Abstract
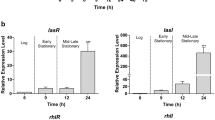
Pseudomonas aeruginosa can regulate its virulence gene expressions by using a signal system called quorum sensing. It is known that inhibition of quorum sensing can block biofilm formation and leave the bacteria defenseless. Therefore, it is necessary to determine natural sources to obtain potential quorum sensing inhibitors. This study aims to investigate an alternative treatment approach by utilizing the carotenoid zeaxanthin to reduce the expressions of P. aeruginosa virulence factors through quorum sensing inhibition. The inhibition potential of zeaxanthin was determined by in silico screening from a library of 638 lichen metabolites. Fluorescent monitor strains were utilized for quorum sensing inhibitor screens, and quantitative reverse-transcriptase PCR assay was performed for evaluating gene expression. Results indicate that zeaxanthin is a better inhibitor than the lichen secondary metabolite evernic acid, which was previously shown to be capable of inhibiting P. aeruginosa quorum sensing systems.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jones RN, Stilwell MG, Rhomberg PR, Sader HS (2009) Antipseudomonal activity of piperacillin/tazobactam: more than a decade of experience from the SENTRY Antimicrobial Surveillance Program (1997-2007). Diagn Micr Infec Dis 65:331–334. doi:10.1016/j.diagmicrobio.2009.06.022
Lambert ML, Suetens C, Savey A, Palomar M, Hiesmayr M, Morales I, Agodi A, Frank U, Mertens K, Schumacher M, Wolkewitz M (2011) Clinical outcomes of health-care-associated infections and antimicrobial resistance in patients admitted to European intensive-care units: a cohort study. Lancet Infect. Dis. 11:30–38. doi:10.1016/S1473-3099(10)70258-9
Zhanel GG, Hoban DJ, Schurek K, Karlowsky JA (2004) Role of efflux mechanisms on fluoroquinolone resistance in Streptococcus pneumoniae and Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Int J Antimicrob Ag 24:529–535. doi:10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2004.08.003
Ciofu O, Tolker-Nielsen T, Jensen PO, Wang H, Hoiby N (2015) Antimicrobial resistance, respiratory tract infections and role of biofilms in lung infections in cystic fibrosis patients. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 85:7–23. doi:10.1016/j.addr.2014.11.017
Brackman G, Coenye T (2015) Quorum sensing inhibitors as anti-biofilm agents. Curr Pharm Design 21:5–11
Jakobsen TH, Bjarnsholt T, Jensen PO, Givskov M, Hoiby N (2013) Targeting quorum sensing in Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilms: current and emerging inhibitors. Future Microbiol 8:901–921. doi:10.2217/fmb.13.57
Girard G, Bloemberg GV (2008) Central role of quorum sensing in regulating the production of pathogenicity factors in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Future Microbiol 3:97–106. doi:10.2217/17460913.3.1.97
Diggle SP, Winzer K, Chhabra SR, Chhabra SR, Worrall KE, Camara M, Williams P (2003) The Pseudomonas aeruginosa quinolone signal molecule overcomes the cell density-dependency of the quorum sensing hierarchy, regulates rhl-dependent genes at the onset of stationary phase and can be produced in the absence of LasR. Mol. Microbiol. 50:29–43. doi:10.1046/j.1365-2958.2003.03672.x
McGrath S, Wade DS, Pesci EC (2004) Dueling quorum sensing systems in Pseudomonas aeruginosa control the production of the Pseudomonas quinolone signal (PQS). FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 230:27–34. doi:10.1016/S0378-1097(03)00849-8
Lee J, Wu J, Deng Y, Wang J, Wang C, Wang J, Chang C, Dong Y, Williams P, Zhang LH (2013) A cell-cell communication signal integrates quorum sensing and stress response. Nat. Chem. Biol. 9:339–343. doi:10.1038/nchembio.1225
