Abstract
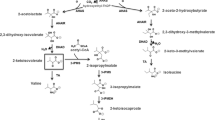
Feeding sodium butyrate (0.25–1 mg/ml) to cultures of Salinispora tropica NPS21184 enhanced the production of salinosporamide B (NPI-0047) by 319% while inhibiting the production of salinosporamide A (NPI-0052) by 26%. Liquid chromatography mass spectrometry analysis of the crude extract from the strain NPS21184 fed with 0.5 mg/ml sodium [U-13C4]butyrate indicated that butyrate was incorporated as a contiguous four-carbon unit into NPI-0047 but not into NPI-0052. Nuclear magnetic resonance analysis of NPI-0047 and NPI-0052 purified from the sodium [U-13C4]butyrate-supplemented culture extract confirmed this incorporation pattern. The above finding is the first direct evidence to demonstrate that the biosynthesis of NPI-0047 is different from NPI-0052, and NPI-0047 is not a precursor of NPI-0052.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Byrnxe KM, Shafiee A, Nielsen J, Arison B, Monaghan RL, Kaplan L (1993) The biosynthesis and enzymology of an immunosuppressant, immunomycin, produced by Streptomyces hygroscopicus var. ascomyceticus. Dev Ind Microbiol 32:29–45
Chauhan D, Catley L, Li G, Podar K, Hideshima T, Velankar M, Mitsiades C, Mitsiades N, Yasui H, Letai A, Ovaa H, Berkers C, Nicholson B, Chao TH, Neuteboom STC, Richardson P, Palladino MA, Anderson KC (2005) A novel orally active proteasome inhibitor induces apoptosis in multiple myeloma cells with mechanisms distinct from Bortezomib. Cancer Cell 8:407–419
Feling RH, Buchanan GO, Mincer TJ, Kauffman CA, Jensen PR, Fenical W (2003) Salinosporamide A: a highly cytotoxic proteasome inhibitor from a novel microbial source, a marine bacterium of the new genus Salinispora. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl 42:355–357
Gersch D, Bocker H, Thrum H (1977) Biosynthetic studies on the macrolide antibiotic turimycin using 14C-labeled precursors. J Antibiot 30:488–493
Groll M, Huber R, Potts BCM (2006) Crystal structures of salinosporamide A (NPI-0052) and B (NPI-0047) in complex with the 20S proteasome reveal important consequences of beta-lactone opening and a mechanism for irreversible binding. J Am Chem Soc 128:5136–5141
Jensen PR, Dwight R, Fenical W (1991) Distribution of actinomycetes in near-shore tropical marine sediments. Appl Environ Microbiol 57:1102–1108
Liu H, Reynolds KA (2001) Precursor supply for polyketide biosynthesis: the role of crotonyl-CoA reductase. Metab Eng 3:40–48
Macherla VR, Mitchell SS, Manam RR, Reed KA, Chao T, Nicholson B, Deyanat-Yazdi G, Mai B, Jensen PR, Fenical WF, Neuteboom STC, Lam KS, Palladino MA, Potts BCM (2005) Structure-activity relationship studies of NPI-0052, a novel marine derived 20S proteasome inhibitor. J Med Chem 48:3684–3687
Omura S, Takeshima H, Nakagawa A, Kanemoto N, Lukacs G (1976) Studies on carboxylic acid metabolism in a macrolide-producing microorganism using carbon-13 magnetic resonance. Bioorg Chem 5:451–454
Omura S, Takeshima H, Nakagawa A, Miyazawa J, Piriou F, Lukacs G (1977) Studies on the biosynthesis of 16-membered macrolide antibiotics using carbon-13 nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Biochemistry 16:2860–2866
Pospisil S, Cimburkova E, Krumphanzl V, Vanek Z (1985) Effect of precursors on biosynthesis of monensins A and B. Folia Microbiol 30:30–33
Reed KA, Manam RR, Mitchell SS, Xu J, Teisan S, Chao TH, Deyanat-Yazdi G, Neuteboom STC, Lam KS, Potts BCM. (2007) Salinosporamides D-J from the marine actinomycete Salinispora tropica, bromosalinosporamide, and thioester derivatives are potent inhibitors of the 20S proteasome. J Nat Prod 70:269–276
Rezanka T, Reichelova J, Kopecky J (1991) Isobutyrate as a precursor of n-butyrate in the biosynthesis of tylosin and fatty acids. FEMS Microbiol Lett 68:33–36
Sherman MM, Hutchinson CR (1987) Biosynthesis of lasalocid A: biochemical mechanism for assembly of the carbon framework. Biochemistry 26:438–445
Williams PG, Buchanan GO, Feling RH, Kauffman CA, Jensen PR, Fenical W (2005) New cytotoxic salinosporamides from the marine actinomycete Salinispora tropica. J Org Chem 70:6196–6203
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tsueng, G., McArthur, K.A., Potts, B.C.M. et al. Unique butyric acid incorporation patterns for salinosporamides A and B reveal distinct biosynthetic origins. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 75, 999–1005 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-007-0899-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-007-0899-7