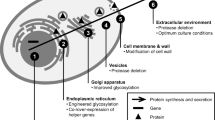
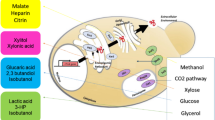
Abstract
Pichia pastoris has been recognized as an important platform for the production of various heterologous proteins in recent years. The strong promoter AOX1, induced by methanol, with the help of the α-pre-pro signal sequence, can lead to a high expression level of extracellular protein. However, this combination was not always efficient, as protein secretion in P. pastoris involves numerous procedures mediated by several cellular proteins, including folding assisted by endoplasmic reticulum (ER) molecular chaperones, degradation through ubiquitination, and an efficient vesicular transport system. Efficient protein expression requires the cooperation of various intracellular pathways. This article summarizes the process of protein secretion, modification, and transportation in P. pastoris. In addition, the roles played by the key proteins in these processes and the corresponding co-expression effects are also listed. It is expected to lay the foundation for the industrial protein production of P. pastoris.
Key points
• Mechanisms of chaperones in protein folding and their co-expression effects are summarized.
• Protein glycosylation modifications are comprehensively reviewed.
• Current dilemmas in the overall protein secretion pathway of Pichia pastoris and corresponding solutions are demonstrated.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aggarwal S, Mishra S (2020) Differential role of segments of α-mating factor secretion signal in Pichia pastoris towards granulocyte colony-stimulating factor emerging from a wild type or codon optimized copy of the gene. Microb Cell Fact 19(1):199. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12934-020-01460-8
Aggarwal S, Mishra S (2021) Modifications in the Kex2 P1’ cleavage site in the α-MAT secretion signal lead to higher production of human granulocyte colony-stimulating factor in Pichia pastoris. World J Microb Biot 37(11). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-021-03167-3
Alva TR, Riera M, Chartron JW (2021) Translational landscape and protein biogenesis demands of the early secretory pathway in Komagataella phaffii. Microb Cell Fact 20(1):19. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12934-020-01489-9
Aw R, McKay PF, Shattock RJ, Polizzi KM (2018) A systematic analysis of the expression of the anti-HIV VRC01 antibody in Pichia pastoris through signal peptide optimization. Protein Expr Purif 149:43–50. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pep.2018.03.013
Bae JH, Sung BH, Seo JW, Kim CH, Sohn JH (2016) A novel fusion partner for enhanced secretion of recombinant proteins in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 100(24):10453–10461. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-016-7722-2
Bankefa OE, Wang M, Zhu T, Li Y (2018) Hac1p homologues from higher eukaryotes can improve the secretion of heterologous proteins in the yeast Pichia pastoris. Biotechnol Lett 40(7):1149–1156. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-018-2571-y
Bao J, Huang M, Petranovic D, Nielsen J (2017) Moderate expression of SEC16 increases protein secretion by Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Appl Environ Microbiol 83(14). https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.03400-16
Bao J, Huang M, Petranovic D, Nielsen J (2018) Balanced trafficking between the ER and the Golgi apparatus increases protein secretion in yeast. AMB Express 8(1):37. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13568-018-0571-x
Barrero JJ, Casler JC, Valero F, Ferrer P, Glick BS (2018) An improved secretion signal enhances the secretion of model proteins from Pichia pastoris. Microb Cell Fact 17(1):161. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12934-018-1009-5
Bashir S, Banday M, Qadri O, Bashir A, Hilal N, Nida IF, Rader S, Fazili KM (2021) The molecular mechanism and functional diversity of UPR signaling sensor IRE1. Life Sci 265:118740. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lfs.2020.118740
Beal DM, Bastow EL, Staniforth GL, von der Haar T, Freedman RB, Tuite MF (2019) Quantitative analyses of the yeast oxidative protein folding pathway in vitro and in vivo. Antioxid Redox Signal 31(4):261–274. https://doi.org/10.1089/ars.2018.7615
Behnia R, Barr FA, Flanagan JJ, Barlowe C, Munro S (2007) The yeast orthologue of GRASP65 forms a complex with a coiled-coil protein that contributes to ER to Golgi traffic. J Cell Biol 176(3):255–261. https://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.200607151
Ben Azoun S, Belhaj AE, Gongrich R, Gasser B, Kallel H (2016) Molecular optimization of rabies virus glycoprotein expression in Pichia pastoris. Microb Biotechnol 9(3):355–368. https://doi.org/10.1111/1751-7915.12350
Bertolotti A, Zhang Y, Hendershot LM, Harding HP, Ron D (2000) Dynamic interaction of BiP and ER stress transducers in the unfolded-protein response. Nat Cell Biol 2(6):326–332. https://doi.org/10.1038/35014014
Burda P, Aebi M (1999) The dolichol pathway of N-linked glycosylation. Biochim Biophys Acta 1426(2):239–257. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0304-4165(98)00127-5
