Abstract
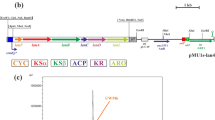
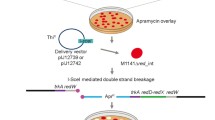
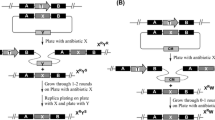
We previously developed an efficient deletion system for streptomycetes based on the positive selection of double-crossover events using bpsA, a gene for producing the blue pigment indigoidine. Using this system, we removed interfering secondary metabolite clusters from Streptomyces lividans TK24, resulting in RedStrep strains with dramatically increased heterologous production of mithramycin A (up to 3-g/l culture). This system, however, required a time-consuming step to remove the resistance marker genes. In order to simplify markerless deletions, we prepared a new system based on the plasmid pAMR18A. This plasmid contains a large polylinker with many unique restriction sites flanked by apramycin and kanamycin resistance genes and the bpsA gene for selecting a double-crossover event. The utility of this new markerless deletion system was demonstrated by its deletion of a 21-kb actinorhodin gene cluster from Streptomyces lividans TK24 with 30% efficiency. We used this system to efficiently remove the matA and matB genes in selected RedStrep strains, resulting in biotechnologically improved strains with a highly dispersed growth phenotype involving non-pelleting small and open mycelia. No further increase in mithramycin A production was observed in these new RedStrep strains, however. We also used this system for the markerless insertion of a heterologous mCherry gene, an improved variant of the monomeric red fluorescent protein, under the control of the strong secretory signal sequence of the subtilisin inhibitor protein, into the chromosome of S. lividans TK24. The resulting recombinant strains efficiently secreted mCherry into the growth medium in a yield of 30 mg/l.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anne J, Maldonado B, van Impe J, Mellart v, Bernaerts K (2012) Recombinant protein production and streptomycetes. J Biotechnol 158:159–167
Ausubel FM, Brent R, Kingston RE, Moore DO, Seidman JS, Smith JA, Struhl K (1995) Current protocols in molecular biology. Wiley, New York
Baltz RH (2012) Streptomyces temperate bacteriophage systems for stable genetic engineering of actinomycetes (and other organisms). J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 39:661–672
Baltz RH (2016) Genetic manipulation of secondary metabolite biosynthesis for improved production in Streptomyces and other actinomycetes. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 43:343–370
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254
Chen JC, Viollier PH, Shapiro L (2005) A membrane metalloprotease participates in the sequential degradation of a Caulobacter polarity determinant. Mol Microbiol 55:1085–1103
Cobb RE, Wang Y, Zhao H (2015) High-efficiency multiplex genome editing of Streptomyces species using an engineered CRISPR/Cas system. ACS Synth Biol 4:723–728
Dubeau M-P, Ghinet MG, Jacques P-E, Clermont N, Beaulieu C, Brzezinski R (2009) Cytosine deaminase as a negative selection marker for gene disruption and replacement in the genus Streptomyces and other actinobacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol 75:1211–1214
Duellman T, Burnett J, Yang J (2015) Quantitation of secreted proteins using mCherry fusion construct and a fluorescent microplate reader. Anal Biochem 473:34–40
Fedoryshyn M, Petzke L, Welle E, Bechthold A, Luzhetskyy A (2008) Marker removal from actinomycetes genome using Flp recpombinase. Gene 419:43–47
Fernandez-Martinez LT, Bibb MJ (2014) Use of the meganuclease I-SceI of Saccharomyces cerevisiae to select for gene deletions in actinomycetes. Sci Rep 4:7100
Gust B, Challis GL, Fowler K, Kieser T, Chater KF (2003) PCR-targeted Streptomyces gene replacement identifies a protein domain needed for biosynthesis of the esquiterpene soil odor geosmin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 18:1541–1548
Hopwood DA (2007) Streptomyces in nature and Mecicine. In: The antibiotic makers. Oxford University Press, New York
Horinouchi S, Hara O, Beppu T (1983) Cloning of a pleiotropic gene that positively controls biosynthesis of A-factor, actinorhodin, and prodigiosin in Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2) and Streptomyces lividans. J Bacteriol 155:1238–1248
Huang H, Zheng G, Jiang W, Hu H, Lu Y (2015) One-step high-efficiency CRISPR/Cas9- mediated genome editing in Streptomyces. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin 47:231–243
Kieser T, Bibb MJ, Buttner MJ, Chater KF, Hopwood DA (2000) Practical Streptomyces genetics. The John Innes Foundation, Norwich
Kim E-S, Hong H-J, Choi C-Y, Cohen SN (2001) Modulation of actinorhodin biosynthesis in Streptomyces lividans by glucose repression of afsR2 gene transcription. J Bacteriol 183:2197–2203
Knirschova R, Novakova R, Feckova L, Timko J, Turna J, Bistakova J, Kormanec J (2007) Multiple regulatory genes in the salinomycin biosynthetic gene cluster of Streptomyces albus CCM 4719. Folia Microbiol 52:359–365
Knirschova R, Novakova R, Mingyar E, Bekeova C, Homerova D, Kormanec J (2015) Utilization of a reporter system based on the blue pigment indigoidine biosynthetic gene bpsA for detection of promoter activity and deletion of genes in Streptomyces. J Microbiol Methods 113:1–3
Kormanec J, Rezuchova B, Farkasovsky M (1993) Optimization of Streptomyces aureofaciens transformation and disruption of the hrdA gene encoding a homologue of the principal sigma factor. J Gen Microbiol 139:2525–2529
