Abstract
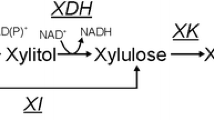
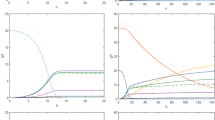
A metabolic flux analysis (MFA) model was developed to optimize the xylose conversion into ethanol using Candida shehatae strain. This metabolic model was compartmented and constructed with xylose as carbon substrate integrating the enzymatic duality of the first step of xylose degradation via an algebraic coefficient. The model included the pentose phosphate pathway, glycolysis, synthesis of major metabolites like ethanol, acetic acid and glycerol, the tricarboxylic acid cycle as well as the respiratory chain, the cofactor balance, and the maintenance. The biomass composition and thus production were integrated considering the major biochemical synthesis reactions from monomers to each constitutive macromolecule (i.e., proteins, lipids, polysaccharides, nucleic acids). The construction of the model resulted into a 122-linear equation system to be resolved. A first experiment allowed was to verify the accuracy of the model by comparing calculated and experimental data. The metabolic model was utilized to determine the theoretical yield taking into account oxido-reductive balance and to optimize ethanol production. The maximal theoretical yield was calculated at 0.62 Cmolethanol/Cmolxylose for an oxygen requirement of 0.33 moloxygen/molxylose linked to the cofactors of the xylose reductase. Cultivations in chemostat mode allowed the fine tuning of both xylose and oxygen uptakes and showed that lower was the oxygen/xylose ratio, higher was the ethanol production yield. The best experimental ethanol production yield (0.51 Cmolethanol/Cmolxylose) was obtained for an oxygen supply of 0.47 moloxygen/molxylose.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abu-Elteen K, Whittaker P (1997) Effect of sub-inhibitory concentration of chlorhexidine on lipid and sterol composition of shape Candida albicans. Mycopathol 140:69–76
Alexander MA, Yang VW, Jeffries TW (1988) Levels of pentose phosphate pathway enzymes from Candida shehatae grown in continuous culture. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 29:282–288
Alfenore S, Molina-Jouve C, Guillouet SE, Uribelarrea JL, Goma G, Benbadis L (2002) Improving ethanol production and viability of Saccharomyces cerevisiae by a vitamin feeding strategy during fed-batch process. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 60:67–72
Atkinson B, Mavituna F (1983) Biochemical engineering and biotechnology handbook vol 1. Trends in Biotechnology, vol 3. Macmillan Publishers Ltd,
Bakker BM, Overkamp KM, van Maris AJA, Kötter P, Luttik MAH, van Dijken JP, Pronk JT (2001) Stoichiometry and compartmentation of NADH metabolism in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. FEMS Microbiol Rev 25:15–37
Bideaux C, Goma G, Uribelarrea J-L, Dahhou B, Roux G (2008) Stoichiometric modelling approach for microbial cultures monitoring. Int J Model Identif Control 3:413–426
Bruinenberg PM, Bot PHM, Dijken JP, Scheffers WA (1983) The role of redox balances in the anaerobic fermentation of xylose by yeasts. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 18:287–292
Bruinenberg PM, Bot PHM, Dijken JP, Scheffers WA (1984) NADH-linked aldose reductase: the key to anaerobic alcoholic fermentation of xylose by yeasts. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 19:256–260
Bruinenberg PM, Van Dijken JP, Gijs Kuenen J, Scheffers WA (1985) Oxidation of NADH and NADPH by mitochondria from the yeast Candida utilis. J Gen Microbiol 131:1043–1051
Carnicer M, Baumann K, Toplitz I, Sanchez-Ferrando F, Mattanovich D, Ferrer P, Albiol J (2009) Macromolecular and elemental composition analysis and extracellular metabolite balances of Pichia pastoris growing at different oxygen levels. Microb Cell Factories 8:65–79
Castro AC, Sinskey AJ, Tannenbaum SR (1971) Reduction of nucleic acid content in Candida yeast cells by bovine pancreatic ribonuclease A treatment. Appl Microbiol 22:422–427
Celton M, Goelzer A, Camarasa C, Fromion V, Dequin S (2012) A constraint-based model analysis of the metabolic consequences of increased NADPH oxidation in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Metab Eng 14:366–379
Du Preez JC, Driessel B, Prior BA (1989) Effect of aerobiosis on fermentation and key enzyme levels during growth of Pichia stipitis, Candida shehatae and Candida tenuis on D-xylose. Arch Microbiol 152:143–147
Du Preez JC, van der Walt JP (1983) Fermentation of D-xylose to ethanol by a strain of Candida shehatae. Biotechnol Lett 5:357–362
DuPreez JC, Driessel B, Prior BA (1989) Ethanol tolerance of Pichia stipitis and Candida shehatae strains in fed-batch cultures at controlled low dissolved oxygen levels. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 30:53–58
Evans C, Ratledge C (1984) Induction of xylulose-5-phosphate phosphoketolase in a variety of yeasts grown on D-xylose: the key to efficient xylose metabolism. Arch Microbiol 139:48–52