Cabral KMS, Almeida MS, Valente AP, Almeida FCL, Kurtenbach E (2003) Production of the active antifungal Pisum sativum defensin 1 (Psd1) in Pichia pastoris: overcoming the inefficiency of the STE13 protease. Protein Expr Purif 31(1):115–122. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1046-5928(03)00136-0
Calfon M, Zeng H, Urano F, Till JH, Hubbard SR, Harding HP, Clark SG, Ron D (2002) IRE1 couples endoplasmic reticulum load to secretory capacity by processing the XBP-1 mRNA. Nature 415(6867):92–96. https://doi.org/10.1038/415092a
Carvalho P, Goder V, Rapoport TA (2006) Distinct ubiquitin-ligase complexes define convergent pathways for the degradation of ER proteins. Cell 126(2):361–373. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2006.05.043
Castillon GA, Watanabe R, Taylor M, Schwabe TM, Riezman H (2009) Concentration of GPI-anchored proteins upon ER exit in yeast. Traffic 10(2):186–200. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-0854.2008.00857.x
Chiba Y, Suzuki M, Yoshida S, Yoshida A, Ikenaga H, Takeuchi M, Jigami Y, Ichishima E (1998) Production of human compatible high mannose-type (Man5GlcNAc2) sugar chains in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Biol Chem 273(41):26298–26304. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.273.41.26298
Chino H, Mizushima N (2020) ER-phagy: quality control and turnover of endoplasmic reticulum. Trends Cell Biol 30(5):384–398. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tcb.2020.02.001
Choi BK, Bobrowicz P, Davidson RC, Hamilton SR, Kung DH, Li H, Miele RG, Nett JH, Wildt S, Gerngross TU (2003) Use of combinatorial genetic libraries to humanize N-linked glycosylation in the yeast Pichia pastoris. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 100(9):5022–5027. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0931263100
Cukan MC, Hopkins D, Burnina I, Button M, Giaccone E, Houston-Cummings NR, Jiang Y, Li F, Mallem M, Mitchell T, Moore R, Nylen A, Prinz B, Rios S, Sharkey N, Zha D, Hamilton S, Li H, Stadheim TA (2012) Binding of DC-SIGN to glycoproteins expressed in glycoengineered Pichia pastoris. J Immunol Methods 386(1–2):34–42. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jim.2012.08.015
Dai Y, Wang C (1997) A mutant truncated protein disulfide isomerase with no chaperone activity. J Biol Chem 272(44):27572–27576. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.272.44.27572
Dai M, Yu C, Fang T, Fu L, Wang J, Zhang J, Ren J, Xu J, Zhang X, Chen W (2015) Identification and functional characterization of glycosylation of recombinant human platelet-derived growth factor-BB in Pichia pastoris. PLoS ONE 10(12):e0145419. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0145419
Damasceno LM, Anderson KA, Ritter G, Cregg JM, Old LJ, Batt CA (2007) Cooverexpression of chaperones for enhanced secretion of a single-chain antibody fragment in Pichia pastoris. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 74(2):381–389. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-006-0652-7
De Wachter C, Van Landuyt L, Callewaert N (2021) Engineering of yeast glycoprotein expression. Adv Biochem Eng Biotechnol 175:93–135. https://doi.org/10.1007/10_2018_69
Demircioglu FE, Burkhardt P, Fasshauer D (2014) The SM protein Sly1 accelerates assembly of the ER-Golgi SNARE complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 111(38):13828–13833. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1408254111
Deng J, Li J, Ma M, Zhao P, Ming F, Lu Z, Shi J, Fan Q, Liang Q, Jia J, Li J, Zhang S, Zhang L (2020) Co-expressing GroEL-GroES, Ssa1-Sis1 and Bip-PDI chaperones for enhanced intracellular production and partial-wall breaking improved stability of porcine growth hormone. Microb Cell Fact 19(1):35. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12934-020-01304-5
Dou W, Feng J, Zhang X, Xu H, Shi J, Xu Z (2013) Expression, purification, and bioactivity of (GLP-1A2G)2-HSA analogs in Pichia pastoris GS115. Biotechnol Bioprocess Eng 18(6):1076–1082. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12257-013-0356-7
Dou WF, Lei JY, Zhang LF, Xu ZH, Chen Y, Jin J (2008) Expression, purification, and characterization of recombinant human serum albumin fusion protein with two human glucagon-like peptide-1 mutants in Pichia pastoris. Protein Expr Purif 61(1):45–49. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pep.2008.04.012
Duan G, Ding L, Wei D, Zhou H, Chu J, Zhang S, Qian J (2019) Screening endogenous signal peptides and protein folding factors to promote the secretory expression of heterologous proteins in Pichia pastoris. J Biotechnol 306:193–202. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbiotec.2019.06.297
Eichler J, Koomey M (2017) Sweet new roles for protein glycosylation in prokaryotes. Trends Microbiol 25(8):662–672. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tim.2017.03.001
Elia F, Yadhanapudi L, Tretter T, Römisch K (2019) The N-terminus of Sec61p plays key roles in ER protein import and ERAD. PLoS ONE 14(4):e0215950. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0215950
