Abstract
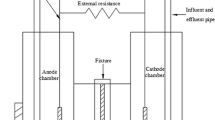
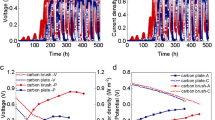
A possible approach to enhance the performance of microbial electrochemical system such as microbial fuel cells is to increase the conductivity of catalytic biofilms and thereby the direct extracellular electron transfer within the biofilms and from the electrode. In the present study, we evaluated the impact of static low-intensity magnetic field on the anodic biofilms in microbial fuel cells (MFCs). Results demonstrated that the application of a low-intensity magnetic field (105 and 150 mT) can significantly shorten the startup time and enhance the overall performance of single-chamber MFCs in terms of current density (300%) and power density (150%). In situ conductance evaluation indicated that short-term application of magnetic field can increase biofilm conductivity, although the long-term enhancements were likely results of increased conductivity of the anodic biofilms associated with enriched population of Geobacteraceae. The peak-manner response of conductivity over gate potentials and the positive response of mature biofilm conductance to low intensity of magnetic field support the redox conduction model of the conductive exoelectrogenic biofilms.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bond DR, Lovley DR (2003) Electricity production by Geobacter sulfurreducens attached to electrodes. Appl Environ Microbiol 69(3):1548–1555
Fadrosh DW, Ma B, Gajer P, Sengamalay N, Ott S, Brotman RM, Ravel J (2014) An improved dual-indexing approach for multiplexed 16S rRNA gene sequencing on the Illumina MiSeq platform. Microbiome 2(1):6
Fan Y, Hu H, Liu H (2007) Enhanced Coulombic efficiency and power density of air-cathode microbial fuel cells with an improved cell configuration. J Power Sources 171(2):348–354
Fan Y, Xu S, Schaller R, Jiao J, Chaplen F, Liu H (2011) Nanoparticle decorated anodes for enhanced current generation in microbial electrochemical cells. Biosens Bioelectron 26(5):1908–1912
Fan Y, Han SK, Liu H (2012) Improved performance of CEA microbial fuel cells with increased reactor size. Energy Environ Sci 5(8):8273–8280
Gu H, Guo J, Sadu R, Huang Y, Haldolaarachchige N, Chen D, Young DP, Wei S, Guo Z (2013) Separating positive and negative magnetoresistance for polyaniline-silicon nanocomposites in variable range hopping regime. Appl Phys Lett 102(21):212403
Gu H, Guo J, Yan X, Wei H, Zhang X, Liu J, Huang Y, Wei S, Guo Z (2014) Electrical transport and magnetoresistance in advanced polyaniline nanostructures and nanocomposites. Polymer 55(17):4405–4419
Holmes DE, Dang Y, Walker DJF, Lovely DR (2016) The electrically conductive pili of Geobacter species are a recently evolved feature for extracellular electron transfer. Microb Genom 2(8):e000072
Hu B, Wu Y (2007) Tuning magnetoresistance between positive and negative values in organic semiconductors. Nat Mater 6:985–991. https://doi.org/10.1038/nmat2034
Janicek A, Fan Y, Liu H (2015) Performance and stability of different cathode base materials for use in microbial fuel cells. J Power Sources 280:159–165
Leang C, Malvankar N, Franks A, Nevin K, Lovley DR (2013) Engineering Geobacter sulfurreducens to produce a highly cohesive conductive matrix with enhanced capacity for current production. Energy Environ Sci 6(6):1901–1908
Lee HS, Dhar B, An J, Rittmann BE, Ryu H, Domingo JW, Ren H, Chae J (2016) The roles of biofilm conductivity and donor substrate kinetics in a mixed-culture biofilm anode. Environ Sci Technol 50(23):12799–12807
