Abstract
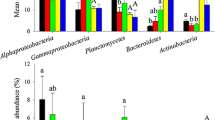
Intestinal bacterial communities play a pivotal role in promoting host health; therefore, the disruption of intestinal bacterial homeostasis could result in disease. However, the effect of the occurrences of disease on intestinal bacterial community assembly remains unclear. To address this gap, we compared the multifaceted ecological differences in maintaining intestinal bacterial community assembly between healthy and diseased shrimps. The neutral model analysis shows that the relative importance of neutral processes decreases when disease occurs. This pattern is further corroborated by the ecosphere null model, revealing that the bacterial community assembly of diseased samples is dominated by stochastic processes. In addition, the occurrence of shrimp disease reduces the complexity and cooperative activities of species-to-species interactions. The keystone taxa affiliated with Alphaproteobacteria and Actinobacteria in healthy shrimp gut shift to Gammaproteobacteria species in diseased shrimp. Changes in intestinal bacterial communities significantly alter biological functions in shrimp. Within a given metabolic pathway, the pattern of enrichment or decrease between healthy and deceased shrimp is correlated with its functional effects. We propose that stressed shrimp are more prone to invasion by alien strains (evidenced by more stochastic assembly and higher migration rate in diseased shrimp), which, in turn, disrupts the cooperative activity among resident species. These findings greatly aid our understanding of the underlying mechanisms that govern shrimp intestinal community assembly between health statuses.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
De Schryver P, Vadstein O (2014) Ecological theory as a foundation to control pathogenic invasion in aquaculture. ISME J 8:2360–2368
Xiong J, Wang K, Wu J, Qiuqian L, Yang K, Qian Y, Zhang D (2015) Changes in intestinal bacterial communities are closely associated with shrimp disease severity. Appl Microbiol Biotech 99:6911–6919
Wang CZ, Lin GR, Yan T, Zheng ZP, Chen B, Sun FL (2014) The cellular community in the intestine of the shrimp Penaeus penicillatus and its culture environments. Fisheries Sci 80:1001–1007
Stecher B, Chaffron S, Käppeli R, Hapfelmeier S, Freedrich S, Weber TC, Kirundi J, Suar M, McCoy KD, von Mering C (2010) Like will to like: abundances of closely related species can predict susceptibility to intestinal colonization by pathogenic and commensal bacteria. PLoS Pathog 6:e1000711
Thitamadee S, Prachumwat A, Srisala J, Jaroenlak P, Salachan PV, Sritunyalucksana K, Flegel TW, Itsathitphaisarn O (2016) Review of current disease threats for cultivated penaeid shrimp in Asia. Aquaculture 452:69–87
Rungrassamee W, Klanchui A, Maibunkaew S, Chaiyapechara S, Jiravanichpaisal P, Karoonuthaisiri N (2014) Characterization of intestinal bacteria in wild and domesticated adult black tiger shrimp (Penaeus monodon). PLoS One 9:e91853
Tzeng TD, Pao YY, Chen PC, Weng CH, Wen DJ, Wang D (2015) Effects of host phylogeny and habitats on gut microbiomes of oriental river prawn (Macrobrachium nipponense). Plos One 10:e0132860
Sullam KE, Essinger SD, Lozupone CA, O’Connor MP, Rosen GL, Knight R, Kilham SS, Russell JA (2012) Environmental and ecological factors that shape the gut bacterial communities of fish: a meta‐analysis. Mol Ecol 21:3363–3378
Schmidt VT, Smith KF, Melvin DW, Amaral‐Zettler LA (2015) Community assembly of a euryhaline fish microbiome during salinity acclimation. Mol Ecol 24:2537–2550
Giatsis C, Sipkema D, Smidt H, Verreth J, Verdegem M (2014) The colonization dynamics of the gut microbiota in tilapia larvae. PLoS One 9:e103641
Rungrassamee W, Klanchui A, Maibunkaew S, Karoonuthaisiri N (2016) Bacterial dynamics in intestines of the black tiger shrimp and the Pacific white shrimp during Vibrio harveyi exposure. J Invertebr Pathol 133:12–19
Silvertown J (2004) Plant coexistence and the niche. Trends Ecol Evol 19:605–611
Pérez T, Balcázar J, Ruiz-Zarzuela I, Halaihel N, Vendrell D, de Blas I, Múzquiz J (2010) Host-microbiota interactions within the fish intestinal ecosystem. Mucosal Immunol 3:355–360