Ellgaard L, Ruddock LW (2005) The human protein disulphide isomerase family: substrate interactions and functional properties. EMBO Rep 6(1):28–32. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.embor.7400311
Fauzee Y, Taniguchi N, Ishiwata-Kimata Y, Takagi H, Kimata Y (2020) The unfolded protein response in Pichia pastoris without external stressing stimuli. FEMS Yeast Res 20(7). https://doi.org/10.1093/femsyr/foaa053
Fu J, Gao J, Liang Z, Yang D (2020) PDI-regulated disulfide bond formation in protein folding and biomolecular assembly. Molecules 26(1). https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26010171
Gasser B, Maurer M, Gach J, Kunert R, Mattanovich D (2006) Engineering of Pichia pastoris for improved production of antibody fragments. Biotechnol Bioeng 94(2):353–361. https://doi.org/10.1002/bit.20851
Gauss R, Jarosch E, Sommer T, Hirsch C (2006) A complex of Yos9p and the HRD ligase integrates endoplasmic reticulum quality control into the degradation machinery. Nat Cell Biol 8(8):849–854. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncb1445
Girrbach V, Strahl S (2003) Members of the evolutionarily conserved PMT family of protein O-mannosyltransferases form distinct protein complexes among themselves. J Biol Chem 278(14):12554–12562. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M212582200
Guan B, Chen F, Su S, Duan Z, Chen Y, Li H, Jin J (2016) Effects of co-overexpression of secretion helper factors on the secretion of a HSA fusion protein (IL2-HSA) in pichia pastoris. Yeast 33(11):587–600. https://doi.org/10.1002/yea.3183
Guerfal M, Ryckaert S, Jacobs PP, Ameloot P, Van Craenenbroeck K, Derycke R, Callewaert N (2010) The HAC1 gene from Pichia pastoris: characterization and effect of its overexpression on the production of secreted, surface displayed and membrane proteins. Microb Cell Fact 9:49. https://doi.org/10.1186/1475-2859-9-49
Guerra-Moreno A, Ang J, Welsch H, Jochem M, Hanna J (2019) Regulation of the unfolded protein response in yeast by oxidative stress. FEBS Lett 593(10):1080–1088. https://doi.org/10.1002/1873-3468.13389
Hamilton SR, Cook WJ, Gomathinayagam S, Burnina I, Bukowski J, Hopkins D, Schwartz S, Du M, Sharkey NJ, Bobrowicz P, Wildt S, Li H, Stadheim TA, Nett JH (2013) Production of sialylated O-linked glycans in Pichia pastoris. Glycobiology 23(10):1192–1203. https://doi.org/10.1093/glycob/cwt056
Hanna MGt, Mela I, Wang L, Henderson RM, Chapman ER, Edwardson JM, Audhya A (2016) Sar1 GTPase activity is regulated by membrane curvature. J Biol Chem 291(3):1014–1027. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M115.672287
Hanson PI, Roth R, Morisaki H, Jahn R, Heuser JE (1997) Structure and conformational changes in NSF and its membrane receptor complexes visualized by quick-freeze/deep-etch electron microscopy. Cell 90(3):523–535. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0092-8674(00)80512-7
Hatahet F, Ruddock LW (2009) Protein disulfide isomerase: a critical evaluation of its function in disulfide bond formation. Antioxid Redox Signal 11(11):2807–2850. https://doi.org/10.1089/ars.2009.2466
He H, Wu S, Mei M, Ning J, Li C, Ma L, Zhang G, Yi L (2020) A combinational strategy for effective heterologous production of functional human lysozyme in Pichia pastoris. Front Bioeng Biotechnol 8:118. https://doi.org/10.3389/fbioe.2020.00118
Helian Y, Gai Y, Fang H, Sun Y, Zhang D (2020) A multistrategy approach for improving the expression of E. coli phytase in Pichia pastoris. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 47(12):1161–1172. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10295-020-02311-6
Heo Y, Yoon HJ, Ko H, Jang S, Lee HH (2020) Crystal structures of Uso1 membrane tether reveal an alternative conformation in the globular head domain. Sci Rep 10(1):9544. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-66480-1
Herrera-Estala AL, Fuentes-Garibay JA, Guerrero-Olazarán M, Viader-Salvadó JM (2022) Low specific growth rate and temperature in fed-batch cultures of a beta-propeller phytase producing Pichia pastoris strain under GAP promoter trigger increased KAR2 and PSA1-1 gene expression yielding enhanced extracellular productivity. J Biotechnol 352:59–67. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbiotec.2022.05.010
Hetz C, Saxena S (2017) ER stress and the unfolded protein response in neurodegeneration. Nat Rev Neurol 13(8):477–491. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrneurol.2017.99
Hetz C, Zhang K, Kaufman RJ (2020) Mechanisms, regulation and functions of the unfolded protein response. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 21(8):421–438. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41580-020-0250-z
Huang H, Liang Q, Wang Y, Chen J, Kang Z (2020a) High-level constitutive expression of leech hyaluronidase with combined strategies in recombinant Pichia pastoris. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 104(4):1621–1632. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-019-10282-7
Huang J, Zhao Q, Chen L, Zhang C, Bu W, Zhang X, Zhang K, Yang Z (2020b) Improved production of recombinant Rhizomucor miehei lipase by coexpressing protein folding chaperones in Pichia pastoris, which triggered ER stress. Bioengineered 11(1):375–385. https://doi.org/10.1080/21655979.2020.1738127
