production on okara-buckwheat husk medium. Bioresour Technol 266:439–446. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2018.07.009
Liu YP, Tang HZ, Lin ZL, Xu P (2015) Mechanisms of acid tolerance in bacteria and prospects in biotechnology and bioremediation. Biotechnol Adv 33(7):1484–1492. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biotechadv.2015.06.001
Miura H, Mogi T, Ano Y, Migita CT, Matsutani M, Yakushi T, Kita K, Matsushita K (2013) Cyanide-insensitive quinol oxidase (CIO) from Gluconobacter oxydans is a unique terminal oxidase subfamily of cytochrome bd. J Biochem 153(6):535–545. https://doi.org/10.1093/jb/mvt019
Okamoto-Kainuma A, Ishikawa M, Nakamura H, Fukazawa S, Tanaka N, Yamagami K, Koizumi Y (2011) Characterization of rpoH in Acetobacter pasteurianus NBRC3283. J Biosci Bioeng 111(4):429–432. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbiosc.2010.12.016
Prust C, Hoffmeister M, Liesegang H, Wiezer A, Fricke WF, Ehrenreich A, Gottschalk G, Deppenmeier U (2005) Complete genome sequence of the acetic acid bacterium Gluconobacter oxydans. Nat Biotechnol 23(2):195–200. https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt1062
Qin ZJ, Yang YT, Yu SQ, Liu L, Chen Y, Chen J, Zhou JW (2021) Repurposing the endogenous type I-E CRISPR/Cas system for gene repression in Gluconobacter oxydans WSH-003. ACS Synth Biol 10(1):84–93. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssynbio.0c00456
Qin ZJ, Yu SQ, Liu L, Wang LL, Chen J, Zhou JW (2021) A SacB-based system for diverse and multiple genome editing in Gluconobacter oxydans. J Biotechnol 338:31–39. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbiotec.2021.07.004
Richhardt J, Bringer S, Bott M (2012) Mutational analysis of the pentose phosphate and Entner-Doudoroff pathways in Gluconobacter oxydans reveals improved growth of a Δedd Δeda mutant on mannitol. Appl Environ Microbiol 78(19):6975–6986. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.01166-12
Richhardt J, Luchterhand B, Bringer S, Buchs J, Bott M (2013) Evidence for a key role of cytochrome bo3 oxidase in respiratory energy metabolism of Gluconobacter oxydans. J Bacteriol 195(18):4210–4220. https://doi.org/10.1128/jb.00470-13
Saito Y, Ishii Y, Hayashi H, Imao Y, Akashi T, Yoshikawa K, Noguchi Y, Soeda S, Yoshida M, Niwa M, Hosoda J, Shimomura K (1997) Cloning of genes coding for L-sorbose and L-sorbosone dehydrogenases from Gluconobacter oxydans and microbial production of 2-keto-L-gulonate, a precursor of L-ascorbic acid, in a recombinant G. oxydans strain. Appl Environ Microbiol 63(2):454–60. https://doi.org/10.1128/aem.63.2.454-460.1997
Shan XY, Liu L, Zeng WZ, Chen J, Zhou JW (2020) High throughput screening platform for a FAD-dependent L-sorbose dehydrogenase. Front Bioeng Biotechnol 8:194. https://doi.org/10.3389/fbioe.2020.00194
Sriherfyna FH, Matsutani M, Hirano K, Koike H, Kataoka N, Yamashita T, Nakamaru-Ogiso E, Matsushita K, Yakushi T (2021) The auxiliary NADH dehydrogenase plays a crucial role in redox homeostasis of nicotinamide cofactors in the absence of the periplasmic oxidation system in Gluconobacter oxydans NBRC3293. Appl Environ Microbiol 87(2):e02155-e2220. https://doi.org/10.1128/aem.02155-20
Tan RQ, Lyu YB, Zeng WZ, Zhou JW (2019) Enhancing scleroglucan production by Sclerotium rolfsii WSH-G01 through a pH-shift strategy based on kinetic analysis. Bioresour Technol 293:122098. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2019.122098
TeruhideSugisawa TH, Masuda S, Setsuko Nomura YS, Tazoe M, Masako Shinjoh SS, Fujiwara A (1990) Microbial production of 2-keto-L-gulonic acid from L-sorbose and D-sorbitol by Gluconobacter melanogenus. Agric Biol Chem 54(5):1201–1209. https://doi.org/10.1080/00021369.1990.10870125
Tian RZ, Liu YF, Chen J, Li JH, Liu L, Du GC, Chen J (2019) Synthetic N-terminal coding sequences for fine-tuning gene expression and metabolic engineering in Bacillus subtilis. Metab Eng 55:131–141. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymben.2019.07.001
Wang PP, Zeng WZ, Xu S, Du GC, Zhou JW, Chen J (2018) Current challenges facing one-step production of L-ascorbic acid. Biotechnol Adv 36(7):1882–1899. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biotechadv.2018.07.006
Xu KD, Tong Y, Li Y, Tao J, Li JH, Zhou JW, Liu S (2021) Rational design of the N-terminal coding sequence for regulating enzyme expression in Bacillus subtilis. ACS Synth Biol 10(2):265–276. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssynbio.0c00309
Xu S, Wang XB, Du GC, Zhou JW, Chen J (2014) Enhanced production of L-sorbose from D-sorbitol by improving the mRNA abundance of sorbitol dehydrogenase in Gluconobacter oxydans WSH-003. Microb Cell Fact 13:146. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12934-014-0146-8
Yuan JF, Wu MB, Lin JP, Yang LR (2016) Combinatorial metabolic engineering of industrial Gluconobacter oxydans DSM2343 for boosting 5-keto-D-gluconic acid accumulation. BMC Biotechnol 16(1):42. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12896-016-0272-y
Yura T (2019) Regulation of the heat shock response in Escherichia coli: history and perspectives. Genes Genet Syst 94(3):103–108. https://doi.org/10.1266/ggs.19-00005
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Key Program, 31830068), the Foundation for Innovative Research Groups of the National Natural Science Foundation of China (32021005), and the National Science Fund for Excellent Young Scholars (21822806).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Z.J. Qin, Y. Chen, and S.Q. Yu performed experiments and data analysis. Z.J. Qin and J.W. Zhou wrote the manuscript and conceived the study. J. Chen and J.W. Zhou coordinated the project. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Qin, Z., Chen, Y., Yu, S. et al. Engineering Gluconobacter cerinus CGMCC 1.110 for direct 2-keto-L-gulonic acid production. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 107, 153–162 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-022-12310-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-022-12310-5