Abstract
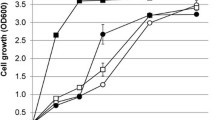
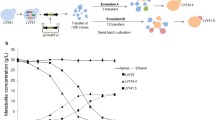
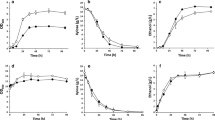
Bioprospecting is an effective way to find novel enzymes from strains with desirable phenotypes. Such bioprospecting has enabled organisms such as Saccharomyces cerevisiae to utilize nonnative pentose sugars. Yet, the efficiency of this pentose catabolism (especially for the case of arabinose) remains suboptimal. Thus, further pathway optimization or identification of novel, optimal pathways is needed. Previously, we identified a novel set of xylan catabolic pathway enzymes from a superior pentose-utilizing strain of Ustilago bevomyces. These enzymes were used to successfully engineer a xylan-utilizing S. cerevisiae through a blended approach of bioprospecting and evolutionary engineering. Here, we expanded this approach to xylose and arabinose catabolic pathway engineering and demonstrated that bioprospected xylose and arabinose catabolic pathways from U. bevomyces offer alternative choices for enabling efficient pentose catabolism in S. cerevisiae. By introducing a novel set of xylose catabolic genes from U. bevomyces, growth rates were improved up to 85 % over a set of traditional Scheffersomyces stipitis pathway genes. In addition, we suggested an alternative arabinose catabolic pathway which, after directed evolution and pathway engineering, enabled S. cerevisiae to grow on arabinose as a sole carbon source in minimal medium with growth rates upwards of 0.05 h−1. This pathway represents the most efficient growth of yeast on pure arabinose minimal medium. These pathways provide great starting points for further strain development and demonstrate the utility of bioprospecting from U. bevomyces.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bae J, Laplaza J, Jeffries T (2008) Effects of gene orientation and use of multiple promoters on the expression of XYL1 and XYL2 in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 145(1–3):69–78. doi:10.1007/s12010-007-8076-0
Becker J, Boles E (2003) A modified Saccharomyces cerevisiae strain that consumes l-arabinose and produces ethanol. Appl Environ Microbiol 69(7):4144–4150. doi:10.1128/aem.69.7.4144-4150.2003
Bengtsson O, Hahn-Hagerdal B, Gorwa-Grauslund M (2009) Xylose reductase from Pichia stipitis with altered coenzyme preference improves ethanolic xylose fermentation by recombinant Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Biotechnol Biofuels 2(1):9
Bera A, Sedlak M, Khan A, Ho NY (2010) Establishment of l-arabinose fermentation in glucose/xylose co-fermenting recombinant Saccharomyces cerevisiae 424A(LNH-ST) by genetic engineering. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 87(5):1803–1811. doi:10.1007/s00253-010-2609-0
Brat D, Boles E, Wiedemann B (2009) Functional expression of a bacterial xylose isomerase in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Appl Environ Microbiol 75(8):2304–2311. doi:10.1128/aem.02522-08
Conesa A, Gotz S (2008) Blast2GO: a comprehensive suite for functional analysis in plant genomics. Int J Plant Genomics 619832(10):619832
Curran KA, Alper HS (2012) Expanding the chemical palate of cells by combining systems biology and metabolic engineering. Metab Eng 14(4):289–297. doi:10.1016/j.ymben.2012.04.006
Giaever G, Chu AM, Ni L, Connelly C, Riles L, Veronneau S, Dow S, Lucau-Danila A, Anderson K, Andre B, Arkin AP, Astromoff A, El-Bakkoury M, Bangham R, Benito R, Brachat S, Campanaro S, Curtiss M, Davis K, Deutschbauer A, Entian KD, Flaherty P, Foury F, Garfinkel DJ, Gerstein M, Gotte D, Guldener U, Hegemann JH, Hempel S, Herman Z, Jaramillo DF, Kelly DE, Kelly SL, Kotter P, LaBonte D, Lamb DC, Lan N, Liang H, Liao H, Liu L, Luo C, Lussier M, Mao R, Menard P, Ooi SL, Revuelta JL, Roberts CJ, Rose M, Ross-Macdonald P, Scherens B, Schimmack G, Shafer B, Shoemaker DD, Sookhai-Mahadeo S, Storms RK, Strathern JN, Valle G, Voet M, Volckaert G, Wang CY, Ward TR, Wilhelmy J, Winzeler EA, Yang Y, Yen G, Youngman E, Yu K, Bussey H, Boeke JD, Snyder M, Philippsen P, Davis RW, Johnston M (2002) Functional profiling of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae genome. Nature 418(6896):387–391
Holt C, Yandell M (2011) MAKER2: an annotation pipeline and genome-database management tool for second-generation genome projects. BMC Bioinformatics 12(1):491
Jeffries TW (2006) Engineering yeasts for xylose metabolism. Curr Opin Biotechnol 17(3):320–326
Jin Y-S, Jones S, Shi N-Q, Jeffries TW (2002) Molecular cloning of XYL3 (D-xylulokinase) from Pichia stipitis and characterization of its physiological function. Appl Environ Microbiol 68(3):1232–1239. doi:10.1128/aem.68.3.1232-1239.2002