Huang M, Gao Y, Zhou X, Zhang Y, Cai M (2017) Regulating unfolded protein response activator HAC1p for production of thermostable raw-starch hydrolyzing α-amylase in Pichia pastoris. Bioprocess Biosyst Eng 40(3):341–350. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00449-016-1701-y
Huang Y, Long Y, Li S, Lin T, Wu J, Zhang Y, Lin Y (2018) Investigation on the processing and improving the cleavage efficiency of furin cleavage sites in Pichia pastoris. Microb Cell Fact 17(1):172. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12934-018-1020-x
Huyer G, Piluek WF, Fansler Z, Kreft SG, Hochstrasser M, Brodsky JL, Michaelis S (2004) Distinct machinery is required in Saccharomyces cerevisiae for the endoplasmic reticulum-associated degradation of a multispanning membrane protein and a soluble luminal protein. J Biol Chem 279(37):38369–38378. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M402468200
Hwang J, Qi L (2018) Quality control in the endoplasmic reticulum: crosstalk between ERAD and UPR pathways. Trends Biochem Sci 43(8):593–605. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tibs.2018.06.005
Inan M, Aryasomayajula D, Sinha J, Meagher MM (2006) Enhancement of protein secretion in Pichia pastoris by overexpression of protein disulfide isomerase. Biotechnol Bioeng 93(4):771–778. https://doi.org/10.1002/bit.20762
Itskanov S, Kuo KM, Gumbart JC, Park E (2021) Stepwise gating of the Sec61 protein-conducting channel by Sec63 and Sec62. Nat Struct Mol Biol 28(2):162–172. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41594-020-00541-x
Iwasaki H, Yorimitsu T, Sato K (2015) Distribution of Sec24 isoforms to each ER exit site is dynamically regulated in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. FEBS Lett 589(11):1234–1239. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.febslet.2015.04.006
Jensen D, Schekman R (2011) COPII-mediated vesicle formation at a glance. J Cell Sci 124(Pt 1):1–4. https://doi.org/10.1242/jcs.069773
Jha V, Kumari T, Manickam V, Assar Z, Olson KL, Min JK, Cho J (2021) ERO1-PDI redox signaling in health and disease. Antioxid Redox Signal 35(13):1093–1115. https://doi.org/10.1089/ars.2021.0018
Jiao L, Zhou Q, Su Z, Xu L, Yan Y (2018a) High-level extracellular production of Rhizopus oryzae lipase in Pichia pastoris via a strategy combining optimization of gene-copy number with co-expression of ERAD-related proteins. Protein Expr Purif 147:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pep.2018.02.005
Jiao L, Zhou Q, Su Z, Yan Y (2018b) Efficient heterologous production of Rhizopus oryzae lipase via optimization of multiple expression-related helper proteins. Int J Mol Sci 19(11). https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19113372
Julius D, Blair L, Brake A, Sprague G, Thorner J (1983) Yeast alpha factor is processed from a larger precursor polypeptide: the essential role of a membrane-bound dipeptidyl aminopeptidase. Cell 32(3):839–852. https://doi.org/10.1016/0092-8674(83)90070-3
Kabani M, Kelley SS, Morrow MW, Montgomery DL, Sivendran R, Rose MD, Gierasch LM, Brodsky JL (2003) Dependence of endoplasmic reticulum-associated degradation on the peptide binding domain and concentration of BiP. Mol Biol Cell 14(8):3437–3448. https://doi.org/10.1091/mbc.e02-12-0847
Kaiser CA, Preuss D, Grisafi P, Botstein D (1987) Many random sequences functionally replace the secretion signal sequence of yeast invertase. Science 235(4786):312–317. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.3541205
Kampinga HH, Craig EA (2010) The HSP70 chaperone machinery: J proteins as drivers of functional specificity. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 11(8):579–592. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrm2941
Kangwa M, Salgado JAG, Fernandez-Lahore HM (2018) Identification and characterization of N-glycosylation site on a Mucor circinelloides aspartic protease expressed in Pichia pastoris: effect on secretion, activity and thermo-stability. AMB Express 8(1):157. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13568-018-0691-3
Kerr H, Herbert AP, Makou E, Abramczyk D, Malik TH, Lomax-Browne H, Yang Y, Pappworth IY, Denton H, Richards A, Marchbank KJ, Pickering MC, Barlow PN (2021) Murine factor H co-produced in yeast with protein disulfide isomerase ameliorated C3 dysregulation in factor H-deficient mice. Front Immunol 12:681098. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2021.681098
Klappa P, Ruddock LW, Darby NJ, Freedman RB (1998) The b′ domain provides the principal peptide-binding site of protein disulfide isomerase but all domains contribute to binding of misfolded proteins. Embo J 17(4):927–935. https://doi.org/10.1093/emboj/17.4.927
Kurokawa K, Okamoto M, Nakano A (2014) Contact of cis-Golgi with ER exit sites executes cargo capture and delivery from the ER. Nat Commun 5:3653. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms4653