Lesnik KL, Liu H (2014) Establishing a core microbiome in acetate-fed microbial fuel cells. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 98(9):4187–4196
Li WW, Sheng GP, Liu XW, Cai PJ, Sun M (2011) Impact of a static magnetic field on the electricity production of Shewanella-inoculated microbial fuel cells. Biosens Bioelectron 26(10):3987–3992
Li C, Lesnik KL, Fan Y, Liu H (2016a) Millimeter scale electron conduction through exoelectrogenic mixed species biofilms. FEMS Microbiol Lett 363(15):fnw153
Li C, Lesnik KL, Fan Y, Liu H (2016b) Redox conductivity of current-producing mixed species biofilms. PLoS One 11(5):e0155247
Li C, Lesnik KL, Liu H (2017) Stay connected: electrical conductivity of microbial aggregates. Biotechnol Adv 35(6):669–680
Li C, Lesnik KL, Liu H (2018) Conductive properties of methanogenic biofilms. Bioelectrochem 119:220–226
Liu Y, Bond DR (2012) Long-distance electron transfer by G. sulfurreducens biofilms results in accumulation of reduced c-type cytochromes. ChemSusChem 5(6):1047–1053
Logan BE (2009) Exoelectrogenic bacteria that power microbial fuel cells. Nat Rev Microbiol 7(5):375–381
Lovley DR (2011a) Live wires: direct extracellular electron exchange for bioenergy and the bioremediation of energy-related contamination. Energy Environ Sci 4(12):4896–4906
Lovley DR (2011b) Reach out and touch someone: potential impact of DIET (direct interspecies energy transfer) on anaerobic biogeochemistry, bioremediation, and bioenergy. Rev Environ Sci Biotechnol 10(2):101–105
Lovley DR, Stolz JF, Nord GL, Phillips EJP (1987) Anaerobic production of magnetite by a dissimilatory iron-reducing microorganism. Nature 330(6145):252–254
Malvankar NS, Vargas M, Nevin KP, Franks AE, Leang C, Kim BC, Inoue K, Mester T, Covalla SF, Johnson JP, Rotello VM, Tuominen MT, Lovley DR (2011) Tunable metallic-like conductivity in microbial nanowire networks. Nat Nanotechnol 6(9):573–579
Malvankar NS, Lau J, Nevin KP, Franks AE, Tuominen MT, Lovley DR (2012a) Electrical conductivity in a mixed-species biofilm. Appl Environ Microbiol 78(16):5967–5971
Malvankar NS, Tuominen MT, Lovley DR (2012b) Lack of cytochrome involvement in long-range electron transport through conductive biofilms and nanowires of Geobacter sulfurreducens. Energy Environ Sci 5(9):8651–8659
Malvankar NS, Tuominen MT, Lovely DR (2012c) Biofilm conductivity is a decisive variable for high-current-density Geobacter sulfurreducens microbial fuel cells. Energy Environ Sci 5(2):5790–5797
Malvankar NS, Vargas M, Nevin K, Tremblay PL, Evans-Lutterodt K, Nykypanchuk D, Martz E, Tuominen MT, Lovley DR (2015) Structural basis for metallic-like conductivity in microbial nanowires. mBio 6(2):e00084–e00015
Nalwa HS (ed) (2001) Handbook of Thin Films, Five-Volume Set (Vol. 5). Elsevier
Okamoto A, Saito K, Inoue K, Nealson KH, Hashimoto K, Nakamura R (2014) Uptake of self-secreted flavins as bound cofactors for extracellular electron transfer in species. Energy Environ Sci 7(4):1357–1361
Parameswaran P, Zhang H, Torres CI, Rittmann BE, Krajmalnik-Brown R (2010) Microbial community structure in a biofilm anode fed with a fermentable substrate: the significance of hydrogen scavengers. Biotechnol Bioeng 105(1):69–78
Phan H, Yates MD, Kirchhofer ND, Bazan GC, Tender LM, Nguyen TQ (2016) Biofilm as a redox conductor: a systematic study of the moisture and temperature dependence of its electrical properties. Phys Chem Chem Phys 18(27):17815–17821
Raikh ME, Czingon J, Ye QT, Koch F, Schoepe W, Ploog K (1992) Mechanisms of magnetoresistance in variable-range-hopping transport for two-dimensional electron systems. Phys Rev B 45(11):6015–6022
