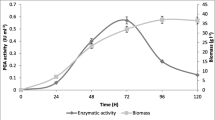
Abstract
Penicillin G acylase (PGA; E.C. 3.5.1.11) is an important enzyme which has broad applications in industries of β-lactim antibiotics production. In this study, a promising PGA gene from Alcaligenes faecalis (afpga) and another pcm gene encoding protein isoaspartate methyltransferase (PIMT) were constructed into pET43.1a(+) and pET28a(+), respectively. The recombinant plasmids pETAFPGA and pETPCM were transformed into the same host cell Escherichia coli BL21 (DE3). Results suggested that the two plasmids could peacefully exist in the host cell and the two genes could be efficiently expressed after induction. The product of pcm gene could function as a helper molecule for enzyme AFPGA. PIMT increased the enzymatic activities in supernatant of ferment broth (1.6 folds) and cell lysate (1.8 folds), while it did not significantly affect the expression level of penicillin G acylase.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254
Clark ED (2001) Protein refolding for industrial processes. Curr Opin Biotechnol 12:202–207
Clarke S (2003) Aging as war between chemical and biochemical processes: protein methylation and the recognition of age-damaged proteins for repair. Ageing Res Rev 2:263–285
Dirnbach E, Steel DG, Gafni A (1999) Proline isomerization is unlikely to be the cause of slow annealing and reactivation during the folding of alkaline phosphatase. J Biol Chem 274:4532–4536
Ellis RJ, Hemmingsen SM (1989) Molecular chaperones: proteins essential for the biogenesis of some macromolecular structures. Trends Biochem Sci 14:339–342
Ermolenko DN, Zherdev AV, Dzantiev BB (2004) Antibodies as specific chaperones. Biochemistry (Mosc) 69:1233–1238
Fahnert B, Lilie H, Neubauer P (2004) Inclusion bodies: formation and utilisation. Adv Biochem Eng Biotechnol 89:93–142
Fu JC, Ding L, Clarke S (1991) Purification, gene cloning, and sequence analysis of an l-isoaspartyl protein carboxyl methyltransferase from Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem 266:14562–14572
Guise AD, West SM, Chaudhuri JB (1996) Protein folding in vivo and renaturation of recombinant proteins from inclusion bodies. Mol Biotechnol 6:53–64
Joshi BH, Puri RK (2005) Optimization of expression and purification of two biologically active chimeric fusion proteins that consist of human interleukin-13 and Pseudomonas exotoxin in Escherichia coli. Protein Expr Purif 39:189–198
Kern R, Malki A, Abdallah J, Liebart JC, Dubucs C, Yu MH, Richarme G (2005) Protein isoaspartate methyltransferase is a multicopy suppressor of protein aggregation in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol 187:1377–1383
Kim SG, Kweon DH, Lee DH, Park YC, Seo JH (2005) Coexpression of folding accessory proteins for production of active cyclodextrin glycosyltransferase of Bacillus macerans in recombinant Escherichia coli. Protein Expr Purif 4:426–432
Kondo A, Kohda J, Endo Y, Shiromizu T, Kurokawa Y, Nishihara K, Yanagi H, Yura T, Fukuda H (2000) Improvement of productivity of active horseradish peroxidase in Escherichia coli by coexpression of Dsb proteins. J Biosci Bioeng 90:600–606
Lee S, Sowa ME, Choi JM, Tsai FT (2004) The ClpB/Hsp104 molecular chaperone—a protein disaggregating machine. J Struct Biol 146:99–105
Liang Y, Li W, Ma Q, Zhang Y (2005) Functional properties of PDIA from Aspergillus niger in renaturation of proteins. FEMS Microbiol Lett 245:363–368
Lin SY, Kondo F (2001) A simple classification method for residual antibiotics using E. coli cells transformed by the calcium chloride method and drug resistance plasmid DNA. Microbios 104:149–158
Liu Y, Zhao TJ, Yan YB, Zhou HM (2005) Increase of soluble expression in Escherichia coli cytoplasm by a protein disulfide isomerase gene fusion system. Protein Expr Purif 44:155–161
Merli S, Corti A, Cassani G (1995) Production of soluble tumor necrosis factor receptor type I in Escherichia coli: optimization of the refolding yields by a microtiter dilution assay. Anal Biochem 230:85–91
Middelberg AP (2002) Preparative protein refolding. Trends Biotechnol 20:437–443
Rupp K, Birnbach U, Lundstrom J, Van PN, Soling HD (1994) Effects of CaBP2, the rat analog of ERp72, and of CaBP1 on the refolding of denatured reduced proteins. Comparison with protein disulfide isomerase. J Biol Chem 269:2501–2507
Ryttersgaard C, Griffith SC, Sawaya MR, MacLaren DC, Clarke S, Yeates TO (2002) Crystal structure of human l-isoaspartyl methyltransferase. J Biol Chem 277:10642–10646
Schiene C, Fischer G (2000) Enzymes that catalyse the restructuring of proteins. Curr Opin Struct Biol 10:40–45
Singh SM, Panda AK (2005) Solubilization and refolding of bacterial inclusion body proteins. J Biosci Bioeng 99:303–310
Sorensen HP, Mortensen KK (2005) Advanced genetic strategies for recombinant protein expression in Escherichia coli. J Biotechnol 115:113–128
Sun QM, Chen LL, Cao L, Fang L, Chen C, Hua ZC (2005) An improved strategy for high-level production of human vasostatin120-180. Biotechnol Prog 21:1048–1052
Wang T, Zhu H, Ma X, Ma Y, Wei D (2006) Structure-based stabilization of an enzyme: the case of penicillin acylase from Alcaligenes faecalis. Prot Peptide Letters 13:177–183
Tsumoto K, Umetsu M, Kumagai I, Ejima D, Arakawa T (2003) Solubilization of active green Xuorescent protein from insoluble particles by guanidine and arginine. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 312:1383–1386
Wei C, Tang B, Zhang Y, Yang K (1999) Oxidative refolding of recombinant prochymosin. Biochem J 340:345–351
Weibezahn J, Schlieker C, Tessarz P, Mogk A, Bukau B (2005) Novel insights into the mechanism of chaperone-assisted protein disaggregation. Biol Chem 386:739–744
Weir MP, Sparks J (1987) Purification and renaturation of recombinant human interleukin-2. Biochem J 245:85–91
Acknowledgement
This work was financially supported by a grant from the National High Technology Research and Development Program of China (No.2002AA2Z345A).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, T., Zhu, H., Ma, X. et al. Enhancing enzymatic activity of penicillin G acylase by coexpressing pcm gene. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 72, 953–958 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-006-0349-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-006-0349-y