Jin Y-S, Ni H, Laplaza JM, Jeffries TW (2003) Optimal growth and ethanol production from xylose by recombinant Saccharomyces cerevisiae require moderate D-xylulokinase activity. Appl Environ Microbiol 69(1):495–503. doi:10.1128/aem.69.1.495-503.2003
Jingping G, Hongbing S, Gang S, Hongzhi L, Wenxiang P (2012) A genome shuffling-generated Saccharomyces cerevisiae isolate that ferments xylose and glucose to produce high levels of ethanol. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 39(5):777–787. doi:10.1007/s10295-011-1076-7
Johansson B, Christensson C, Hobley T, Hahn-Hagerdal B (2001) Xylulokinase overexpression in two strains of Saccharomyces cerevisiae also expressing xylose reductase and xylitol dehydrogenase and its effect on fermentation of xylose and lignocellulosic hydrolysate. Appl Environ Microbiol 67(9):4249–4255. doi:10.1128/aem.67.9.4249-4255.2001
Karhumaa K, Påhlman A-K, Hahn-Hägerdal B, Levander F, Gorwa-Grauslund M-F (2009) Proteome analysis of the xylose-fermenting mutant yeast strain TMB 3400. Yeast 26(7):371–382. doi:10.1002/yea.1673
Karhumaa K, Sanchez R, Hahn-Hagerdal B, Gorwa-Grauslund M-F (2007) Comparison of the xylose reductase-xylitol dehydrogenase and the xylose isomerase pathways for xylose fermentation by recombinant Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Microb Cell Factories 6(1):5
Kim SR, Skerker JM, Kang W, Lesmana A, Wei N, Arkin AP, Jin YS (2013) Rational and evolutionary engineering approaches uncover a small set of genetic changes efficient for rapid xylose fermentation in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. PLoS One 8(2):26
Kötter P, Amore R, Hollenberg C, Ciriacy M (1990) Isolation and characterization of the Pichia stipitis xylitol dehydrogenase gene, XYL2, and construction of a xylose-utilizing Saccharomyces cerevisiae transformant. Curr Genet 18(6):493–500. doi:10.1007/bf00327019
Krahulec S, Klimacek M, Nidetzky B (2012) Analysis and prediction of the physiological effects of altered coenzyme specificity in xylose reductase and xylitol dehydrogenase during xylose fermentation by Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Biotechnol 158(4):192–202. doi:10.1016/j.jbiotec.2011.08.026
Kuyper M, Harhangi HR, Stave AK, Winkler AA, Jetten MSM, de Laat WTAM, den Ridder JJJ, Op den Camp HJM, van Dijken JP, Pronk JT (2003) High-level functional expression of a fungal xylose isomerase: the key to efficient ethanolic fermentation of xylose by Saccharomyces cerevisiae. FEMS Yeast Res 4(1):69–78
Lee S-M, Jellison T, Alper HS (2012) Directed evolution of xylose isomerase for improved xylose catabolism and fermentation in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Appl Environ Microbiol 78(16):5708–5716. doi:10.1128/aem.01419-12
Lee S-M, Jellison T, Alper HS (2014) Systematic and evolutionary engineering of a xylose isomerase-based pathway in Saccharomyces cerevisiae for efficient conversion yields. Biotechnol Biofuels 7:122
Lee S-M, Jellison T, Alper HS (2015) Xylan catabolism is improved by blending bioprospecting and metabolic pathway engineering in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Biotechnol J 10(4):575–583
Liu L, Redden H, Alper HS (2013) Frontiers of yeast metabolic engineering: diversifying beyond ethanol and Saccharomyces. Curr Opin Biotechnol 24(6):1023–1030. doi:10.1016/j.copbio.2013.03.005
Metz B, Mojzita D, Herold S, Kubicek CP, Richard P, Seiboth B (2013) A novel l-xylulose reductase essential for l-arabinose catabolism in Trichoderma reesei. Biochemistry 52(14):2453–2460. doi:10.1021/bi301583u
Mojzita D, Vuoristo K, Koivistoinen OM, Penttila M, Richard P (2010) The ’true’ L-xylulose reductase of filamentous fungi identified in Aspergillus niger. FEBS Lett 584(16):3540–3544
Mumberg D, Müller R, Funk M (1995) Yeast vectors for the controlled expression of heterologous proteins in different genetic backgrounds. Gene 156(1):119–122
Nevoigt E (2008) Progress in metabolic engineering of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 72(3):379–412. doi:10.1128/mmbr.00025-07
Nielsen J, Jewett MC (2008) Impact of systems biology on metabolic engineering of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. FEMS Yeast Res 8(1):122–131. doi:10.1111/j.1567-1364.2007.00302.x
Richard P, Londesborough J, Putkonen M, Kalkkinen N, Penttila M (2001) Cloning and expression of a fungal L-arabinitol 4-dehydrogenase gene. J Biol Chem 276(44):40631–40637. doi:10.1074/jbc.M104022200
