Abstract
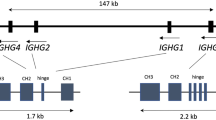
Eleven genomic porcine Cγ gene sequences are described that represent six putative subclasses that appear to have originated by gene duplication and exon shuffle. The genes previously described as encoding porcine IgG1 and IgG3 were shown to be the IgG1a and IgG1b allelic variants of the IGHG1 gene, IgG2a and IgG2b are allelic variants of the IGHG2 gene, while “new” IgG3 is monomorphic, has an extended hinge, is structurally unique, and appears to encode the most evolutionarily conserved porcine IgG. IgG5b differs most from its putative allele, and its CH1 domain shares sequence homology with the CH1 of IgG3. Four animals were identified that lacked either IgG4 or IgG6. Alternative splice variants were also recovered, some lacking the CH1 domain and potentially encoding heavy chain only antibodies. Potentially, swine can transcribe >20 different Cγ chains. A comparison of mammalian Cγ gene sequences revealed that IgG diversified into subclasses after speciation. Thus, the effector functions for the IgG subclasses of each species should not be extrapolated from “same name subclasses” in other species. Sequence analysis identified motifs likely to interact with Fcγ receptors, FcRn, protein A, protein G, and C1q. These revealed IgG3 to be most likely to activate complement and bind FcγRs. All except IgG5a and IgG6a should bind to FcγRs, while all except IgG6a and the putative IgG5 subclass proteins should bind well to porcine FcRn, protein A, and protein G.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Auchincloss H Jr, Sachs DH (1998) Xenogeneic transplantation. Annu Rev Immunol 16:433–470
Bianchi ATJ, Schotten JW, Jongenelen IMCA, Koch G (1990) The use of monoclonal antibodies in an enzyme immunospot assay to detect isotype-specific antibody secreting cells in pigs and chickens. Vet Immunol Immunopathol 24:125–134
Birshstein BK, Campbell R, Greenberg ML (1980) A γ2b–γ2a hybrid immunoglobulin heavy chain produced by a variant of the MPC11 mouse myeloma cell line. Biochem 19:1730–1737
Brambell FWR (1971) The transmission of passive immunity from mother to young. Frontiers of Biology Series. North Holland, Amsterdam
Brown WR, Kacskovics I, Amendt B, Shinde R, Blackmore N, Rothschild M, Butler JE (1995) The hinge deletion variant of porcine IgA results from a mutation at the splice acceptor site in the first Cα intron. J Immunol 154:3836–3842
Burnett RC, Hanly WC, Zhai S-K, Knight KL (1989) The IgA heavy chain gene family in rabbit: cloning and sequence analyses of 13 Cα genes. EMBO J 8:4041–4047
Burton DR, Boyd J, Brampton AD, Easterbrook-Smith SB, Emanuel J, Novotny EJ, Rademacher TW, van Schravendijk MR, Sternberg MJ, Dwek RA (1980) The Clq receptor site on immunoglobulin G. Nature 288:338–344
Butler JE (1969) Bovine immunoglobulins. J Dairy Sci 52:1895–1909
Butler JE (1974) Immunoglobulins of the mammary secretions. In: Larson BL, Smith V (eds) Lactation, a comprehensive treatise. Academic Press, New York Vol. III, Chapter V:217–55
Butler JE (1983) Bovine immunoglobulins: An augmented review. Vet Immunol Immunopathol 4:43–152
Butler JE (1997) Immunoglobulin gene organization and the mechanism of repertoire development. Scand J Immunol 45:455–462
Butler JE (2006) Preface: Why I agreed to do this. In: Butler JE, guest ed. Antibody repertoire development. Dev Comp Immunol 30:1–17
Butler JE, Wertz N (2006) Antibody repertoire development in fetal and neonatal pigs. XVII. IgG subclass transcription in newborns revisited with emphasis on new IgG3. J Immunol 177:5480–5489
Butler JE, Sun J, Weber P, Francis D (2000) Antibody repertoire development in fetal and neonatal piglets. III. Colonization of the gastrointestinal tracts results in preferential diversification of the pre-immune mucosal B-cell repertoire. Immunol Br 100:119–130
Butler JE, Sun J, Weber P, Ford SP, Rehakova Z, Sinkora J, Lager KM (2001) Antibody repertoire development in fetal and neonatal piglets. IV. Switch recombination, primary in fetal thymus occurs independent of environmental antigen and is only weakly associated with repertoire diversification. J Immunol 167:3239–3249
Butler JE, Weber P, Sinkora M, Baker D, Schoenherr A, Mayer B, Francis D (2002) Antibody repertoire development in fetal and neonatal piglets. VIII. Colonization is required for newborn piglets to make serum antibodies to T-dependent and type 2 T-independent antigens. J Immunol 169:6822–6830
Butler JE, Francis D, Freeling J, Weber P, Sun J, Krieg AM (2005) Antibody repertoire development in fetal and neonatal piglets. IX. Three PAMPs act synergistically to allow germfree piglets to respond to TI-2 and TD antigens. J Immunol 175:6772–6785
Butler JE, Lemke CD, Weber P, Sinkora M, Lager KM (2007) Antibody repertoire development in fetal and neonatal piglets. XIX. Undiversified B cells with hydrophobic HCDR3s preferentially proliferate in PRRS. J Immunol 178:6320–6331
Butler JE, Weber P, Wertz N, Lager KM (2008a) Porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus (PRRSV) subverts development of adaptive immunity by proliferation of germline-encoded B cells with hydrophobic HCDR3s. J Immunol 180:2347–2356
Butler JE, Lager KM, Splichal I, Francis D, Kacskovics I, Sinkora M, Wertz N, Sun J, Zhao Y, Brown WR, DeWald R, Dierks S, Muyldermanns S, Lunney JK, McCray PB, Rogers CS, Welsh MJ, Navarro P, Klobasa F, Habe F, Ramsoondar J (2008b) The piglet as a model for B cell and immune system development. Vet Immunol Immunopathol (in press).
