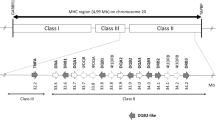
Abstract
Genes of the vertebrate major histocompatibility complex (MHC) are crucial to defense against infectious disease, provide an important measure of functional genetic diversity, and have been implicated in mate choice and kin recognition. As a result, MHC loci have been characterized for a number of vertebrate species, especially mammals; however, elephants are a notable exception. Our study is the first to characterize patterns of genetic diversity and natural selection in the elephant MHC. We did so using DNA sequences from a single, expressed DQA locus in elephants. We characterized six alleles in 30 African elephants (Loxodonta africana) and four alleles in three Asian elephants (Elephas maximus). In addition, for two of the African alleles and three of the Asian alleles, we characterized complete coding sequences (exons 1–5) and nearly complete non-coding sequences (introns 2–4) for the class II DQA loci. Compared to DQA in other wild mammals, we found moderate polymorphism and allelic diversity and similar patterns of selection; patterns of non-synonymous and synonymous substitutions were consistent with balancing selection acting on the peptides involved in antigen binding in the second exon. In addition, balancing selection has led to strong trans-species allelism that has maintained multiple allelic lineages across both genera of extant elephants for at least 6 million years. We discuss our results in the context of MHC diversity in other mammals and patterns of evolution in elephants.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alberts SC (1999) Thirteen Mhc-DQA1 alleles from two populations of baboons. Immunogenetics 49:825–827
Antunes SG, de Groot NG, Brok H, Doxiadis G, Menezes AAL, Otting N, Bontrop RE (1998) The common marmoset: a new world primate species with limited MHC class II variability. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 95:11745–11750
Archie EA, Moss CJ, Alberts SC (2003) Characterization of tetranucleotide microsatellite loci in the African savannah elephant (Loxodonta africana africana). Mol Ecol Notes 3:244–246
Archie EA, Moss CJ, Alberts SC (2006) The ties that bind: genetic relatedness predicts the fission and fusion of groups in wild African elephants (Loxodonta africana). Proc Roy Soc London 273:513–522
Archie EA, Hollister-Smith JA, Poole JH, Lee PC, Moss CJ, Maldonado JE, Fleischer RC, Alberts SC (2007) Behavioral inbreeding avoidance in wild African elephants. Mol Ecol 16:4138–4148
Archie EA, Maldonado JE, Hollister-Smith JA, Poole JH, Moss CJ, Fleischer RC, Alberts SC (2008) Fine-scale population genetic structure in a fission–fusion society. Mol Ecol 17:2666–2679
Armbruster P, Lande R (1993) A population viability analysis for African elephant (Loxodonta africana): how big should reserves be? Conserv Biol 7:602–610
Borriello F, Krauter KS (1990) Reactive site polymorphism in the murine protease inhibitor gene family is delineated using a modification of the PCR reaction. Nucleic Acids Res 18:5481–5487
Brown JL, Eklund A (1994) Kin recognition and the major histocompatibility complex: an integrative review. Am Nat 143:435–461
Caughley G, Dublin HT, Parker ISC (1990) Projected decline of the African elephant. Biol Conserv 54:157–164
Cheetham SA, Thom MD, Jury F, Ollier WER, Beynon RJ, Hurst JL (2007) The genetic basis of individual-recognition signals in the mouse. Curr Biol 17:1771–1777
Cutrera AP, Lacey EA (2006) Major histocompatibility complex variation in talas tuco-tucos: the influence of demography on selection. J Mammal 87:706–716
Decker DJ, Stewart BS, Lehman N (2002) Major histocompatibility complex class II DOA sequences from three Antarctic seal species verify stabilizing selection on the DO locus. Tissue Antigens 60:534–538
Garrigan D, Hedrick PW (2003) Perspective: detecting adaptive molecular polymorphism: lessons from the MHC. Evolution 57:1707–1722
Gaudier S, Dawkins RL, Habara K, Kulski JK, Gojobori T (2000) SNP profile within the human major histocompatibility complex reveals and extreme and interrupted level of nucleotide diversity. Genome Res 10:1579–1586