Lang BJ, Guerrero ME, Prince TL, Okusha Y, Bonorino C, Calderwood SK (2021) The functions and regulation of heat shock proteins; key orchestrators of proteostasis and the heat shock response. Arch Toxicol 95(6):1943–1970. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-021-03070-8
Larburu N, Adams CJ, Chen CS, Nowak PR, Ali MMU (2020) Mechanism of Hsp70 specialized interactions in protein translocation and the unfolded protein response. Open Biol 10(8):200089. https://doi.org/10.1098/rsob.200089
Larsen ISB, Narimatsu Y, Clausen H, Joshi HJ, Halim A (2019) Multiple distinct O-Mannosylation pathways in eukaryotes. Curr Opin Struct Biol 56:171–178. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sbi.2019.03.003
Lee MC, Orci L, Hamamoto S, Futai E, Ravazzola M, Schekman R (2005) Sar1p N-terminal helix initiates membrane curvature and completes the fission of a COPII vesicle. Cell 122(4):605–617. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2005.07.025
Li D, Wu J, Chen J, Zhang D, Zhang Y, Qiao X, Yu X, Zheng Q, Hou J (2020) Optimized expression of classical swine fever virus E2 protein via combined strategy in Pichia pastoris. Protein Expr Purif 167:105527. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pep.2019.105527
Li X, Liu Z, Wang G, Pan D, Jiao L, Yan Y (2016) Overexpression of Candida rugosa lipase Lip1 via combined strategies in Pichia pastoris. Enzyme Microb Technol 82:115–124. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enzmictec.2015.09.003
Li Z, Moy A, Gomez SR, Franz AH, Lin-Cereghino J, Lin-Cereghino GP (2010) An improved method for enhanced production and biological activity of human secretory leukocyte protease inhibitor (SLPI) in Pichia pastoris. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 402(3):519–524. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2010.10.067
Lin-Cereghino GP, Stark CM, Kim D, Chang J, Shaheen N, Poerwanto H, Agari K, Moua P, Low LK, Tran N, Huang AD, Nattestad M, Oshiro KT, Chang JW, Chavan A, Tsai JW, Lin-Cereghino J (2013) The effect of alpha-mating factor secretion signal mutations on recombinant protein expression in Pichia pastoris. Gene 519(2):311–317. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gene.2013.01.062
Liu C, Chen KX, Wang YT, Shao ML, Xu ZH, Rao ZM (2022) Identification of a novel cytochrome P450 17A2 enzyme catalyzing the C17 alpha hydroxylation of progesterone and its application in engineered Pichia pastoris. Biochem Eng J 177.https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bej.2021.108264
Liu YY, Woo JH, Neville DM Jr (2005) Overexpression of an anti-CD3 immunotoxin increases expression and secretion of molecular chaperone BiP/Kar2p by Pichia pastoris. Appl Environ Microbiol 71(9):5332–5340. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.71.9.5332-5340.2005
Man Z, Rao Z, Xu M, Guo J, Yang T, Zhang X, Xu Z (2016) Improvement of the intracellular environment for enhancing l-arginine production of Corynebacterium glutamicum by inactivation of H(2)O(2)-forming flavin reductases and optimization of ATP supply. Metab Eng 38:310–321. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymben.2016.07.009
Marcinowski M, Höller M, Feige MJ, Baerend D, Lamb DC, Buchner J (2011) Substrate discrimination of the chaperone BiP by autonomous and cochaperone-regulated conformational transitions. Nat Struct Mol Biol 18(2):150–158. https://doi.org/10.1038/nsmb.1970
Miao T, Basit A, Liu J, Zheng F, Rahim K, Lou H, Jiang W (2021a) Improved production of xylanase in Pichia pastoris and its application in xylose production from xylan. Front Bioeng Biotechnol 9:690702. https://doi.org/10.3389/fbioe.2021.690702
Miao T, Basit A, Wen J, Liu J, Zheng F, Cao Y, Jiang W (2021b) High efficient degradation of glucan/glucomannan to cello-/mannan-oligosaccharide by endoglucanase via tetrasaccharide as intermediate. Food Chem 350:129175. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2021.129175
Mille C, Bobrowicz P, Trinel PA, Li H, Maes E, Guerardel Y, Fradin C, Martínez-Esparza M, Davidson RC, Janbon G, Poulain D, Wildt S (2008) Identification of a new family of genes involved in beta-1,2-mannosylation of glycans in Pichia pastoris and Candida albicans. J Biol Chem 283(15):9724–9736. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M708825200
Miller EA, Beilharz TH, Malkus PN, Lee MCS, Hamamoto S, Orci L, Schekman R (2003) Multiple cargo binding sites on the COPII subunit Sec24p ensure capture of diverse membrane proteins into transport vesicles. Cell 114(4):497–509. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0092-8674(03)00609-3
Mohanty S, Chaudhary BP, Zoetewey D (2020) Structural insight into the mechanism of N-linked glycosylation by oligosaccharyltransferase. Biomolecules 10(4). https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10040624
Montegna EA, Bhave M, Liu Y, Bhattacharyya D, Glick BS (2012) Sec12 binds to Sec16 at transitional ER sites. PLoS ONE 7(2):e31156. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0031156
Neiers F, Belloir C, Poirier N, Naumer C, Krohn M, Briand L (2021) Comparison of different signal peptides for the efficient secretion of the sweet-tasting plant protein brazzein in Pichia pastoris. Life (Basel) 11(1). https://doi.org/10.3390/life11010046