Fromanger R, Guillouet SE, Uribelarrea JL, Molina-Jouve C, Cameleyre X (2010) Effect of controlled oxygen limitation on Candida shehatae physiology for ethanol production from xylose and glucose. Journal of Industrial Microbiology & Biotechnology 37:437–445
Girio FM, Peito MA, Amaral-Collaco MT (1989) Enzymatic and physiological study of D-xylose metabolism by Candida shehatae. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 32:199–204
Granström T, Aristidou AA, Leisola M (2002) Metabolic flux analysis of Candida tropicalis growing on xylose in an oxygen-limited chemostat. Metab Eng 4:248–256
Granström TB, Aristidou AA, Jokela J, Leisola M (2000) Growth characteristics and metabolic flux analysis of Candida milleri. Biotechnol Bioeng 70:197–207
Lange HC, Heijnen JJ (2001) Statistical reconciliation of elemental and molecular biomass composition of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Biotechnol Bioeng 75:334–344
Llaneras F, Picó J (2008) Stoichiometric modelling of cell metabolism. J Biosci Bioeng 105:1–11
Nissen TL, Schulze U, Nielsen J, Villadsen J (1997) Flux distributions in anaerobic, glucose-limited continuous cultures of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Microbiol 143:203–218
Pagliardini J, Hubmann G, Alfenore S, Nevoigt E, Bideaux C, Guillouet SE (2013) The metabolic costs of improving ethanol yield by reducing glycerol formation capacity under anaerobic conditions in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Microb Cell Factories 12:29
Pagliardini J, Hubmann G, Bideaux C, Alfenore S, Nevoigt E, Guillouet S (2010) Quantitative evaluation of yeast’s requirement for glycerol formation in very high ethanol performance fed-batch process. Microb Cell Factories 9:36
Passoth V, Zimmermann M, Klinner U (1996) Peculiarities of the regulation of fermentation and respiration in the crabtree-negative, xylose-fermenting yeast Pichia stipitis. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 57-8:201–212
Ratledge C, Wilkinson SG (1988) Microbial lipids. Academic Press, London
Rattray JB, Schibeci A, Kidby DK (1975) Lipids of yeasts. Bacteriol Rev 39:197–231
Sánchez S, Bravo V, Castro E, Moya AJ, Camacho F (1997) The influence of pH and aeration rate on the fermentation of xylose by Candida shehatae. Enzym Microb Technol 21:355–360
Singh A, Mishra P (1995) Microbial pentose utilization: current applications in biotechnology. Elsevier Science
Slininger PJ, Bothast RJ, Okos MR, Ladisch MR (1985) Comparative evaluation of ethanol production by xylose fermenting yeasts presented high xylose concentrations. Biotechnol Lett 7:431–436
Stephanopoulos G, Aristidou A, Nielsen J (1998) Metabolic engineering: principles and methodologies, 1st edn. Academic Press, San Diego
Thorpe RF, Ratledge C (1972) Fatty acid distribution in triglycerides of yeasts grown on glucose or n-alkanes. J Gen Microbiol 72:151–163. doi:10.1099/00221287-72-1-151
Toivola A, Yarrow D, Van Den Bosch E, Van Dijken JP, Scheffers WA (1984) Alcoholic fermentation of D-xylose by yeasts. Appl Environ Microbiol 47:1221–1223
Unrean P, Nguyen NA (2012) Metabolic pathway analysis of Scheffersomyces (Pichia) stipitis: effect of oxygen availability on ethanol synthesis and flux distributions. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 94:1387–1398
Van Gulik WM, Heijnen JJ (1995) A metabolic network stoichiometry analysis of microbial growth and product formation. Biotechnol Bioeng 48:681–698
Vanrolleghem PA, de Jong-Gubbels P, van Gulik WM, Pronk JT, van Dijken JP, Heijnen S (1996) Validation of a metabolic network for Saccharomyces cerevisiae using mixed substrate studies. Biotechnol Prog 12:434–448. doi:10.1021/bp960022i
Verduyn C, Stouthamer AH, Scheffers WA, Van Dijken JP (1991) A theoretical evaluation of growth yields of yeasts. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 59:49–63
Yablochkova EN, Bolotnikova OI, Mikhailova NP, Nemova NN, Ginak AI (2003) The activity or xylose reductase and xylitol dehydrogenase in yeasts. Microbiol 72:414–417
Yablochkova EN, Bolotnikova OI, Mikhailova NP, Nemova NN, Ginak AI (2004) The activity of key enzymes in xylose-assimilating yeasts at different rates of oxygen transfer to fermentation medium. Microbiol 73:129–133
Acknowledgments
This work was carried out as part of the futurolproject, and the authors want to thank OSEO Innovation for its financial support and Dr. P. Winterton for the help in preparing the English manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
All the authors declare that there is no potential conflict of interest (financial or non-financial), and that this research work did involve neither human participants nor animals.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(PDF 30.9 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bideaux, C., Montheard, J., Cameleyre, X. et al. Metabolic flux analysis model for optimizing xylose conversion into ethanol by the natural C5-fermenting yeast Candida shehatae . Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 100, 1489–1499 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-015-7085-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-015-7085-0