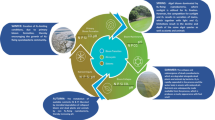
Abstract
Cyanobacteria blooms are since early times a cause for environmental concern because of their negative impact through the release of odors, water discoloration, and more dangerously through the release of toxic compounds (i.e. the cyanotoxins) that can affect both human and animal welfare. Surveillance of the aquatic ecosystems is therefore obligatory, and methods to achieve such require a prompt answer not only regarding the species that are producing the blooms but also the cyanotoxins that are being produced and/or released. Moreover, besides this well-known source of possible intoxication, it has been demonstrated the existence of several other potential routes of exposure, either for humans or other biota such as through food additives and in terrestrial environments (in plants, lichens, biological soil crusts) and the recognition of their harmful impact on less studied ecosystems (e.g. coral reefs). Nowadays, the most frequent approaches to detect toxic cyanobacteria and/or their toxins are the chemical-, biochemical-, and molecular-based methods. Above their particular characteristics and possible applications, they all bring to the environmental monitoring several aspects that are needed to be discussed and scrutinized. The end outcome of this review will be to provide newer insights and recommendations regarding the methods needed to apply in an environmental risk assessment program. Therefore, a current state of the knowledge concerning the three methodological approaches will be presented, while highlighting positive and negative aspects of each of those methods within the purpose of monitoring or studying cyanobacteria and their toxins in the environment.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Al-Sammak MA, Hoagland KD, Snow DD, Cassada D (2013) Methods for simultaneous detection of the cyanotoxins BMAA, DABA, and anatoxin-a in environmental samples. Toxicon 76:316–325
Al-Sammak MA, Hoagland KD, Cassada D, Snow DD (2014) Co-occurrence of the cyanotoxins BMAA, DABA and anatoxin-a in Nebraska reservoirs, fish, and aquatic plants. Toxin 6:488–508. doi:10.3390/toxins6020488
Amorim A, Vasconcelos V (1999) Dynamics of microcystins in the mussel Mytilus galloprovincialis. Toxicon 37:1041–1052
An J, Carmichael WW (1994) Use of a colorimetric protein phosphatase assay and enzyme linked immunoassay for the study of microcystins and nodularin. Toxicon 12:1495–1507
Aráoz R, Guerineau V, Rippka R, Palibroda N, Herdman M, Laprevote O, von Dohren H, Tandeau de Marsac N, Erhard M (2008) MALDI-TOF-MS detection of the low molecular weight neurotoxins anatoxin-a and homoanatoxin-a on lyophilized and fresh filaments of axenic Oscillatoria strains. Toxicon 51:1308–1315
Azevedo J, Osswald J, Guilhermino L, Vasconcelos V (2011) Development and validation of an SPE-HPLC-FL method for the determination of anatoxin-a in water and trout (Oncorhyncus mykiss). Anal Lett 44:1431–1441
Ballot A, Pflugmacher S, Wiegand C, Kotut K, Krienitz LC, Baker JA, Entsch B, Neilan BA, McKay DB (2002) Monitoring changing toxigenicity of a cyanobacterial bloom by molecular methods. Appl Environ Microbiol 68(12):6070–6076
Blahova L, Babica P, Adamovsky O, Kohoutek J, Marsalek B, Blaha L (2008) Analyses of cyanobacterial toxins (microcystins, cylindrospermopsin) in the reservoirs of the Czech Republic and evaluation of health riks. Environ Chem Lett 6:223–227
Bláhová L, Oravec M, Maršálek B, Šejnohová L, Šimek Z, Bláha L (2009) The first occurrence of the cyanobacterial alkaloid toxin cylindrospermopsin in the Czech Republic as determined by immunochemical and LC/MS methods. Toxicon 53:519–524
Brito Â, Ramos V, Seabra R, Santos A, Santos CL, Lopo M, Tamagnini P (2012) Culture-dependent characterization of cyanobacterial diversity in the intertidal zones of the Portuguese coast: a polyphasic study. Syst Appl Microbiol 35(2):110–119
Carmichael WW, Liu RH (2006) Cyanobacterial toxins in the Salton Sea. Saline Systems 2:5
Carmichael WW, Azevedo S, An JS, Molica R, Jochimsen E, Lau S, Rinehart KL, Shaw GR, Eaglesham GK (2001) Human fatalities from cyanobacteria: chemical and biological evidences for cyanotoxins. Environ Health Perspect 109:663–668
Castiglioni B, Rizzi E, Frosini A, Sivonen K, Rajaniemi P, Rantala A, De Bellis G (2004) Development of a universal microarray based on the ligation detection reaction and 16S rRNA gene polymorphism to target diversity of cyanobacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol 70(12):7161–7172
Cox PA, Banack SA, Murch SJ, Rasmussen U, Tien G, Bidigare RR, Metcalf JS, Morrison LF, Codd GA, Bergman B (2005) Diverse taxa of cyanobacteria produce β-N-methylamino-L-alanine, a neurotoxic amino acid. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 102(14):5074–5078
Dai M, Xie P, Liang G, Chen J, Lei H (2008) Simultaneous determination of microcystin-LR and its glutathione conjugate in fish tissues by liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr B 862:43–50
Elliot CT, Redshaw CH, George SE, Campbell K (2013) First development and characterization of polyclonal and monoclonal antibodies to the merging fresh water toxin cylindrospermpsin. Harmful Algae 24:10–19
Fastner J, Codd GA, Metcalf JS, Woitke P, Wiedner C, Utkilen H (2002) An international intercomparison exercise for the determination of purified microcystin-LR and microcystins in cyanobacterial field material. Anal Bioanal Chem 374:437–444
Fergusson KM, Saint PC (2003) Multiplex PCR Assay for Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii and cylindrospermopsin-producing cyanobacteria. Environ Toxicol 18(2):120–125
Ferrão-Filho ADS, Kozlowsky-Suzuki B (2011) Cyanotoxins: bioaccumulation and effects on aquatic animals. Mar Drugs 9(12):2729–2772
Fewer DP, Köykkä M, Halinen K, Jokela J, Lyra C, Sivonen K (2009) Culture‐independent evidence for the persistent presence and genetic diversity of microcystin‐producing Anabaena (Cyanobacteria) in the Gulf of Finland. Environ Microbiol 11(4):855–866
Fischer WJ, Garthwaite I, Miles CO, Ross KM, Aggen JB, Chamberlin AR, Towers NR, Dietrich DR (2001) Congener-independent immunoassay for microcystins and nodularins, Env. Sci Technol 35:4849–4856
Foss AJ, Aubel MT (2013) The extraction and analysis of cylindrospermopsin from human serum and urine. Toxicon 70:54–61
Furukawa K, Noda N, Tsuneda S, Saito T, Itayama T, Inamori Y (2006) Highly sensitive real-time PCR assay for quantification of toxic cyanobacteria based on microcystin synthetase A gene. J Biosci Bioeng 102(2):90–96
Gaget V, Gribaldo S, Tandeau de Marsac N (2011) An rpoB signature sequence provides unique resolution for the molecular typing of cyanobacteria. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 61:170–183
Gantar M, Sekar R, Richardson LL (2009) Cyanotoxins from black band disease of corals and from other coral reef environments. Microb Ecol 58(4):856–864
Garcia-Pichel F (2008) Molecular ecology and environmental genomics of cyanobacteria. In: Herrero A, Flores E (eds) The cyanobacteria: molecular biology, genomics and evolution. Caister Academic Press, Norfolk, pp 59–87
Gehringer MM, Adler L, Roberts AA, Moffitt MC, Mihali TK, Mills TJT, Fieker C, Neilan BA (2012) Nodularin, a cyanobacterial toxin, is synthesized in planta by symbiotic Nostoc sp. ISME J 6(10):1834–1847
Geis-Asteggiante L, Lehotay SJ, Fortis LL, Paoli G, Wijey C, Heinzen H (2011) Development and validation of a rapid method for microcystins in fish and comparing LC-MS/MS results with ELISA. Anal Bioanal Chem 401:2617–2630
Heresztyn T, Nicholson BC (2001) Determination of cyanobacterial hepatotoxins directly in water using a protein phosphatase inhibition assay. Water Res 35:3049–3056
Hisbergues M, Christiansen G, Rouhiainen L, Sivonen K, Börner T (2003) PCR-based identification of microcystin-producing genotypes of different cyanobacterial genera. Arch Microbiol 180(6):402–410
Humpage AR, Froscio SM, Lau H-M, Murphy D, Blackbeard J (2012) Evaluation of the Abraxis Strip Test for microcystin for use with wastewater effluent and reservoir water. Water Res 46:1556–1565
Ikehara T, Imamura S, Oshiro N, Ikehara S, Shinjo F, Yasumoto T (2008) A protein phosphatase 2A (PP2A) inhibition assay using a recombinant enzyme for rapid detection of microcystins. Toxicon 51:1368–1373
Ionescu D, Hindiyeh M, Malkawi H, Oren A (2010) Biogeography of thermophilic cyanobacteria: insights from the ZerkaMa’ in hot springs (Jordan). FEMS Microbiol Ecol 72:103–113
Iteman I, Rippka R, Tandeau de Marsac N, Herdman M (2000) Comparison of conserved structural and regulatory domains within divergent 16S rRNA–23S rRNA spacer sequences of cyanobacteria. Microbiology 146:1275–1286
Izaguirre G, Hwang CJ, Krasner SW, McGuire MJ (1982) Geosmin and 2-methylisoborneol from cyanobacteria in three water supply systems. Appl Environ Microbiol 43(3):708–714
Janse I, Kardinaal WEA, Meima M, Fastner J, Visser PM, Zwart G (2004) Toxic and nontoxic Microcystis colonies in natural populations can be differentiated on the basis of rRNA gene internal transcribed spacer diversity. Appl Environ Microbiol 70(7):3979–3987
Jungblut AD, Neilan BA (2006) Molecular identification and evolution of the cyclic peptide hepatotoxins, microcystin and nodularin, synthetase genes in three orders of cyanobacteria. Arch Microbiol 185(2):107–114
Jungblut A-D, Hawes I, Mountfort D, Hitzfeld B, Dietrich DR, Burns BP, Neilan BA (2005) Diversity within cyanobacterial mat communities in variable salinity meltwater ponds of McMurdo Ice Shelf, Antarctica. Environ Microbiol 7(4):519–529
Kaasalainen U, Fewer DP, Jokela J, Wahlsten M, Sivonen K, Rikkinen J (2012) Cyanobacteria produce a high variety of hepatotoxic peptides in lichen symbiosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 109(15):5886–5891
Kellmann R, Michali TK, Neilan BA (2008) Identification of a saxitoxin biosynthesis gene with a history of frequent horizontal gene transfer. J Mol Evol 67:526–538
Kurmayer R, Kutzenberger T (2003) Application of real-time PCR for quantification of microcystin genotypes in a population of the toxic cyanobacterium Microcystis sp. Appl Environ Microbiol 69(11):6723–6730
Lawrence JF, Niedzwiadek B, Menard C (2005) Quantitative determination of paralytic shell fish poisoning toxins in shell fish using pre-chromatographic oxidation and liquid chromatography with fluorescence detection: collaborative study. J AOAC Int 88:1714–1732
Lawton LA, Edwards C, Codd GA (1994) Extraction and high-performance liquid chromatographic method for the determination of microcystins in raw and treated waters. Analyst 11(9):1525–1530
Lawton LA, Chambers H, Edwards C, Nwaopara AA, Healy M (2010) Rapid detection of microcystins in cells and water. Toxicon 55:973–978
Li H, Singh AK, McIntyre LM, Sherman LA (2004) Differential gene expression in response to hydrogen peroxide and the putative PerR regulon of Synechocystis sp. Strain PCC 6803. J Bacteriology 186(11):3331–3345
Li W, Duan J, Niu C, Qiang N, Mulcahy D (2011) Determination of microcystin-LR in drinking water using UPLC tandem mass spectrometry–matrix effects and measurement. J Chromatogr Sci 49:665–670
Lopes VR, Ramos V, Martins A, Sousa M, Welker M, Antunes A, Vasconcelos VM (2012) Phylogenetic, chemical and morphological diversity of cyanobacteria from Portuguese temperate estuaries. Mar Environ Res 73:7–16
Martins JC, Vasconcelos VM (2009) Microcystin distribution and dynamics in aquatic organisms—a review. J Toxicol Environ Health Part B Critical reviews 12:1–18
Meisen I, Distler U, Muthing J, Berkenkamp S, Dreisewerd S, Mathys W, Karch H, Mormann M (2009) Direct coupling of high-performance thin-layer chromatography with UV spectroscopy and IR-MALDI orthogonal TOF MS for the analysis of cyanobacterial toxins. Anal Chem 81:3858–3866
Metcalf JS, Reilly M, Young FM, Codd GA (2009) Localization of microcystin synthetase genes in colonies of the cyanobacterium Microcystis using fluorescence in situ hybridization. J Phycol 45(6):1400–1404
Metcalf JS, Richer R, Cox PA, Codd GA (2012) Cyanotoxins in desert environments may present a risk to human health. Sci Total Environ 421–422:118–123
Mihali TK, Kellmann R, Muenchhoff J, Barrow KD, Neilan BA (2008) Characterization of the gene cluster responsible for cylindrospermopsin biosynthesis. Appl Environ Microbiol 74(3):716–722
Moffitt MC, Neilan BA (2001) On the presence of peptide synthetase and polyketide synthase genes in the cyanobacterial genus Nodularia. FEMS Microbiol Lett 196(2):207–214
Moreira C, Martins A, Azevedo J, Freitas M, Regueiras A, Vale M, Antunes A, Vasconcelos V (2011) Application of real-time PCR in the assessment of the toxic cyanobacterium Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii abundance and toxicological potential. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 92:189–197
Mountfort DO, Holland P, Sprosen J (2005) Method for detecting classes of microcystins by combination of protein phosphatase inhibition assay and ELISA: comparison with LC-MS. Toxicon 45:199–206
Neilan BA, Jacobs D, Goodman AE (1995) Genetic diversity and phylogeny of toxic cyanobacteria determined by DNA polymorphisms within the phycocyanin locus. Appl Environ Microbiol 61(11):3875–3883
Neilan BA, Jacobs D, Del Dot T, Blackall LL, Hawkins PR, Cox PT, Goodman AE (1997) rRNA sequences and evolutionary relationships among toxic and non-toxic cyanobacteria of the genus Microcystis. Int J Syst Bacteriol 47:693–697
Nübel U, Garcia-Pichel F, Muyzer G (1997) PCR primers to amplify 16S rRNA genes from cyanobacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol 63(8):3327–3332
Oksanen I, Jokela J, Fewer DP, Wahlsten M, Rikkinen J, Sivonen K (2004) Discovery of rare and highly toxic microcystins from lichen-associated cyanobacterium Nostoc sp. strain IO-102-I. Appl Environ Microbiol 70(10):5756–5763
Ortelli D, Edder P, Cognard E, Jan P (2008) Fast screening and quantitation of microcystins in microalgae dietary supplement products and water by liquid chromatography coupled to time of flight mass spectrometry. Anal Chim Acta 617(1–2):230–237
Ouahid Y, Pérez-Silva G, del Campo FF (2005) Identification of potentially toxic environmental Microcystis by individual and multiple PCR amplification of specific microcystin synthetase gene regions. Environ Toxicol 20(3):235–242
Ouellette AJ, Handy SM, Wilhelm SW (2006) Toxic Microcystis is widespread in Lake Erie: PCR detection of toxin genes and molecular characterization of associated cyanobacterial communities. Microl Ecol 51(2):154–165
Papke RT, Ramsing NB, Bateson MM, Ward DM (2003) Geographic isolation in hot spring cyanobacteria. Environ Microbiol 5:650–659
Penn K, Wang J, Fernando SC, Thompson JR (2014) Secondary metabolite gene expression and interplay of bacterial functions in a tropical freshwater cyanobacterial bloom. ISME J. doi:10.1038/ismej.2014.27
Pereira S, Vasconcelos V, Antunes A (2010) The phosphoprotein phosphatase family of Ser/Thr phosphatases as principal targets of naturally occurring toxins. Crit Rev Toxicol 41:83–110
Pope PB, Patel BKC (2008) Metagenomic analysis of a freshwater toxic cyanobacteria bloom. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 64(1):9–27
Rantala A, Fewer DP, Hisbergues M, Rouhiainen L, Vaitomaa J, Börner T, Sivonen K (2004) Phylogenetic evidence for the early evolution of microcystin synthesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 101(2):568–573
Rantala A, Rizzi E, Castiglioni B, de Bellis G, Sivonen K (2008) Identification of hepatotoxin-producing cyanobacteria by DNA-chip. Environ Microbiol 10(3):653–664
Rantala-Ylinen A, Känä S, Wang H, Rouhiainen L, Wahlsten M, Rizzi E, Sivonen K (2011) Anatoxin-a synthetase gene cluster of the cyanobacterium Anabaena sp. strain 37 and molecular methods to detect potential producers. Appl Environ Microbiol 77(20):7271–7278
Rinta-Kanto JM, Ouellette AJA, Boyer GL, Twiss MR, Bridgeman TB, Wilhelm SW (2005) Quantification of toxic Microcystis spp. during the 2003 and 2004 blooms in western Lake Erie using quantitative real-time PCR. Environ Sci Technol 39:4198–4205
Rivasseau C, Racaud P, Deguin A, Hennion M-C (1999) Evaluation of an ELISA kit for the monitoring of microcystins (cyanobacterial toxins) in water and algae environmental samples. Environ Sci Technol 33:1520–1527
Robillot C, Hennion M-C (2004) Issues arising when interpreting the results of the protein phosphatase 2A inhibition assay for the monitoring of microcystins. Anal Chim Acta 512:339–346
Rodriguez V, Yonamine M, Pinto E (2006) Determination of anatoxin-a in environmental water samples by solid-phase microextraction and gas chromatography–mass spectrometry. J Sep Sci 29:2085–2090
Romana R-B, Ujević I (2014) PSP toxins profile in ascidian Microcosmus vulgaris (Heller, 1877) after human poisoning in Croatia (Adriatic Sea). Toxicon 79:28–36
Rothrock MJ, Garcia Pichel F (2005) Microbial diversity of benthic mats along a tidal desiccation gradient. Environ Microbiol 7(4):593–601
Rudi K, Skulberg OM, Skulberg R, Jakobsen KS (2000) Application of sequence-specific labeled 16S rRNA gene oligonucleotide probes for genetic profiling of cyanobacterial abundance and diversity by array hybridization. Appl Environ Microbiol 66(9):4004–4011
Saker ML, Jungblut AD, Neilan BA, Rawn DFK, Vasconcelos VM (2005) Detection of microcystin synthetase genes in health food supplements containing the freshwater cyanobacterium Aphanizomenon flos-aquae. Toxicon 46(5):555–562
Saker ML, Welker M, Vasconcelos VM (2007) Multiplex PCR for the detection of toxigenic cyanobacteria in dietary supplements produced for human consumption. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 73(5):1136–1142
Saker M, Moreira C, Martins J, Neilan B, Vasconcelos VM (2009) DNA profiling of complex bacterial populations: toxic cyanobacterial blooms. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 85:237–252
Schönhuber W, Zarda B, Eix S, Rippka R, Herdman M, Ludwig W, Amann R (1999) In Situ identification of cyanobacteria with horseradish peroxidase-labeled, rRNA-targetedoligonucleotide probes. Appl Environ Microbiol 65(3):1259–1267
Sipari H, Rantala-Ylinen A, Jokela J, Oksanen I, Sivonen K (2010) Development of a chip assay and quantitative PCR for detecting microcystin synthetase E gene expression. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 76(12):3797–3805
Skulberg OM, Carmichael WW, Andersen RA, Matsunaga S, Moore RE, Skulberg R (1992) Investigations of a neurotoxic oscillatorialean strain (Cyanophyceae) and its toxin. Isolation and characterization of homoanatoxin-a. Environ Toxicol Chem 11(3):321–329
Steffen MM, Li Z, Effler TC, Hauser LJ, Boyer GL, Wilhelm SW (2012) Comparative metagenomics of toxic freshwater cyanobacteria bloom communities on two continents. PLoS ONE 7(8)
Stücken K, Murillo AA, Soto-Liebe K, Fuentes-Valdés JJ, Méndez MA, Vásquez M (2009) Toxicity phenotype does not correlate with phylogeny of Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii strains. Syst Appl Microbiol 32(1):37–48
Sukenik A, Hadas O, Kaplan A, Quesada A (2012) Invasion of Nostocales (cyanobacteria) to subtropical and temperate freshwater lakes—physiological, regional, and global driving forces. Front Microbiol 3:86. doi:10.3389/fmicb.2012.00086
Tidgewell K, Clark BR, Gerwick WH (2010) The natural products chemistry of cyanobacteria. In: Mander L, Lui H-W (eds) Comprehensive natural products II. Chemistry and biology, vol 2. Elsevier, Oxford, pp 141–188
Tillett D, Dittmann E, Erhard M, von Döhren H, Börner T, Neilan BA (2000) Structural organization of microcystin biosynthesis in Microcystis aeruginosa PCC7806: an integrated peptide-polyketide synthetase system. Chem Biol 7(10):753–764
Tillett D, Parker DL, Neilan BA (2001) Detection of toxigenicity by a probe for the microcystinsynthetase A gene (mcyA) of the cyanobacterial genus Microcystis: comparison of toxicities with 16S rRNA and phycocyanin operon (phycocyaninintergenic spacer) phylogenies. Appl Environ Microbiol 67(6):2810–2818
Ueno Y, Nagata S, Tsutsumi T, Hasegawa A, Yoshiuda F, Sutajjit M, Mebs D, Vasconcelos V (1996) Survey of microcystins in environmental water by a highly sensitive immunoassay based on monoclonal antibody. Nat Toxins 4:271–276
Valério E, Chambel L, Paulino S, Faria N, Pereira P, Tenreiro R (2009) Molecular identification, typing and traceability of cyanobacteria from freshwater reservoirs. Microbiology 155(2):642–656
Vareli K, Jaeger W, Touka A, Frillingos S, Briasoulis E, Sainis I (2013) Hepatotoxic seafood poisoning (HSP) due to microcystins: a threat from the ocean? Mar Drugs 11(8):2751–2768
Vasas G, Gáspár A, Páger C, Surányi G, Máthé C, Hamvas MM, Borbely G (2004) Analysis of cyanobacterial toxins (anatoxin-a, cylindrospermopsin, microcystin-LR) by capillary electrophoresis. Electrophoresis 25:108–115
Vichi S, Lavorini P, Funari E, Scardala S, Testai E (2012) Contamination by Microcystis and microcystins of blue-green algae food supplements (BGAS) on the Italian market and possible risk for the exposed population. Food Chem Toxicol 50(12):4493–4499
Wang L, Chen W, Xu D, Shim BS, Zhu Y, Sun F, Liu L, Peng C, Jin Z, Xu C, Kotov NA (2009) Simple, rapid, sensitive and versatile SWNT-paper sensor for environmental toxin detection competitive with ELISA. Nano Letters 9:4147–4152
Wang X, Sun M, Xie M, Liu M, Luo L, Li P, Kong F (2013) Differences in microcystin production and genotype composition among Microcystis colonies of different sizes in Lake Taihu. Water Res 47(15):5659–5669
Watanabe R (2013) Quantitative determination of paralytic shellfish toxins in cultured toxic algae by LC-MS/MS Food Additives &Amp. Contaminants Part A 30(8):1351–1357
Welker M, Bickel H, Fastner J (2002) HPLC-PDA detection of cylindrospermopsin—opportunities and limits. Water Res 36:4659–4663
Wilson KM, Schembri MA, Baker PD, Saint CP (2000) Molecular characterization of the toxic cyanobacterium Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii and design of a species-specific PCR. Appl Environ Microbiol 66(1):332–338
Worden AZ, Chisholm SW, Binder BJ (2000) In situ hybridization of Prochlorococcus and Synechococcus (marine cyanobacteria) spp. with rRNA-targeted peptide nucleic acid probes. Appl Environ Microbiol 66(1):284–289
Ye W, Liu X, Tan J, Li D, Yang H (2009) Diversity and dynamics of microcystins—producing cyanobacteria in China’s third largest lake, Lake Taihu. Harmful Algae 8(5):637–644
Yu F-Y, Liu B-H, Chou H-N, Chu FS (2002) Development of a sensitive ELISA for the determination of microcystin in algae. J Agric Food Chem 50:4176–4182
Yuan M, Carmichael WW (2004) Detection and analysis of the cyanobacterial peptide hepatotoxins microcystin and nodularin using SELDI-TOF mass spectrometry. Toxicon 44(5):561–570
Zakhia F, Jungblut A-D, Taton A, Vincent WF, Wilmotte A (2008) Cyanobacteria in cold ecosystems. Springer-Verlag, Berlin, pp 121–135
Zeisbergerová M, Koštál V, Šrámková M, Babica P, Bláha L, Glatz Z, Kahle V (2006) Separation of microcystins by capillary electrochromatography in monolithic columns. J Chromatogr B 841(1–2):140–144
Acknowledgments
This research was funded by the PesT-C/MAR/LA0015/2013 project from Fundação para a Ciência e Tecnologia and by the project MARBIOTECH (reference NORTE-07-0124-FEDER-000047), co-financed by the North Portugal Regional Operational Programme (ON.2—O Novo Norte), under the National Strategic Reference Framework (NSRF), through the ERDF.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Moreira, C., Ramos, V., Azevedo, J. et al. Methods to detect cyanobacteria and their toxins in the environment. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 98, 8073–8082 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-014-5951-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-014-5951-9