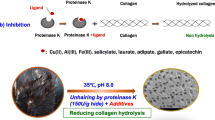
Abstract
Enzymatic dehairing, as a crucial part of cleaner leather processing, has reached processive advancement with potentially replacing the traditional hair removal due to increasing pressure from environmental demand. However, this cleaner technology based on proteases has a problem that the hide grain (collagen-rich structure) is susceptible to be hydrolyzed, decreasing the quality of finished leather. From the perspective of improving the stability of collagen fibers and their resistance to proteolysis, a method for protecting the hide grain during the enzymatic dehairing process was developed. The results showed that calcium ions had a swelling effect on collagen fibers under near-neutral conditions (pH 6.0–10.0), decreasing the thermal stability of collagen and the proteolysis resistance of collagen significantly. The alkaline environment (pH 10.0–12.0) will promote the dissociation of carboxyl groups in hide collagen, promoting the combination of calcium ions and carboxyl groups. This strategy can change the surface charge of collagen fibers and strengthen the connection between collagen fibers, thus improving protease resistance and the thermal stability of collagen. However, collagen fibers could swell violently once the alkalinity of the solution environment was extreme. Despite the above situation, calcium ion was still conducive to maintain the structural stability of collagen fibers. At pH 10.0–12.0, pretreating animal hide with a solution containing calcium ions can improve the protease resistance of hide grain, making the hide grain well-protected. This method provided an effective way to establish a safer enzymatic unhairing technology based on substrate protection.
Key points
• A collagen protection method for hair removal of animal hide was developed.
• This method applied calcium ions to collagen at alkaline conditions (pH 10.0–12.0).
• Pretreatment results of calcium ions at different pH values on animal hide were compared.










Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and material
The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Code availability
Not applicable
References
Akram F, Haq IU, Jabbar Z (2020) Production and characterization of a novel thermo- and detergent stable keratinase from Bacillus sp. NKSP-7 with perceptible applications in leather processing and laundry industries. Int J Biol Macromol 164:371–383. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.07.146
Andrioli E, Petry L, Gutterres M (2015) Environmentally friendly hide unhairing: enzymatic-oxidative unhairing as an alternative to use of lime and sodium sulfide. Process Saf Environ 93:9–17. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psep.2014.06.001
Bagewadi ZK, Mulla SI, Ninnekar HZ (2018) Response surface methodology based optimization of keratinase production from Trichoderma harzianum isolate HZN12 using chicken feather waste and its application in dehairing of hide. J Environ Chem Eng 6(4):4828–4839. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2018.07.007
Boki K, Kawasaki N (1994) Moisture sorption characteristics of collagen-fibers prepared in different acidic pH solutions. J Colloid Interf Sci 164(2):364–369. https://doi.org/10.1006/jcis.1994.1178
Boryskina OP, Bolbukh TV, Semenov MA, Gasan AI, Maleev VY (2007) Energies of peptide–peptide and peptide–water hydrogen bonds in collagen: evidences from infrared spectroscopy, quartz piezogravimetry and differential scanning calorimetry. J Mol Struct 827(1–3):1–10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molstruc.2006.05.002
Cao S, Zeng Y, Cheng B, Zhang W, Liu B (2016) Effect of pH on Al/Zr-binding sites between collagen fibers in tanning process. J Am Leather Chem as 111:242–249
Cao S, Li D, Ma X, Xin Q, Song J, Lu F, Li Y (2019) A novel unhairing enzyme produced by heterologous expression of keratinase gene (kerT) in Bacillus subtilis. World J Microb Biot 35:122. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-019-2701-2
Chang EP, Chien JCW (1973) The effect of ions on the superstructures of reconstituted collagen. Biopolymers 12(5):1063–1069. https://doi.org/10.1002/bip.1973.360120510
Cheng H, Chen M, Liao L, Li Z (2009) Chemical and physical behaviour of collagen fibre in alkaline solutions. J Soc Leath Tech Ch 93(4):140–144
Cheng H, Chen M, Li Z (2010) Properties of collagen fibre in alkali and neutral salt solutions. J Soc Leath Tech Ch 94(2):65–69