Geluk A, Elferink DG, Slierendregt BL, Vanmeijgaarden KE, de Vries RRP, Ottenhoff THM, Bontrop RE (1993) Evolutionary conservation of major histocompatibility complex-DR/peptide/T cell interactions in primates. J Exp Med 177:979–987
Grobler DG, Raath JP, Braak LE, Keet DF, Gerdes GH, Barnard BJ, Kriek NP, Jardine J, Swanepoel R (1995) An outbreak of encephalomyocarditis-virus infection in free-ranging African elephants in the Kruger National Park. Onderstepoort J Vet Res 62:97–108
Harrigan RJ, Mazza ME (2008) Computation vs. cloning: evaluation of two methods for haplotype determination. Mol Ecol Resour 8:1239–1248
Hollister-Smith JA, Poole JH, Archie EA, Vance EA, Georgiadis NJ, Moss CJ, Alberts SC (2007) Age, musth and paternity in wild male African elephants, Loxodonta africana. Anim Behav 74:287–296
Hughes AL (1999) Adaptive evolution of genes and genomes. Oxford University Press, New York
Hughes AL, Nei M (1989) Nucleotide substitution at major histocompatibility complex class II loci evidence for overdominant selection. Proc Natl Acad Sci 86:958–962
Hughes AL, Yeager M (1998) Natural selection at major histocompatibility complex loci of vertebrates. Annu Rev Genet 32:415–435
Klein J (1980) Generation of diversity at MHC loci: implications for T-cell receptor repertoires. In: Fougereau M, Dausset J (eds) Immunology 80. Academic, London, pp 239–235
Klein J (1986) Natural history of the major histocompatibility complex, 1st edn. Wiley, New York
Krause J, Dear PH, Pollack JL, Slatkin M, Spriggs H, Barnes I, Lister AM, Ebersberger I, Paabo S, Hofreiter M (2006) Multiplex amplification of the mammoth mitochondrial genome and the evolution of elephantidae. Nature 439:724–727
Kriegs JO, Churakov G, Kiefmann M, Jordan U, Brosius J, Schmitz J (2006) Retroposed elements as archives for the evolutionary history of placental mammals. PLoS Biol 4(4):e91
Kumar S, Tamura K, Jakobsen IB, Nei M (2001) MEGA2: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis software. Bioinformatics 17:1244–1245
L’Abbe D, Belmaaza A, Decary F, Chartrand P (1992) Elimination of heteroduplex artifacts when sequencing HLA genes amplified by polymerase chain reaction. Immunogenetics 35:395–397
Lehman N, Decker DJ, Stewart BS (2004) Divergent patterns of variation in major histocompatibility complex class II alleles among Antarctic phocid pinnipeds. J Mammal 85:1215–1224
Lindique PM, Turnbull PCB (1994) Ecology and epidemiology of anthrax in the Etosha National Park, Namibia. Onderstepoort J Vet Res 61:71–83
Manning CJ, Wakeland EK, Potts WK (1992) Communal nesting patterns in mice implicate MHC genes in kin recognition. Nature 360:581–583
Mbise AN, Mlengeya TDK, Mollel JO (1998) Septicaemic salmonellosis of elephants in Tanzania. Bull Anim Health Prod Afr 46:95–100
Meyer-Lucht Y, Sommer S (2005) MHC diversity and the association to nematode parasitism in the yellow-necked mouse (Apodemus flavicollis). Mol Ecol 14:2233–2243
Murphy WJ, Eizrik E, O’Brien SJ, Madsen O, Scally M, Douady CJ, Teeling E, Ryder OA, Stanhope MJ, de Jong WW, Springer MS (2001) Resolution of the early placental mammal radiation using Bayesian phylogenetics. Science 294:2348–2351
Naruse TK, Kawata H, Anzai T, Takashige N, Kagiya M, Nose Y, Nabeya N, Isshiki G, Tatsumi N, Inoko H (1999) Limited polymorphism in the HLA-DOA gene. Tissue Antigens 53:359–365
Nei M, Gojobori T (1986) Simple methods for estimating the numbers of synonymous and nonsynonymous nucleotide substitutions. Mol Biol Evol 3:418–426
Nei M, Kumar S (2000) Molecular evolution and phylogenetics. Oxford University Press, New York
Paterson S, Wilson K, Pemberton JM (1998) Major histocompatibility complex variation associated with juvenile survival and parasite resistance in a large unmanaged ungulate population (Ovis aries L.). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 95:3714–3719
Penn DJ, Damjanovich K, Potts WK (2002) MHC heterozygosity confers a selective advantage against multiple-strain infections. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 99:11260–11264