Nett JH, Cook WJ, Chen MT, Davidson RC, Bobrowicz P, Kett W, Brevnova E, Potgieter TI, Mellon MT, Prinz B, Choi BK, Zha D, Burnina I, Bukowski JT, Du M, Wildt S, Hamilton SR (2013) Characterization of the Pichia pastoris protein-O-mannosyltransferase gene family. PLoS ONE 8(7):e68325. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0068325
Neubert P, Halim A, Zauser M, Essig A, Joshi HJ, Zatorska E, Larsen IS, Loibl M, Castells-Ballester J, Aebi M, Clausen H, Strahl S (2016) Mapping the O-mannose glycoproteome in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Proteomics 15(4):1323–1337. https://doi.org/10.1074/mcp.M115.057505
Noda Y, Yamagishi T, Yoda K (2007) Specific membrane recruitment of Uso1 protein, the essential endoplasmic reticulum-to-Golgi tethering factor in yeast vesicular transport. J Cell Biochem 101(3):686–694. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcb.21225
Okamoto M, Kurokawa K, Matsuura-Tokita K, Saito C, Hirata R, Nakano A (2012) High-curvature domains of the ER are important for the organization of ER exit sites in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Cell Sci 125(Pt 14):3412–3420. https://doi.org/10.1242/jcs.100065
Orci L, Ravazzola M, Meda P, Holcomb C, Moore HP, Hicke L, Schekman R (1991) Mammalian Sec23p homologue is restricted to the endoplasmic reticulum transitional cytoplasm. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 88(19):8611–8615. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.88.19.8611
Park SM, Kang TI, So JS (2021) Roles of XBP1s in transcriptional regulation of target genes. Biomedicines 9(7). https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines9070791
Pellowe GA, Booth PJ (2020) Structural insight into co-translational membrane protein folding. Biochim Biophys Acta Biomembr 1:183019. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbamem.2019.07.007
Peña DA, Gasser B, Zanghellini J, Steiger MG, Mattanovich D (2018) Metabolic engineering of Pichia pastoris. Metab Eng 50:2–15. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymben.2018.04.017
Pérez-Rodriguez S, Wulff T, Voldborg BG, Altamirano C, Trujillo-Roldán MA, Valdez-Cruz NA (2021) Compartmentalized proteomic profiling outlines the crucial role of the classical secretory pathway during recombinant protein production in Chinese hamster ovary cells. ACS Omega 6(19):12439–12458. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsomega.0c06030
Piirainen MA, Frey AD (2020) Investigating the role of ERAD on antibody processing in glycoengineered Saccharomyces cerevisiae. FEMS Yeast Res 20(1). https://doi.org/10.1093/femsyr/foaa002
Pobre KFR, Poet GJ, Hendershot LM (2019) The endoplasmic reticulum (ER) chaperone BiP is a master regulator of ER functions: Getting by with a little help from ERdj friends. J Biol Chem 294(6):2098–2108. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.REV118.002804
Pool MR (2005) Signal recognition particles in chloroplasts, bacteria, yeast and mammals (review). Mol Membr Biol 22(1–2):3–15. https://doi.org/10.1080/09687860400026348
Pool MR (2022) Targeting of proteins for translocation at the endoplasmic reticulum. Int J Mol Sci 23(7):3773
Prates ET, Guan X, Li Y, Wang X, Chaffey PK, Skaf MS, Crowley MF, Tan Z, Beckham GT (2018) The impact of O-glycan chemistry on the stability of intrinsically disordered proteins. Chem Sci 9(15):3710–3715. https://doi.org/10.1039/c7sc05016j
Radanović T, Ernst R (2021) The unfolded protein response as a guardian of the secretory pathway. Cells 10(11). https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10112965
Radoman B, Grünwald-Gruber C, Schmelzer B, Zavec D, Gasser B, Altmann F, Mattanovich D (2021) The degree and length of O-glycosylation of recombinant proteins produced in Pichia pastoris depends on the nature of the protein and the process type. Biotechnol J 16(3):e2000266. https://doi.org/10.1002/biot.202000266
Raschmanova H, Weninger A, Knejzlik Z, Melzoch K, Kovar K (2021) Engineering of the unfolded protein response pathway in Pichia pastoris: enhancing production of secreted recombinant proteins. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 105(11):4397–4414. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-021-11336-5
Resina D, Bollók M, Khatri NK, Valero F, Neubauer P, Ferrer P (2007) Transcriptional response of P. pastoris in fed-batch cultivations to Rhizopus oryzae lipase production reveals UPR induction. Microb Cell Fact 6:21. https://doi.org/10.1186/1475-2859-6-21
Roth G, Vanz AL, Lünsdorf H, Nimtz M, Rinas U (2018) Fate of the UPR marker protein Kar2/Bip and autophagic processes in fed-batch cultures of secretory insulin precursor producing Pichia pastoris. Microb Cell Fact 17(1):123. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12934-018-0970-3
Sallada ND, Harkins LE, Berger BW (2019) Effect of gene copy number and chaperone coexpression on recombinant hydrophobin HFBI biosurfactant production in Pichia pastoris. Biotechnol Bioeng 116(8):2029–2040. https://doi.org/10.1002/bit.26982
Samuel P, Prasanna Vadhana AK, Kamatchi R, Antony A, Meenakshisundaram S (2013) Effect of molecular chaperones on the expression of Candida antarctica lipase B in Pichia pastoris. Microbiol Res 168(10):615–620. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micres.2013.06.007