Clark MR (1997) IgG effector mechanisms. Chem Immunol 65:88–110
Colle JH, Perret R, Truffa-Bachi P (1987) Hybrid polypeptide heavy chains produced by two hybridoma lines. Mol Immunol 24:39–46
Crawley A, Wilkie BN (2003) Porcine Ig isotypes: function and molecular characteristics. Vaccine 21:2911–2922
Dall’Acqua WF, Cook KE, Damschroder MD, Woos RM, Wu H (2006) Modulation of the effector functions of a human IgG1 through engineering of its hinge. J Immunol 177:1129–1138
Deisenhofer J (1981) Crystallographic refinement and atomic models of a human Fc fragment and its complex with fragment B of protein A from Staphylococcus aureus at 2.9- and 2.8-A resolution. Biochem 20:2361–2370
Duncan AR, Winter G (1988) The binding site for C1q on IgG. Nature 332:738–740
Emanuel EJ, Brampton AD, Burton DR, Dwek RA (1982) Formation of complement subcomponent C1q–immunoglobulin G complex. Thermodynamic and chemical-modification studies. Biochem J 205:361–372
Franek F, Riha I (1964) Purification and structural characterization of 5 S γ-globulin of newborn pigs. Immunochemistry 1:49–63
Franklin EC, Lowenstein J, Bigelow B, Meltzer M (1964) Heavy chain disease—a new disorder of serum γ-globulins. Am J Med 37:332–350
Gaboriaud C, Juanhuix J, Gruez A, Lacroix M, Darnault C, Pignol D, Verger D, Fontecilla-Camps JC, Arlaud GJ (2003) The crystal structure of the globular head of complement protein C1q provides a basis for its versatile recognition properties. J Biol Chem 278:46974–46982
Grey HM, Abel CA, Jount WJ, Kunkel HG (1968) A subclass of human γA-globulins (γA2) which lacks the disulfide bonds linking heavy and light chains. J Exp Med 128:1223–1236
Hamers-Castermann C, Atarhouch T, Muyldermans S, Robinson G, Hamers C, Songa EB, Bendahman N, Hamers R (1993) Naturally occurring antibodies devoid of light chains. Nature 363:446–448
Hunkapillar T, Hood L (1989) Diversity of the immunoglobulin gene superfamily. Adv Immunol 44:1–63
Idusogie EE, Presta LG, Gazzano-Santoro H, Totpal K, Wong PY, Ultsch M, Meng YG, Mulkerrin MG (2000) Mapping of the C1q binding site on rituxan, a chimeric antibody with a human IgG1 Fc. J Immunol 164:4178–4184
Janeway CA Jr, Travers P, Walport M, Shlomchik MJ (2005) Immunobiology Garland Press, N.Y. 823 pp
Kacskovics I, Sun J, Butler JE (1994) Five subclasses of swine IgG identified from the cDNA sequences of a single animal. J Immunol 153:3566–3573
Kacskovics I, Mayer B, Kis Z, Frenyo LV, Zhao Y, Muyldermans S, Hammarstrom L (2006) Cloning and characterization of the dromedary (Camelus dromedarius) neonatal Fc receptor (drFcRn). Dev Comp Immunol 30:1203–1215
Kaltreider HB, Johnson JS (1972) Porcine immunoglobulins. I. Identification of subclasses and preparation of specific antisera. J Immunol 109:992–998
Kehoe JM, Capra JD (1974) Nature and significance of immunoglobulin subclasses. N Y State J Med 74:489–491
Kilian M, Russell MW (2004) Microbial evasion of IgA function. In: Mestecky J, Lamm ME, Strober W, Bienenstock J, McGhee JR, Mayer L (eds) Mucosal immunology. Elsevier/Academic, Amsterdam, pp 291–303
Kunkel HG, Natvig JB, Jostin FG (1969) A “lepore” type of hybrid γ globulin. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 62:144–149
Lefranc M-P, Lefranc G (2001) The immunoglobulin facts book. Academic, NY
Lefranc M-P, Lefranc G, Rabbitts TH (1982) Inherited deletion of immunoglobulin heavy chain constant region genes in normal individuals. Nature 300:760–762
Lemke CD, Haynes JS, Spaete R, Adolphson D, Vorwald A, Lager KM, Butler JE (2004) Lymphoid hyperplasia resulting in immune dysregulation is caused by PRRSV infection in pigs. J Immunol 172:1916–1925
Lopez-Carvalho T, Foote J, Kearney JF (2005) Marginal zone B cells in lymphocyte activation and regulation. Curr Opin Immunol 17:244–250