Courts A (1960) Structural changes in collagen. Biochem J 74(2):238–247. https://doi.org/10.1042/bj0740238
Emran MA, Ismail SA, Abdel-Fattah AM (2020) Valorization of feather via the microbial production of multi-applicable keratinolytic enzyme. Biocatal Agric Biotechnol 27:101674. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bcab.2020.101674
Fietzek PP, Rexrodt FW, Wendt P, Stark M, Kühn K (1972) The covalent structure of collagen. Eur J Biochem 30(1):163–168. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1432-1033.1973.tb03072.x
Finch A, Ledward DA (1973) Differential scanning calorimetric study of collagen fibres swollen in aqueous neutral salt solutions. BBA - Protein Struct M 295(1):296–300. https://doi.org/10.1016/0005-2795(73)90096-2
Freudenberg U, Behrens SH, Welzel PB, Müller M, Grimmer M, Salchert K, Taeger T, Schmidt K, Pompe W, Werner C (2007) Electrostatic interactions modulate the conformation of collagen I. Biophys J 92(6):2108–2119. https://doi.org/10.1529/biophysj.106.094284
Gross J, Highberger JH, Schmitt FO (1955) Extraction of collagen from connective tissue by neutral salt solutions. P Natl Acad Sci Usa 41(1): 1-7. http://www.jstor.org/stable/88998
Hamiche S, Mechri S, Khelouia L, Annane R, El Hattab M, Badis A, Jaouadi B (2019) Purification and biochemical characterization of two keratinases from Bacillus amyloliquefaciens S13 isolated from marine brown alga Zonaria tournefortii with potential keratin-biodegradation and hide-unhairing activities. Int J Biol Macromol 122:758–769. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2018.10.174
Jaquess PA, Elmore ME, Miguel NB (1999) Advances in stabilized enzymes for leather processing. J Am Leather Chem as 94(9):355–361
Jenkins CL, Vasbinder MM, Miller SJ, Raines RT (2005) Peptide bond isosteres: ester or (E)-alkene in the backbone of the collagen triple helix. Org Lett 7(13):2619–2622. https://doi.org/10.1021/ol050780m
Joshi N, Kocher GS, Kalia A, Banga HS (2020) Development of nano-silver alkaline protease bio-conjugate depilating eco-benign formulation by utilizing potato peel based medium. Int J Biol Macromol 152:261–271. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.02.251
Joshi N, Kocher GS, Kalia A, Banga HS (2021) Bacillus circulans MTCC 7906 aided facile development of bioconjugate nano-silica alkaline protease formulation with superlative dehairing potential. Environ Pollut 285:117181. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2021.117181
Kanagaraj J, Senthilvelan T, Panda RC, Kavitha S (2015) Eco-friendly waste management strategies for greener environment towards sustainable development in leather industry: a comprehensive review. J Clean Prod 89:1–17. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2014.11.013
Kavitha M, Shanthi C, Chandrababu NK (2018) Cold active lipase from Pseudomonas sp. VITCLP4 as degreasing agent in leather processing. Indian J Chem Tech 25: 482-488. http://hdl.handle.net/10603/151861
Kerouaz B, Jaouadi B, Brans A, Saoudi B, Habbeche A, Haberra S, Belghith H, Gargroui A, Ladjama A (2021) Purification and biochemical characterization of two novel extracellular keratinases with feather-degradation and hide-dehairing potential. Process Biochem 106:137–148. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procbio.2021.04.009
Khambhaty Y (2020) Applications of enzymes in leather processing. Environ Chem Lett 18(3):747–769. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10311-020-00971-5
Kikuchi M, Itoh S, Ichinose S, Shinomiya K, Tanaka J (2001) Self-organization mechanism in a bone-like hydroxyapatite/collagen nanocomposite synthesized in vitro and its biological reaction in vivo. Biomaterials 22(13):1705–1711. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0142-9612(00)00305-7
Kronick PL, Cooke P (1996) Thermal stabilization of collagen fibers by calcification. Connect Tissue Res 33(4):275–282. https://doi.org/10.3109/03008209609028885
Li Y, Zhu D, Jin L, Fan G, Mu J (2006) The combination between collagen polypeptide and calcium. J Soc Leath Tech Ch 90(3):123–126
Li YH, Luo FX, Peng BY, Xu BB (2015) Impact of typical surfactants on the collagenolytic and elastionolytic activities of proteases. J Am Leather Chem as 110:227–236