Hentzer M, Eberl L, Nielsen J, Givskov M (2003) Quorum sensing—a novel target for the treatment of biofilm infections. BioDrugs 17:241–250. doi:10.2165/00063030-200317040-00003
Zeng Z, Qian L, Cao L, Tan H, Huang Y, Xue X, Shen Y, Zhou S (2008) Virtual screening for novel quorum sensing inhibitors to eradicate biofilm formation of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Appl Microbiol Biot 79:119–126. doi:10.1007/s00253-008-1406-5
Pompilio A, Pomponio S, Di Vincenzo V, Crocetta V, Nicoletti M, Piovano M, Garbarino JA, Di Bonaventura G (2013) Antimicrobial and antibiofilm activity of secondary metabolites of lichens against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus strains from cystic fibrosis patients. Future Microbiol 8:281–292. doi:10.2217/Fmb.12.142
Lal B, Upreti DK (1995) Ethnobotanical notes on three Indian lichens. Lichenologist 27:77–79. doi:10.1006/lich.1995.0006
Malhotra S, Subban R, Singh A (2008) Lichens—role in traditional medicine and drug discovery. The Internet Journal of Alternative Medicine 5:151–170
Štepigová J, Vráblíková H, Lang J, Večeřová K, Barták M (2007) Glutathione and zeaxanthin formation during high light stress in foliose lichens. Plant Soil Environ. 53:340–344
Sajilata M, Singhal R, Kamat M (2008) The carotenoid pigment zeaxanthin—a review. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 7:29–49
Kim S, Thiessen PA, Bolton EE, Chen J, Fu G, Gindulyte A, Han L, He J, He S, Shoemaker BA, Wang J, Yu B, Zhang J, Bryant SH (2016) PubChem substance and compound databases. Nucleic Acids Res. 44:D1202–D1213. doi:10.1093/nar/gkv951
Irwin JJ, Sterling T, Mysinger MM, Bolstad ES, Coleman RG (2012) ZINC: a free tool to discover chemistry for biology. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 52:1757–1768. doi:10.1021/ci3001277
Annapoorani A, Umamageswaran V, Parameswari R, Pandian SK, Ravi AV (2012) Computational discovery of putative quorum sensing inhibitors against LasR and RhlR receptor proteins of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J. Comput. Aided Mol. Des. 26:1067–1077. doi:10.1007/s10822-012-9599-1
Gould TA, Schweizer HP, Churchill ME (2004) Structure of the Pseudomonas aeruginosa acyl-homoserinelactone synthase LasI. Mol. Microbiol. 53:1135–1146. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2958.2004.04211.x
Berman HM, Westbrook J, Feng Z, Gilliland G, Bhat TN, Weissig H, Shindyalov IN, Bourne PE (2000) The protein data bank. Nucleic Acids Res. 28:235–242
Thomsen R, Christensen MH (2006) MolDock: a new technique for high-accuracy molecular docking. J. Med. Chem. 49:3315–3321
Tateda K, Comte R, Pechere J-C, Köhler T, Yamaguchi K, Van Delden C (2001) Azithromycin inhibits quorum sensing in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Antimicrob Agents Ch 45:1930–1933
Holloway BW, Morgan AF (1986) Genome organization in Pseudomonas. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 40:79–105. doi:10.1146/annurev.micro.40.1.79
Hentzer M, Riedel K, Rasmussen TB, Heydorn A, Andersen JB, Parsek MR, Rice SA, Eberl L, Molin S, Hoiby N, Kjelleberg S, Givskov M (2002) Inhibition of quorum sensing in Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilm bacteria by a halogenated furanone compound. Microbiol-Sgm 148:87–102
Yang L, Rybtke MT, Jakobsen TH, Hentzer M, Bjarnsholt T, Givskov M, Tolker-Nielsen T (2009) Computer-aided identification of recognized drugs as Pseudomonas aeruginosa quorum-sensing inhibitors. Antimicrob Agents Ch 53:2432–2443. doi:10.1128/Aac.01283-08
Bjarnsholt T, van Gennip M, Jakobsen TH, Christensen LD, Jensen PO, Givskov M (2010) In vitro screens for quorum sensing inhibitors and in vivo confirmation of their effect. Nat. Protoc. 5:282–293. doi:10.1038/nprot.2009.205