Marquart M, Deisenhofer J (1982) The three-dimensional structure of antibodies. Immunol Today 3:160–166
Martin WL, West AP Jr, Gan L, Bjorkman PJ (2001) Crystal structure at 2.8 A of an FcRn/heterodimeric Fc complex: mechanism of pH-dependent binding. Mol Cell 7:867–877
McAleer J, Weber P, Sun J, Butler JE (2005) Antibody repertoire development in fetal and neonatal piglets. XI. The thymic B cell repertoire develops independently from that in blood and mesenteric lymph nodes. Immunology 114:171–183
McCall MN, Easterbrook-Smith SB (1989) Comparison of the role of tyrosine residues in human IgG and rabbit IgG in binding of complement subcomponent C1q. Biochem J 257:845–851
Mendicino M, Ramsoondar J, Phelps C, Vaught T, Ball S, Dai Y, LeRoith T, Monahan J, Chen S, Dandro A, Boone J, Jobst P, Vance A, Wertz N, Polejaeva I, Butler J, Ayares D, Wells K (2009) Targeted disruption of the porcine immunoglobulin heavy chain locus produces a B cell null phenotype. Nature Biotechnology (pending)
Mestecky J, Moro I, Kerr MA, Woof JM (2004) Mucosal immunoglobulins. In: Mestecky J, Lamm ME, Strober W, Bienenstock J, McGhee JR, Mayers L (eds) Mucosal immunology. Elsevier/Academic, Burlington, MA, pp 153–181
Metzger JJ, Fougereau M (1967) Characterization of two subclasses of γG immunoglobulin in swine. CR Hebd Seances Acad Sci Ser P Sci Nat 265:724–727
Migone N, Oliviero S, de Lange G, Delacroix DL, Boschis D, Altruda F, Silengo L, DeMarchi M, Carbonara AO (1984) Multiple gene deletions within the human immunoglobulin heavy chain cluster. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 81:5811–5815
Mihaesco E, Gendron M-C, Congy N, Frangione B (1988) Protein ROU, a human IgA hybrid. J Immunol 140:1236–1238
Navarro P, Christenson R, Ekhardt G, Lunney JK, Rothschild M, Bosworth B, Lemke J, Butler JE (2000a) Genetic differences in the frequency of the hinge variants of porcine IgA is breed dependent. Vet Immunol Immunopathol 73:287–295
Navarro P, Christenson R, Weber P, Rothschild M, Erhardt G, Lemky J, Butler JE (2000b) Porcine IgA allotypes are not equally transcribed or expressed in heterozygous swine. Mol Immunol 37:653–664
Nezlin R (1994) Immunoglobulin structure and function. In: van Oss CJ, van Regenmortel MHV (eds) Immunochemistry. Marcel Dekker, New York, pp 3–45
Nezlin R, Ghetie V (2004) Interactions of immunoglobulins outside the antigen-binding site. Adv Immunol 82:155–215
Olsson PG, Rabbani H, Hammarstrom L, Smith CIE (1993) Novel human immunoglobulin heavy chain constant region gene deletion haplotypes characterized by pulse-filed electrophoresis. Clin Exp Immunol 94:84–90
Osserman EF, Takatsuki K (1964) Clinical and immunochemical studies of four cases of heavy (Hγ2) chain disease. Am J Med 37:351–373
Pan Q, Hammarstrom L (2000) Molecular basis of IgG subclass deficiency. Immunol Rev 178:99–110
Plaut AG, Gilbert JV, Artenstern MA, Capra JD (1975) Neisseria gonorrhoeae and Neisseria meningitidis: extracellular enzyme cleaves human immunoglobulin A. Science 193:1103–1105
Rabbani H, Brown WR, Butler JE, Hammarström L (1997) Polymorphism of the IgHG3 gene in cattle. Immunogenetic 46:326–331
Radaev S, Sun PD (2001) Recognition of IgG by Fcgamma receptor. The role of Fc glycosylation and the binding of peptide inhibitors. J Biol Chem 276:16478–16483
Radaev S, Motyka S, Fridman WH, Sautes-Fridman C, Sun PD (2001) The structure of a human type III Fc gamma receptor in complex with Fc. J Biol Chem 276:16469–16477
Rapacz J, Hasler-Rapacz J (1982) Immunogenetic studies on polymorphism, postnatal passive acquisition and development of immunoglobulin gamma (IgG) in swine. In: Proc 2nd Int. Congress Gen and Appl Livestock Production. Vol III. Editoral Garsi, Madrid