Laemmli UK (1970) Cleavage of structural proteins during assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 227:680–685
Lammertyn E, Van Mellaert L, Schacht S, Dillen C, Sablon E, Van Broekhoven A, Anne J (1997) Evaluation of a novel subtilisin inhibitor gene and mutant derivatives for the expression and secretion of mouse tumor necrosis factor alpha by Streptomyces lividans. Appl Environ Microbiol 63:1808–1813
Li P, Li J, Guo Z, Tang W, han J, meng X, Hao T, Zhu Y, Zhang L, Chen Y (2015) An efficient blue-white screening based gene inactivation system for Streptomyces. Appl Microbiol Biotechol 99:1923–1933
Myronovskyi M, Luzhetskyy A (2013) Genome engineering in actinomycetes using site-specific recombinases. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 97:4701–4712
Myronovskyi M, Rosenkranzer B, Luzhetskyy A (2014) Iterative marker excision system. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 98:4557–4570
Novakova R, Núñez LE, Homerova D, Knirschova R, Feckova L, Rezuchova B, Sevcikova B, Menéndez N, Morís F, Cortés J, Kormanec J (2018) Increased heterologous production of the Antitumoral polyketide Mithramycin a by engineered Streptomyces lividans TK24 strains. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 102:857–869
Novakova R, Odnogova Z, Kutas P, Feckova L, Kormanec J (2010) Identification and characterization of an indigoidine-like gene for a blue pigment biosynthesis in Streptomyces aureofaciens CCM3239. Folia Microbiol 55:119–125
Olano C, Garcia I, Gonzales A, Rodriguez M, Rozas D, Rubio J, Sanchez-Hidalgo M, Brana AF, Mendez C, Salas JA (2014) Activation and identification of five clusters for secondary metabolites in Streptomyces albus J1074. Microb Biotechnol 7:242–256
Rückert C, Albersmeier A, Busche T, Jaenicke S, Winkler A, Friethjonsson OH, Hreggviethsson GO, Lambert C, Badcock D, Bernaerts K, Anne J, Economou A, Kalinowski J (2015) Complete genome sequence of Streptomyces lividans TK24. J Biotechnol 199:21–22
Shaner NC, Campbell RE, Steinbach PA, Giepmans BNG, Palmer AE, Tsien RY (2004) Improved monomeric red, orange and yellow fluorescent proteins derived from Discosoma sp. red fluorescent protein. Nat Biotechnol 22:1567–1572
Sianidis G, Pozidis C, Becker F, Vrancken K, Sjoeholm C, Karamanou S, Takamiya-Wik M, van Mellaert L, Schaefer T, Anne J, Economou A (2006) Functional large-scale production of a novel Jonesia sp. xyloglucanase by heterologous secretion from Streptomyces lividans. J Biotechnol 21:498–507
Siegl T, Luzhetskyy A (2012) Actinomycetes genome engineering approaches. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 102:503–516
Siegl T, Petzke L, Welle E, Luzhetskyy A (2010) I-SceI endonuclease: a new tool for DNA repair studies and genetic manipulations in streptomycetes. App Microbiol Biotechnol 87:1525–1532
Strickler JE, Berka TR, Gorniak J, Fornwald J, Keys R, Rowland JJ, Rosenberg M, Taylor DP (1992) Two novel Streptomyces protein protease inhibitors. J Biol Chem 267:3236–3241
Taguchi S, Maeno M, Momose H (1992) Extracellular production system of a heterologous peptide driven by a secretory protease inhibitor of Streptomyces. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 36:749–753
Takahashi H, Kumagai T, Kitani K, Mori M, Matoba Y, Sugiyama M (2007) Cloning and characterization of a Streptomyces single module type non-ribosomal peptide synthetase catalyzing a blue pigment synthesis. J Biol Chem 282:9073–9081
van Dissel D, Claessen D, Roth M, van Wezel GP (2015) A novel locus for mycelial aggregation forms a gateway to improved Streptomyces cell factories. Microb Cell Factories 14:44
Yu D, Xu F, Valiente J, Wang S, Zhang J (2013) An indigoidine biosynthetic gene cluster from Streptomyces chromofuscus ATCC 49982 contains an unusual IndB homologue. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 40:159–168
Zheng H, Wen S, Xu W, He Z, Zhai G, Liu Y, Deng Z, Sun Y (2015) Highly efficient editing of the actinorhodin polyketide chain length factor gene in Streptomyces coelicolor M145 using CRISPR/Cas9-CodA(sm) combined system. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 99:10575–10585
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to Jacob Bauer for critically reading the manusrtipt and correcting the English. We are also grateful to Dr. Bertold Gust (John Innes Centre, Norwich, UK) for the pIJ773 plasmid.
Funding
This work was supported by the Slovak Research and Development Agency under contract No. APVV-15-0410 and by VEGA grant 2/0002/16 from the Slovak Academy of Sciences. The research leading to these results has received funding from the European Commission’s Seventh Framework Programme (FP7/2007-2013) under the grant agreement STREPSYNTH (project No. 613877). This work was co-funded by the Slovak Research and Development Agency under contract No. DO7RP-0037-12.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rezuchova, B., Homerova, D., Sevcikova, B. et al. An efficient blue-white screening system for markerless deletions and stable integrations in Streptomyces chromosomes based on the blue pigment indigoidine biosynthetic gene bpsA. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 102, 10231–10244 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-018-9393-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-018-9393-7