De Kievit T (2009) Quorum sensing in Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilms. Environ. Microbiol. 11:279–288
Hentzer M, Wu H, Andersen JB, Riedel K, Rasmussen TB, Bagge N, Kumar N, Schembri MA, Song ZJ, Kristoffersen P, Manefield M, Costerton JW, Molin S, Eberl L, Steinberg P, Kjelleberg S, Hoiby N, Givskov M (2003) Attenuation of Pseudomonas aeruginosa virulence by quorum sensing inhibitors. EMBO J. 22:3803–3815. doi:10.1093/emboj/cdg366
Fux CA, Costerton JW, Stewart PS, Stoodley P (2005) Survival strategies of infectious biofilms. Trends Microbiol. 13:34–40. doi:10.1016/j.tim.2004.11.010
Al-Ani I, Zimmermann S, Reichling J, Wink M (2015) Pharmacological synergism of bee venom and melittin with antibiotics and plant secondary metabolites against multi-drug resistant microbial pathogens. Phytomedicine 22:245–255. doi:10.1016/j.phymed.2014.11.019
Azimi H, Khakshur AA, Aghdasi I, Fallah-Tafti M, Abdollahi M (2012) A review of animal and human studies for management of benign prostatic hyperplasia with natural products: perspective of new pharmacological agents. Inflamm Allergy Drug Targets 11:207–221
Savo V, Joy R, Caneva G, McClatchey WC (2015) Plant selection for ethnobotanical uses on the Amalfi Coast (Southern Italy). J. Ethnobiol. Ethnomed. 11:58. doi:10.1186/s13002-015-0038-y
Truchado P, Tomas-Barberan FA, Larrosa M, Allende A (2012) Food phytochemicals act as quorum sensing inhibitors reducing production and/or degrading autoinducers of Yersinia enterocolitica and Erwinia carotovora. Food Control 24:78–85. doi:10.1016/j.foodcont.2011.09.006
Gokalsin B, Sesal NC (2016) Lichen secondary metabolite evernic acid as potential quorum sensing inhibitor against Pseudomonas aeruginosa. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 32:150. doi:10.1007/s11274-016-2105-5
Jakobsen TH, van Gennip M, Phipps RK, Shanmugham MS, Christensen LD, Alhede M, Skindersoe ME, Rasmussen TB, Friedrich K, Uthe F, Jensen PO, Moser C, Nielsen KF, Eberl L, Larsen TO, Tanner D, Hoiby N, Bjarnsholt T, Givskov M (2012) Ajoene, a sulfur-rich molecule from garlic, inhibits genes controlled by quorum sensing. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 56:2314–2325. doi:10.1128/AAC.05919-11
Jakobsen TH, Bragason SK, Phipps RK, Christensen LD, van Gennip M, Alhede M, Skindersoe M, Larsen TO, Hoiby N, Bjarnsholt T, Givskov M (2012) Food as a source for quorum sensing inhibitors: iberin from horseradish revealed as a quorum sensing inhibitor of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Appl Environ Microb 78:2410–2421. doi:10.1128/Aem.05992-11
Rasmussen TB, Skindersoe ME, Bjarnsholt T, Phipps RK, Christensen KB, Jensen PO, Andersen JB, Koch B, Larsen TO, Hentzer M, Eberl L, Hoiby N, Givskov M (2005) Identity and effects of quorum-sensing inhibitors produced by Penicillium species. Microbiology 151:1325–1340. doi:10.1099/mic.0.27715-0
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by The Scientific and Technological Research Council of Turkey (TUBITAK) [113S306 COST FA1202]. We thank Tim Holm Jakobsen and Michael Givskov for providing the monitor strains.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Barış Gökalsın and Busecan Aksoydan contributed equally to this study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gökalsın, B., Aksoydan, B., Erman, B. et al. Reducing Virulence and Biofilm of Pseudomonas aeruginosa by Potential Quorum Sensing Inhibitor Carotenoid: Zeaxanthin. Microb Ecol 74, 466–473 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00248-017-0949-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00248-017-0949-3