Ratcliffe MJH (2006) Antibodies, immunoglobulin genes and the bursa of Fabricius in chicken B cell development. Dev Comp Immunol 30:101–118
Ravetch JV, Kinet J-P (1991) Fc receptors. Annu Rev Immunol 9:457–492
Rogers CS, Stoltz DA, Meyerholz DK, Ostedgaards LS, Rokhlina T, Taft PJ, Rogan MP, Pezuzulo AA, Karp PH, Itani OA, Kabel AC, Wohlford-Lenane CL, Davis GJ, Hanfland RA, Smith TL, Samuel M, Wax D, Murphy CN, Rieke A, Whitworth K, Uc A, Starner TD, Brogden KA, Shilyansky J, McCray PB Jr, Zabner J, Prather RS, Welsh MJ (2008) Disruption of the CFTR gene produces a model of cystic fibrosis in newborn pigs. Science 321:1837–1841
Roopenian DC, Akilesh S (2007) FcRn: the neonatal Fc receptor comes of age. Nat Rev Immunol 7:715–725
Sauer-Eriksson AE, Kleywegt GJ, Uhlen M, Jones TA (1995) Crustal structure of the C2 fragment of streptococcal protein G in complex with the Fc domain of human IgG. Structure 3:265–278
Sinkora M, Sun J, Butler JE (2000) Antibody repertoire development in fetal and neonatal piglets. V. VDJ gene chimeras resembling gene conversion products are generated at high frequency by PCR in vitro. Mol Immunol 37:1025–1034
Spieker-Polet H, Yam P-C, Knight KL (1993) Differential expression of 13 IgA heavy chain genes in rabbit lymphoid tissues. J Immunol 150:5457–5465
Sun J, Butler JE (1996) Molecular characteristics of VDJ transcripts from a newborn piglet. Immunol Br 88:331–339
Sun J, Hayward C, Shinde R, Christenson R, Ford SP, Butler JE (1998) Antibody repertoire development in fetal and neonatal piglets. I. Four VH genes account for 80% of VH usage during 84 days of fetal life. J Immunol 161:5070–5078
Tamura K, Dudley J, Nei M, Kumar S (2007) MEGA4: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis (MEGA) Software Version 4.0. Mol Biol Evol
Terada T, Kneko H, Li AL, Kasahara K, Ibe M, Yokota S, Kondo N (2001) Analysis of Ig subclass deficiency: first reported case of IgG2, IgG4 and IgA deficiency caused by deletion of C alpha1, PSI C gamma, C gamma 2, C gamma 4 and C epsilon in a Mongoloid patient. J Allergy Clin Immunol 108:602–606
Vincent AL, Lager KM, Ma W, Lekcharoensuk P, Gramer MR, Loiacona C, Richt JA (2006) Evaluation of hemagglutinin subtypes 1 swine influenza viruses from the United States. Vet Microbiol 118:212–222
Waltz E (2006) Polyclonal antibodies step out of the shadow. Nat Biotechnol 24:1181
Williams AF (1987) A year in the life of the immunoglobulin superfamily. Immunol Today 8:298–303
Zhao Y, Pan-Hammarstrom Q, Kacskovics I, Hammarstrom L (2003) The porcine Ig δ gene: Unique chimeric splicing of the first constant region domain in its heavy chain transcripts. J Immunol 171:1312–1318
Zhao Y, Pan-Hammarstrom Q, Yu S, Wertz N, Zhang X, Li N, Butler JE, Hammarstrom L (2006) Identification of IgF, a hinge-region containing Ig class and IgD in Xenopus tropicalis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103:12087–12092
Acknowledgements
This research supported by Cooperative Agreement IOWR 2003-02669 with the USDA-ARS, The University of Iowa Carver Trust and Grants 05-015 and 06-043 from the National Porkboard and grant OTKA T049015 from the Hungarian Academy of Sciences.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
An erratum to this article can be found at http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s00251-009-0356-0
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Butler, J.E., Wertz, N., Deschacht, N. et al. Porcine IgG: structure, genetics, and evolution. Immunogenetics 61, 209–230 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00251-008-0336-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00251-008-0336-9