Shrestha PM, Malvankar NS, Werner JJ, Franks AE, Rotaru AE, Shrestha M, Liu F, Nevin K, Angenent LT, Lovely DR (2014) Correlation between microbial community and granule conductivity in anaerobic bioreactors for brewery wastewater treatment. Bioresour Technol 174:306–310
Snider RM, Strycharz-Glaven SM, Tsoi SD, Erickson JS, Tender LM (2012) Long-range electron transport in Geobacter sulfurreducens biofilms is redox gradient-driven. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 109(38):15467–15472
Tan Y, Adhikari RY, Malvankar NS, Ward JE, Nevin KP, Woodard TL, Smith JA, Snoeyenbos-West O, Franks A, Lovley DR (2016) The low conductivity of Geobacter uraniireducens pili suggests a diversity of extracellular electron transfer mechanisms in the genus Geobacter. Front Microbiol 7:980
Tao Q, Zhou S (2014) Effect of static magnetic field on electricity production and wastewater treatment in microbial fuel cells. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 98(23):9879–9887
Vali H, Weiss B, Li Y-L, Sears SK, Kim SS, Kirschvink JL, Zhang CL (2004) Formation of tabular singledomain magnetite induced by Geobacter metallireducens GS-15. Proc Natl Acad Sci 101(46):16121–16126
Vargas M, Malvankar NS, Tremblay PL, Leang C, Smith JA, Patel P, Synoeyenbos-West O, Nevin KP, Lovley DR (2013) Aromatic amino acids required for pili conductivity and long-range extracellular electron transport in Geobacter sulfurreducens. mBio 4(2):e00105–e00113
Yates MD, Eddie BJ, Kotloski NJ, Lebedev N, Malanoski AP, Lin B, Strycharz-Glaven SM, Tender LM (2016a) Toward understanding long-distance extracellular electron transport in an electroautotrophic microbial community. Energy Environ Sci 9(11):3544–3558
Yates MD, Strycharz-Glaven SM, Golden JP, Roy J, Tsoi S, Erickson JS, El-Naggar MY, Barton S, Tender LM (2016b) Measuring conductivity of living Geobacter sulfurreducens biofilms. Nat Nanotechnol 11(11):910–913
Yin Y, Huang G, Tong Y, Liu Y, Zhang L (2013) Electricity production and electrochemical impedance modeling of microbial fuel cells under static magnetic field. J Power Sources 237:58–63
Zhang X, Philips J, Roume H, Guo K, Rabaey K, Prévoteau A (2017) Rapid and quantitative assessment of redox conduction across electroactive biofilms via double potential step chronoamperometry. ChemElectroChem 4(5):1026–1036
Zhang X, Xia X, Ivanov I, Huang X, Logan BE (2014) Enhanced activated carbon cathode performance for microbial fuel cell by blending carbon black. Environ Sci Technol 48(3):2075–2081. https://doi.org/10.1021/es405029y
Zhao YN, Li XF, Ren YP, Wang XH (2016) Effect of static magnetic field on the performances of and anode biofilms in microbial fuel cells. RSC Adv 6(85):82301–82308
Zhou H, Liu B, Wang Q, Sun J, Xie G, Ren N, Ren ZJ, Xing D (2017) Pulse electromagnetic fields enhance extracellular electron transfer in magnetic bioelectrochemical systems. Biotechnol Biofuels 10(1):238
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to acknowledge Keaton Larson Lesnik and Ningshengjie Gao for their valuable discussion.
Funding
This study was funded by U.S. National Science Foundation (CBET 0955124) and U.S. Department of Energy (DE-EE0007269).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(PDF 315 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, C., Wang, L. & Liu, H. Enhanced redox conductivity and enriched Geobacteraceae of exoelectrogenic biofilms in response to static magnetic field. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 102, 7611–7621 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-018-9158-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-018-9158-3