Piertney SB, Olivier MK (2006) The evolutionary ecology of the major histocompatibility complex. Heredity 96:7–21
Posada D, Crandall KA (1998) MODEL TEST: testing the model of DNA substitution. Bioinformatics 14:817–818
Rajakaruna RS, Brown A, Kaukinen KH, Miller KM (2006) Major histocompatibility complex and kin discrimination in Atlantic salmon and brook trout. Mol Ecol 15:4569–4575
Reche PA, Reinherz EL (2003) Sequence variability analysis of human class I and class II molecules: functional and structural correlates of amino acid polymorphisms. J Mol Biol 331:623–641
Richman LK, Montali RJ, Garber RL, Kennedy MA, Lehnhardt J, Hildebrandt T, Schmitt D, Hardy D, Alcendor DJ, Hayward GS (1999) Novel endotheliotropic herpesviruses fatal for Asian and African elephants. Science 283:1171–1176
Richman LK, Montali RJ, Hayward GS (2000) Review of a newly recognized disease of elephants caused by endotheliotropic herpesviruses. Zoo Biol 19:383–392
Rozen S, Skaletsky HJ (2000) Primer3 on the WWW for general users and for biologist programmers. In: Krawetz S, Misener S (eds) Bioinformatics methods and protocols: methods in molecular biology. Humana Press, Totowa, NJ, pp 365–386 Source code available at http://fokker.wi.mit.edu/primer3/.
Ryan SJ, Thompson SD (2001) Disease risk and inter-institutional transfer of specimens in cooperative breeding programs: herpes and the elephant species survival plan. Zoo Biol 20:89–101
Scally M, Madsen O, Douady CJ, de Jong WW, Stanhope MJ (2001) Molecular evidence for the major clades of placental mammals. J Mamm Evol 8:239–277
Slade RW, Moritz C, Heideman A, Hale PT (1993) Rapid assessment of single-copy nuclear DNA variation in diverse species. Mol Ecol 2:359–373
Swofford DL (2002) Phylogenetic analysis using parsimony (*and other methods). Sinauer, Sunderland
Takahata N, Nei M (1990) Allelic genealogy under overdominant and frequency-dependent selection and polymorphism at the major histocompatibility complex loci. Genetics 124:967–978
Waddell PJ, Shelley S (2003) Evaluating placental inter-ordinal phylogenies with novel sequences including RAG1, [gamma]-fibrinogen, ND6, and mt-tRNA, plus MCMC-driven nucleotide, amino acid, and codon models. Mol Phylogenet Evol 28:197–224
Weber DS, Brent SS, Schienman J, Lehman N (2004) Major histocompatibility complex variation at three class II loci in the northern elephant seal. Mol Ecol 13:711–718
Westerdahl H, Walenstrom J, Hansson B, Hasselquist D, von Schantz T, and Bensch S (2005) Associations between malaria and MHC genes in a migratory songbird. Proceedings of the Royal Society of London 272:1511–1518
Zelano B, Edwards SV (2002) An MHC component to kin recognition and mate choice in birds: predictions, progress, and prospects. Am Nat 160:S225–S237
Acknowledgments
We thank the Office of the President of Kenya for permission to work in Amboseli National Park under permit number MOES&T 13/001/30C 72/7. We thank the Kenya Wildlife Service for local sponsorship. We thank the Amboseli Elephant Research project for invaluable scientific and logistical support, particularly the team of N. Njiraini, K. Sayialel, and S. Sayialel who contributed greatly to the collection of genetic samples. We thank the Smithsonian National Zoo, the Philadelphia Zoo in Philadelphia, PA, the Gladys Porter Zoo in Brownsville, TX, and the Six Flags Wild Safari Park in Jackson, NJ for their support and cooperation in sample collection. This research was supported by the Smithsonian Institution Abbott Endowment Fund, the National Zoo’s Institution Center for Conservation and Evolutionary Genetics, the Friends of the National Zoo, the National Science Foundation (IBN0091612 to SCA), the Amboseli Trust for Elephants, the Amboseli Elephant Research Project, and Duke University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Archie, E.A., Henry, T., Maldonado, J.E. et al. Major histocompatibility complex variation and evolution at a single, expressed DQA locus in two genera of elephants. Immunogenetics 62, 85–100 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00251-009-0413-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00251-009-0413-8