Santana-Molina C, Gutierrez F, Devos DP (2021) Homology and modular evolution of CATCHR at the origin of the eukaryotic endomembrane system. Genome Biol Evol 13(7). https://doi.org/10.1093/gbe/evab125
Sato K, Nakano A (2004) Reconstitution of coat protein complex II (COPII) vesicle formation from cargo-reconstituted proteoliposomes reveals the potential role of GTP hydrolysis by Sar1p in protein sorting. J Biol Chem 279(2):1330–1335. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.C300457200
Schuck S, Prinz WA, Thorn KS, Voss C, Walter P (2009) Membrane expansion alleviates endoplasmic reticulum stress independently of the unfolded protein response. J Cell Biol 187(4):525–536. https://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.200907074
Schweizer A, Fransen JA, Matter K, Kreis TE, Ginsel L, Hauri HP (1990) Identification of an intermediate compartment involved in protein transport from endoplasmic reticulum to Golgi apparatus. Eur J Cell Biol 53(2):185–196
Sha C, Yu XW, Lin NX, Zhang M, Xu Y (2013) Enhancement of lipase r27RCL production in Pichia pastoris by regulating gene dosage and co-expression with chaperone protein disulfide isomerase. Enzyme Microb Technol 53(6–7):438–443. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enzmictec.2013.09.009
Shen Q, Wu M, Wang HB, Naranmandura H, Chen SQ (2012) The effect of gene copy number and co-expression of chaperone on production of albumin fusion proteins in Pichia pastoris. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 96(3):763–772. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-012-4337-0
Shen Q, Yu Z, Lv PJ, Li Q, Zou SP, Xiong N, Liu ZQ, Xue YP, Zheng YG (2020) Engineering a Pichia pastoris nitrilase whole cell catalyst through the increased nitrilase gene copy number and co-expressing of ER oxidoreductin 1. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 104(6):2489–2500. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-020-10422-4
Shrimal S, Gilmore R (2019) Oligosaccharyltransferase structures provide novel insight into the mechanism of asparagine-linked glycosylation in prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. Glycobiology 29(4):288–297. https://doi.org/10.1093/glycob/cwy093
Smith JD, Tang BC, Robinson AS (2004) Protein disulfide isomerase, but not binding protein, overexpression enhances secretion of a non-disulfide-bonded protein in yeast. Biotechnol Bioeng 85(3):340–350. https://doi.org/10.1002/bit.10853
Song H, Wickner WT (2021) Fusion of tethered membranes can be driven by Sec18/NSF and Sec17/αSNAP without HOPS. Elife 10.https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.73240
Suda Y, Kurokawa K, Nakano A (2017) Regulation of ER-Golgi transport dynamics by GTPases in budding yeast. Front Cell Dev Biol 5:122. https://doi.org/10.3389/fcell.2017.00122
Sun XX, Dai Y, Liu HP, Chen SM, Wang CC (2000) Contributions of protein disulfide isomerase domains to its chaperone activity. Biochim Biophys Acta 1481(1):45–54. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0167-4838(00)00122-9
Theron CW, Vandermies M, Telek S, Steels S, Fickers P (2020) Comprehensive comparison of Yarrowia lipolytica and Pichia pastoris for production of Candida antarctica lipase B. Sci Rep 10(1):1741. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-58683-3
Torres M, Dickson AJ (2022) Reprogramming of Chinese hamster ovary cells towards enhanced protein secretion. Metab Eng 69:249–261. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymben.2021.12.004
Tu BP, Weissman JS (2002) The FAD- and O(2)-dependent reaction cycle of Ero1-mediated oxidative protein folding in the endoplasmic reticulum. Mol Cell 10(5):983–994. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1097-2765(02)00696-2
Vadhana AK, Samuel P, Berin RM, Krishna J, Kamatchi K, Meenakshisundaram S (2013) Improved secretion of Candida antarctica lipase B with its native signal peptide in Pichia pastoris. Enzyme Microb Technol 52(3):177–183. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enzmictec.2013.01.001
van den Berg B, Chung EW, Robinson CV, Mateo PL, Dobson CM (1999) The oxidative refolding of hen lysozyme and its catalysis by protein disulfide isomerase. Embo J 18(17):4794–4803. https://doi.org/10.1093/emboj/18.17.4794
Vanz AL, Nimtz M, Rinas U (2014) Decrease of UPR- and ERAD-related proteins in Pichia pastoris during methanol-induced secretory insulin precursor production in controlled fed-batch cultures. Microb Cell Fact 13(1):23. https://doi.org/10.1186/1475-2859-13-23
Vembar SS, Jonikas MC, Hendershot LM, Weissman JS, Brodsky JL (2010) J domain co-chaperone specificity defines the role of BiP during protein translocation. J Biol Chem 285(29):22484–22494. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M110.102186
Wang J, Wu Z, Zhang T, Wang Y, Yang B (2019) High-level expression of Thermomyces dupontii thermophilic lipase in Pichia pastoris via combined strategies. 3 Biotech 9(2):62. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-019-1597-8