Lima EED, Franco DG, Galeano RMS, Guimarães NCDA, Masui DC, Giannesi GC, Zanoelo FF (2021) Biochemical characterization of a partially purified protease from Aspergillus terreus 7461 and its application as an environmentally friendly dehairing agent for leather industry. Prep Biochem Biotech 51(4):320–330. https://doi.org/10.1080/10826068.2020.1815058
Matkawala F, Nighojkar S, Kumar A, Nighojkar A (2019) Enhanced production of alkaline protease by Neocosmospora sp. N1 using custard apple seed powder as inducer and its application for stain removal and dehairing. Biocatal Agric Biotechnol 21: 101310. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bcab.2019.101310
Myllyharju J, Kivirikko KI (2001) Collagens and collagen-related diseases. Ann Med 33:7–21. https://doi.org/10.3109/07853890109002055
Nazer DW, Al-Sa’Ed RM, Siebel MA (2006) Reducing the environmental impact of the unhairing–liming process in the leather tanning industry. J Clean Prod 14(1):65–74. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2005.04.002
Petrova AV, Sergeeva IA, Petrova GP, Mitrofanova AV (2020) The features of interaction of collagen and collagenase molecules in the presence of chromium and calcium ions in solutions by dynamic light scattering. Mosc U Phys B+ 75(6): 611-617. https://doi.org/10.3103/S0027134920060168
Philominathan ST, Matsushita O, Gensure R, Sakon J (2009) Ca2+-induced linker transformation leads to a compact and rigid collagen-binding domain of Clostridium histolyticum collagenase. FEBS J 276(13):3589–3601. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1742-4658.2009.07078.x
Reinhardt DP, Ono RN, Sakai LY (1997) Calcium stabilizes fibrillin-1 against proteolytic degradation. J Biol Chem 272(2):1231–1236. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.272.2.1231
Riaz T, Zeeshan R, Zarif F, Ilyas K, Muhammad N, Safi SZ, Rizvi SAA, Rehman IU (2018) FTIR analysis of natural and synthetic collagen. Appl Spectrosc Rev 53(9):703–746. https://doi.org/10.1080/05704928.2018.1426595
Saito H, Taguchi T, Aoki H, Murabayashi S, Mitamura Y, Tanaka J, Tateishi T (2000) pH-responsive swelling behavior of collagen gels prepared by novel crosslinkers based on naturally derived di- or tricarboxylic acids. Acta Biomater 3(1):89–94. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actbio.2006.08.003
Santha Kalaikumari S, Vennila T, Monika V, Chandraraj K, Gunasekaran P, Rajendhran J (2019) Bioutilization of poultry feather for keratinase production and its application in leather industry. J Clean Prod 208:44–53. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.10.076
Saranya R, Prasanna R, Jayapriya J, Aravindhan R, Tamil Selvi A (2016) Value addition of fish waste in the leather industry for dehairing. J Clean Prod 118:179–186. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2015.12.103
Sarkar G, Suthindhiran K (2020) Extraction and characterization of alkaline protease from Streptomyces sp. GS-1 and its application as dehairing agent. Biocatal Agric Biotechnol 25: 101590. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bcab.2020.101590
Scott PG (1985) Spectroscopic study of environment-dependent changes in the conformation of the isolated carboxy-terminal telopeptide of type I collagen. Biochemistry-US 25:974–980. https://doi.org/10.1021/bi00353a005
Shakilanishi S, Shanthi C (2017) Specificity studies on proteases for dehairing in leather processing using decorin as model conjugated protein. Int J Biol Macromol 103:1069–1076. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2017.05.134
Shoulders MD, Raines RT (2009) Collagen structure and stability. Annu Rev Biochem 78:929–958. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.biochem.77.032207.120833
Sizeland KH, Edmonds RL, Basil-Jones MM, Kirby N, Hawley A, Mudie S, Haverkamp RG (2015) Changes to collagen structure during leather processing. J Agr Food Chem 63(9):2499–2505. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf506357j
Song J, Tao W, Chen W (2015) A way to reduce injury to skin in enzymatic unhairing. J Soc Leath Tech Ch 99(3):115–119
Spichtin H, Verzár F (1969) Calcium as stabilizing factor of collagen macromolecule. Experientia 25(1):9–11. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01903859
Sujitha P, Shanthi C (2021) Insights into substrate specificity of proteases for screening efficient dehairing enzymes. Int J Biol Macromol 172:360–370. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2021.01.065