Richard P, Putkonen M, Väänänen R, Londesborough J, Penttilä M (2002) The missing link in the fungal l-arabinose catabolic pathway, identification of the l-xylulose reductase gene. Biochemistry 41(20):6432–6437. doi:10.1021/bi025529i
Richard P, Verho R, Putkonen M, Londesborough J, Penttilä M (2003) Production of ethanol from l-arabinose by Saccharomyces cerevisiae containing a fungal l-arabinose pathway. FEMS Yeast Res 3(2):185–189. doi:10.1016/s1567-1356(02)00184-8
Runquist D, Hahn-Hagerdal B, Bettiga M (2010) Increased ethanol productivity in xylose-utilizing Saccharomyces cerevisiae via a randomly mutagenized xylose reductase. Appl Environ Microbiol 76(23):7796–7802. doi:10.1128/aem.01505-10
Sambrook J, Fritch E, Maniatis T (1989) Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual, 2nd edn. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, New York
Scalcinati G, Otero JM, Van Vleet JRH, Jeffries TW, Olsson L, Nielsen J (2012) Evolutionary engineering of Saccharomyces cerevisiae for efficient aerobic xylose consumption. FEMS Yeast Res 12(5):582–597. doi:10.1111/j.1567-1364.2012.00808.x
Subtil T, Boles E (2011) Improving L-arabinose utilization of pentose fermenting Saccharomyces cerevisiae cells by heterologous expression of L-arabinose transporting sugar transporters. Biotechnol Biofuels 4(1):38
Sun J, Wen F, Si T, Xu JH, Zhao H (2012) Direct conversion of xylan to ethanol by recombinant Saccharomyces cerevisiae strains displaying an engineered minihemicellulosome. Appl Environ Microbiol 78(11):3837–3845
Tantirungkij M, Nakashima N, Seki T, Yoshida T (1993) Construction of xylose-assimilating Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Ferment Bioeng 75:83–88
Van Vleet JH, Jeffries TW (2009) Yeast metabolic engineering for hemicellulosic ethanol production. Curr Opin Biotechnol 20(3):300–306
Van Vleet JH, Jeffries TW, Olsson L (2008) Deleting the para-nitrophenyl phosphatase (pNPPase), PHO13, in recombinant Saccharomyces cerevisiae improves growth and ethanol production on d-xylose. Metab Eng 10(6):360–369. doi:10.1016/j.ymben.2007.12.002
Walfridsson M, Anderlund M, Bao X, Hahn-Hagerdal B (1997) Expression of different levels of enzymes from the Pichia stipitis XYL1 and XYL2 genes in Saccharomyces cerevisiae and its effects on product formation during xylose utilisation. Appl Micribiol Biotechnol 48:218–224
Wei N, Quarterman J, Kim SR, Cate JH, Jin YS (2013) Enhanced biofuel production through coupled acetic acid and xylose consumption by engineered yeast. Nat Commun 4(2580)
Wisselink HW, Toirkens MJ, del Rosario Franco Berriel M, Winkler AA, van Dijken JP, Pronk JT, van Maris AJA (2007) Engineering of Saccharomyces cerevisiae for efficient anaerobic alcoholic fermentation of l-arabinose. Appl Environ Microbiol 73(15):4881–4891. doi:10.1128/aem.00177-07
Young E, Lee S-M, Alper H (2010) Optimizing pentose utilization in yeast: the need for novel tools and approaches. Biotechnol Biofuels 3(1):24
Young E, Poucher A, Comer A, Bailey A, Alper H (2011) Functional survey for heterologous sugar transport proteins, using Saccharomyces cerevisiae as a host. Appl Environ Microbiol 77(10):3311–3319
Young EM, Tong A, Bui H, Spofford C, Alper HS (2014) Rewiring yeast sugar transporter preference through modifying a conserved protein motif. PNAS 111(1):131–136. doi:10.1073/pnas.1311970111
Zerbino DR, Birney E (2008) Velvet: algorithms for de novo short read assembly using de Bruijn graphs. Genome Res 18(5):821–829. doi:10.1101/gr.074492.107
Zhang F, Qiao D, Xu H, Liao C, Li S, Cao Y (2009) Cloning, expression, and characterization of xylose reductase with higher activity from Candida tropicalis. J Microbiol 47(3):351–357. doi:10.1007/s12275-008-0225-9
Acknowledgments
We acknowledge financial support for this project from the University of Texas at Austin Research Grant Program, DuPont Young Investigator Award, and National Science Foundation under Grant CBET-1067506. We thank Scott Hunicke-Smith and the UT GSAF for assistance in whole genome sequencing and analysis.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Funding
This study was funded by National Science Foundation (CBET-1067506).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(PDF 163 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, SM., Jellison, T. & Alper, H.S. Bioprospecting and evolving alternative xylose and arabinose pathway enzymes for use in Saccharomyces cerevisiae . Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 100, 2487–2498 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-015-7211-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-015-7211-z