Wang QH, Liang L, Liu WC, Gong T, Chen JJ, Hou Q, Yang JL, Zhu P (2017a) Enhancement of recombinant BmK AngM1 production in Pichia pastoris by regulating gene dosage, co-expressing with chaperones and fermenting in fed-batch mode. J Asian Nat Prod Res 19(6):581–594. https://doi.org/10.1080/10286020.2017.1311872
Wang XD, Jiang T, Yu XW, Xu Y (2017b) Effects of UPR and ERAD pathway on the prolyl endopeptidase production in Pichia pastoris by controlling of nitrogen source. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 44(7):1053–1063. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10295-017-1938-8
Wang S, Rong Y, Wang Y, Kong D, Wang PG, Chen M, Kong Y (2020) Homogeneous production and characterization of recombinant N-GlcNAc-protein in Pichia pastoris. Microb Cell Fact 19(1):7. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12934-020-1280-0
Weiss RG, Losfeld ME, Aebi M, Riniker S (2021) N-glycosylation enhances conformational flexibility of protein disulfide isomerase revealed by microsecond molecular dynamics and Markov state modeling. J Phys Chem B 125(33):9467–9479. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jpcb.1c04279
Werten MWT, Eggink G, Cohen Stuart MA, de Wolf FA (2019) Production of protein-based polymers in Pichia pastoris. Biotechnol Adv 37(5):642–666. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biotechadv.2019.03.012
Whyteside G, Alcocer MJ, Kumita JR, Dobson CM, Lazarou M, Pleass RJ, Archer DB (2011) Native-state stability determines the extent of degradation relative to secretion of protein variants from Pichia pastoris. PLoS ONE 6(7):e22692. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0022692
Wildt S, Gerngross TU (2005) The humanization of N-glycosylation pathways in yeast. Nat Rev Microbiol 3(2):119–128. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrmicro1087
Wu M, Liu W, Yang G, Yu D, Lin D, Sun H, Chen S (2014) Engineering of a Pichia pastoris expression system for high-level secretion of HSA/GH fusion protein. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 172(5):2400–2411. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-013-0688-y
Wu X, Siggel M, Ovchinnikov S, Mi W, Svetlov V, Nudler E, Liao M, Hummer G, Rapoport TA (2020) Structural basis of ER-associated protein degradation mediated by the Hrd1 ubiquitin ligase complex. Science 368(6489). https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aaz2449
Xia X (2019) Translation Control of HAC1 by Regulation of Splicing in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Int J Mol Sci 20(12). https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20122860
Xiang ZX, Gong JS, Li H, Shi WT, Jiang M, Xu ZH, Shi JS (2021) Heterologous expression, fermentation strategies and molecular modification of collagen for versatile applications. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. https://doi.org/10.1080/10408398.2021.2016599
Yan P, Zou Z, Zhang S, Wang R, Niu T, Zhang X, Liu D, Zhou X, Chang AK, Milton NGN, Jones GW, He J (2021) Defining the mechanism of PDI interaction with disulfide-free amyloidogenic proteins: Implications for exogenous protein expression and neurodegenerative disease. Int J Biol Macromol 174:175–184. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2021.01.172
Yang J, Lu Z, Chen J, Chu P, Cheng Q, Liu J, Ming F, Huang C, Xiao A, Cai H, Zhang L (2016) Effect of cooperation of chaperones and gene dosage on the expression of porcine PGLYRP-1 in Pichia pastoris. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 100(12):5453–5465. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-016-7372-4
Zahrl RJ, Mattanovich D, Gasser B (2018) The impact of ERAD on recombinant protein secretion in Pichia pastoris (syn Komagataella spp.). Microbiology (Reading) 164(4):453–463. https://doi.org/10.1099/mic.0.000630
Zhang Y, Huang H, Yao X, Du G, Chen J, Kang Z (2018) High-yield secretory production of stable, active trypsin through engineering of the N-terminal peptide and self-degradation sites in Pichia pastoris. Bioresour Technol 247:81–87. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2017.08.006
Zheng F, Liu J, Basit A, Miao T, Jiang W (2018) Insight to improve α-L-arabinofuranosidase productivity in Pichia pastoris and its application on corn stover degradation. Front Microbiol 9:3016. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2018.03016
Funding
This work was financially supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (No. 2021YFC2100900), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 21978116 and 32171261), and the Postgraduate Research & Practice Innovation Program of Jiangsu Province (No. KYCX22_2439).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
JG and JS conceived of and designed the article. CS, Hui Li, Heng Li, and ZR analyzed the data. ZX performed the research. CL wrote the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, C., Gong, JS., Su, C. et al. Pathway engineering facilitates efficient protein expression in Pichia pastoris. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 106, 5893–5912 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-022-12139-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-022-12139-y