Sujitha P, Kavitha S, Shakilanishi S, Babu NKC, Shanthi C (2018) Enzymatic dehairing: A comprehensive review on the mechanistic aspects with emphasis on enzyme specificity. Int J of Biol Macromol 118:168–179. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2018.06.081
Suzuki K, Ohno S (1990) Calcium activated neutral protease-structure-function relationship and functional implications. Cell Struct and Funct 15(1):1–6. https://doi.org/10.1247/csf.15.1
Thanikaivelan P, Rao JR, Nair BU, Ramasami T (2004) Progress and recent trends in biotechnological methods for leather processing. Trends Biotechnol 22(4):181–188. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tibtech.2004.02.008
Tian J, Xu Z, Long X, Tian Y, Shi B (2019) High-expression keratinase by Bacillus subtilis SCK6 for enzymatic dehairing of goatskins. Int J Biol Macromol 135:119–126. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2019.05.131
Titova II, Titov AO, Goncharova NV, Titov OP (2013) The possibilities of interaction of leather fabric collagen polypeptides with chemical materials. Nanotechnics 3:63–67
Vanamee P, Porter KR (1951) Observations with the electron microscope on the solvation and reconstitution of collagen. J Exp Med 94(3):255–266. https://doi.org/10.1084/jem.94.3.255
Veis A, Cohen J (1955) The degradation of collagen. II. the solubilization process in the acid pH range. J Am Chem Soc 77(9): 2364-2368. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja01614a003
Wang Y, Zeng Y, Liao X, Zhang W, Shi B (2013) Removal of calcium from pelt during bating process: An effective approach for non-ammonia bating. J Am Leather Chem as 108(4):120–127
Warrier B, Mallipeddi R, Yoo JW, Lee C (2007) Effects of the surface pH on interfacial interactions of collagen-elastin matrix. J Appl Biomater Biomech 5(3):140–148. https://doi.org/10.1089/ham.2007.8311
Wells HC, Holmes G, Haverkamp RG (2016) Looseness in bovine leather: microstructural characterization. J Sci Food Agr 96(8):2731–2736. https://doi.org/10.1002/jsfa.7392
Xia C, Luo Z, Fan H, Chen X (2011) Effect of carboxyl group content of collagen on chromium absorption. J Soc Leath Tech Ch 95(3):104–108
Xu B, Li C, Wang R, Zhang C, Peng B (2012) The impact of proteases on elastin in leather manufacture. J Soc Leath Tech Ch 96(3):100–105
Yoshida C, Tanzawa A, Tamura A, Ikeda J (2012) The biological properties of the alkali-treated collagen and gelatin - a preliminary study of their influence on cell growth when used as scaffolds. Science and Engineering Review of Doshisha University 53(3):121–126
Zhang R, Gong J, Su C, Qin J, Li H, Li H, Shi J, Xu Z (2020) Recombinant expression and molecular engineering of the keratinase from Brevibacillus parabrevis for dehairing performance. J Biotechnol 320:57–65. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbiotec.2020.06.016
Zhang Y, Chen Z, Liu X, Shi J, Chen H, Gong Y (2021) SEM, FTIR and DSC investigation of collagen hydrolysate treated degraded leather. J Cult Herit 48:205–210. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.culher.2020.11.007
Zhang X, Wan X, Xian J, Peng B (2018) Enzymatic bating technology for wet blue: I. Characterization of protease activities towards chrome-tanned elastin and collagen fibers. J Am Leather Chem As 113(7): 217-224.
Zhong Z, Li C, Gu H, Dou H, Zhou L (2007) Effect of temperature on the secondary structure of fish scale collagen. Spectrosc Spect Anal 27(10):1970–1976
Acknowledgements
We thank Qingshuang Song and Zhonghui Wang for their technical help at Sichuan University.
Funding
This work was financially supported by the National Key R&D Program of China (2017YFB0308402).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
MG: Investigation, formal analysis, resources, data curation, writing—original draft. YT: Writing—review and editing. XZ: Investigation, validation. CZ: Validation. BP: Conceptualization, methodology, supervision, project administration. All authors read and approved the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Consent to participate
The authors consent to participate.
Consent to publication
The authors consent to publication.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gao, M., Tian, Y., Zhang, X. et al. A substrate protection approach to applying the calcium ion for improving the proteolysis resistance of the collagen. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 105, 9191–9209 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-021-11704-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-021-11704-1