Robinson CJ, Schloss P, Ramos Y, Raffa K, Handelsman J (2010) Robustness of the bacterial community in the cabbage white butterfly larval midgut. Microb Ecol 59:199–211
Li CC, Chen JC (2009) The immune response of white shrimp Litopenaeus vannamei and its susceptibility to Vibrio alginolyticus under low and high pH stress. Fish Shellfish Immun 25:701–709
Burns AR, Stephens WZ, Stagaman K, Wong S, Rawls JF, Guillemin K, Bohannan BJ (2016) Contribution of neutral processes to the assembly of gut microbial communities in the zebrafish over host development. ISME J 10:655–664
Yan Q, Li J, Yu Y, Wang J, He Z, Van Nostrand JD, Kempher ML, Wu L, Wang Y, Liao L, Li X, Wu S, Ni J, Wang C, Zhou J (2016) Environmental filtering decreases with fish development for the assembly of gut microbiota. Environ Microbiol. doi:10.1111/1462-2920.13365
Shade A, Peter H, Allison SD, Baho DL, Berga M, Bürgmann H, Huber DH, Langenheder S, Lennon JT, Martiny JB (2012) Fundamentals of microbial community resistance and resilience. Front Microbiol 3:417
Chase JM, Kraft NJ, Smith KG, Vellend M, Inouye BD (2011) Using null models to disentangle variation in community dissimilarity from variation in α-diversity. Ecosphere 2:art24
Xiong J, Chen H, Hu C, Ye X, Kong D, Zhang D (2015) Evidence of bacterioplankton community adaptation in response to long-term mariculture disturbance. Sci Rep 5:15274
Chase JM, Myers JA (2011) Disentangling the importance of ecological niches from stochastic processes across scales. Philos T R Soci B 366:2351–2363
Loudon AH, Venkataraman A, Vantreuren W, Woodhams D, Parfrey LW, Mckenzie V, Knight R, Schmidt T, Harris R (2016) Vertebrate hosts as islands: dynamics of selection, immigration, loss, persistence, and potential function of bacteria on Salamander skin. Front Microbiol 7:333
Vanwonterghem I, Jensen PD, Dennis PG, Hugenholtz P, Rabaey K, Tyson GW (2014) Deterministic processes guide long-term synchronised population dynamics in replicate anaerobic digesters. ISME J 8:2015–2018
Lepori F, Malmqvist B (2009) Deterministic control on community assembly peaks at intermediate levels of disturbance. Oikos 118:471–479
Xiong J, Dai W, Li C (2016) Advances, challenges, and directions in shrimp disease control: the guidelines from an ecological perspective. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 100:6947–6954
Fan L, Wang A, Miao Y, Liao S, Ye C, Lin Q (2016) Comparative proteomic identification of the hepatopancreas response to cold stress in white shrimp, Litopenaeus vannamei. Aquaculture 202:651–654
Allison SD, Martiny JB (2008) Resistance, resilience, and redundancy in microbial communities. Proc Nat Acad Sci USA 105:11512–11519
Mcfrederick QS, Mueller UG, James RR (2014) Interactions between fungi and bacteria influence microbial community structure in the Megachile rotundata larval gut. P Roy Soc B-Biol Sci 281:85–94
Faust K, Raes J (2012) Microbial interactions: from networks to models. Nat Rev Microbiol 10:538–550
Deng Y, Zhang P, Qin Y, Tu Q, Yang Y, He Z, Schadt CW, Zhou J (2016) Network succession reveals the importance of competition in response to emulsified vegetable oil amendment for uranium bioremediation. Environ Microbiol 18:205–218
Zhang P, Wu W-M, Van Nostrand JD, Deng Y, He Z, Gihring T, Zhang G, Schadt CW, Watson D, Jardine P (2015) Dynamic succession of groundwater functional microbial communities in response to emulsified vegetable oil amendment during sustained in situ U (VI) reduction. Appl Environ Microbiol 81:4164–4172
Caporaso JG, Bittinger K, Bushman FD, DeSantis TZ, Andersen GL, Knight R (2010) PyNAST: a flexible tool for aligning sequences to a template alignment. Bioinformatics 26:266–267
Langille MG, Zaneveld J, Caporaso JG, McDonald D, Knights D, Reyes JA, Clemente JC, Burkepile DE, Thurber RLV, Knight R (2013) Predictive functional profiling of microbial communities using 16S rRNA marker gene sequences. Nat Biotech 31:814–821
Clarke KR (1993) Non-parametric multivariate analyses of changes in community structure. Aust Ecol 18:117–143
Wu J, Xiong J, Hu C, Shi Y, Wang K, Zhang D (2015) Temperature sensitivity of soil bacterial community along contrasting warming gradient. Appl Soil Ecol 94:40–48
Xiong J, Fei P, Sun H, Xian X, Chu H (2014) Divergent responses of soil fungi functional groups to short-term warming. