Abstract
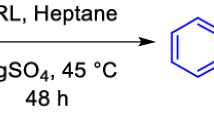
Long-chain alkyl benzoates, e.g., lauryl 4-hydroxybenzoate, palmityl 4-hydroxybenzoate, and oleyl 4-hydroxy-3-methoxybenzoate, are formed in high to moderate conversion by lipase-catalyzed transesterification of the corresponding short-chain alkyl benzoates (0.3 to 1 mmol) with fatty alcohols in an equimolar ratio. The substrates are reacted in vacuo in the absence of solvents and drying agents in the reaction mixture. Immobilized lipase B from Candida antarctica (Novozym 435) demonstrates higher activity for the transesterification of various methyl (hydroxy)benzoates with long-chain alcohols than for the corresponding esterification reactions. For example, transesterification activity is around 25-fold higher than esterification activity for the preparation of oleyl 4-hydroxybenzoate. The relative transesterification activities of methoxy- and hydroxy-substituted methyl benzoates found for Novozym 435 are as follows: 2-methoxybenzoate ≈ 3-methoxybenzoate > 4-methoxybenzoate > 3-hydroxybenzoate ≈ 2-hydroxybenzoate > 4-hydroxybenzoate ≈ 4-hydroxy-3-methoxybenzoate ≈ 3-hydroxy-4-methoxybenzoate > > 3,4-dihydroxybenzoate. With respect to the position of the substituents at the phenyl moiety of methyl benzoates, transesterification activity of Novozym 435 increases in the order ortho ≈ meta > para. Compounds with inverse chemical structure, e.g., (methoxy)benzyl alkanoates, are formed in much higher rates both by esterification and transesterification than the analogous alkyl benzoates. Purification by deacidification, crystallization, or vacuum distillation yielded 74% to 89% of the reaction products.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baderschneider B, Winterhalter P (2001) Isolation and characterization of novel benzoates, cinnamates, flavonoids, and lignans from Riesling wine and screening for antioxidant activity. J Agric Food Chem 49:2788–2798
Buisman GJH, van Helteren CTW, Kramer GFH, Veldsink JW, Derksen JTP, Cuperus FP (1998) Enzymatic esterifications of functionalized phenols for the synthesis of lipophilic antioxidants. Biotechnol Lett 20:131–136
Chang C-S, Wu P-L (2007) Synthesis of triglycerides of phenylalkanoic acids by lipase-catalyzed esterification in a solvent-free system. J Biotechnol 127:694–702
CIR (Cosmetic Ingredient Review) (1984) Final report on the safety assessment of methylparaben, ethylparaben, propylparaben, and butylparaben. J Am Coll Toxicol 3:147–209
Figueroa-Espinoza M-C, Villeneuve P (2005) Phenolic acids enzymatic lipophilization. J Agric Food Chem 53:2779–2787
Kobayashi T, Adachi S, Matsumo R (2003) Lipase-catalyzed condensation of p-methoxyphenethyl alcohol and carboxylic acids with different steric and electrical properties in acetonitrile. Biotechnol Lett 25:3–7
Kohrman KA, Booman KA, Dorsky J, Rothenstein AS, Sedlak RI, Steltenkamp RJ, Thompson GR (1983) Benzyl salicylate: a survey of consumer patch-test sensitization. Food Chem Toxicol 21:741–744
Kupferwasser LI, Yeaman MR, Nast CC, Kupferwasser D, Xiong YQ, Palma M, Cheung AL, Bayer AS (2003) Salicylic acid attenuates virulence in endovascular infections by targeting global regulatory pathways in Staphylococcus aureus. J Clin Invest 112:222–233
Larios A, Garcia HS, Oliart RM, Valerio-Alfaro G (2004) Synthesis of flavor and fragrance esters using Candida antarctica lipase. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 65:373–376
Leopoldini M, Marino T, Russo N, Toscano M (2004) Antioxidant properties of phenolic compounds. H-atom versus electron-transfer mechanism. J Phys Chem A 108:4916–4922
Liao X, Raghavan GSV, Yaylayan VA (2002) A novel way to prepare n-butylparaben under microwave irradiation. Tetrahedron Lett 43:45–48
Mattila P, Hellström J, Törrönen R (2006) Phenolic acids in berries, fruits and beverages. J Agric Food Chem 54:7193–7199
Otto RT, Scheib H, Bornscheuer UT, Pleiss J, Syldatk C, Schmid RD (2000) Substrate specificity of lipase B from Candida antarctica in the synthesis of arylaliphatic glycolipids. J Mol Catal B Enzym 8:201–211
Paterson JR, Srivastava R, Baxter GJ, Graham AB, Lawrence JR (2006) Salicylic acid content of spices and its implications. J Agric Food Chem 54:2891–2896
Sefkow M, Kaatz H (1999) Selective protection of either phenol or the hydroxy group in hydroxyalkyl phenols. Tetrahedron Lett 40:6561–6562
Soni MG, Carabin IG, Burdock GA (2005) Safety assessment of esters of p-hydroxybenzoic acid (parabens). Food Chem Toxicol 43:985–1015
Stamatis H, Sereti V, Kolisis FN (1999) Studies on the enzymatic synthesis of lipophilic derivatives of natural antioxidants. J Am Oil Chem Soc 76:1505–1510
Stöckmann H, Schwarz K, Huynh-Ba T (2000) The influence of various emulsifiers on the partitioning and antioxidant activity of hydroxybenzoic acids and their derivatives in oil-in-water emulsions. J Am Oil Chem Soc 77:535–542
Vasyukova NI, Ozeretskovskaya OL (2007) Induced plant resistance and salicylic acid: a review. Appl Biochem Microbiol 43:367–373
Vosmann K, Weitkamp P, Weber N (2006) Solvent-free lipase-catalyzed preparation of long-chain alkyl phenylpropanoates and phenylpropyl alkanoates. J Agric Food Chem 54:2969–2976
Walker TS, Bais HP, Halligan KM, Stermitz FR, Vivanco JM (2003) Metabolic profiling of root exudates of Arabidopsis thaliana. J Agric Food Chem 51:2548–2554
Weitkamp P, Vosmann K, Weber N (2006) Highly efficient preparation of lipophilic hydroxycinnamates by solvent-free lipase-catalyzed transesterification. J Agric Food Chem 54:7062–7068
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM
Electronic Supporting Material (DOC 543 KB)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vosmann, K., Wiege, B., Weitkamp, P. et al. Preparation of lipophilic alkyl (hydroxy)benzoates by solvent-free lipase-catalyzed esterification and transesterification. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 80, 29–36 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-008-1534-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-008-1534-y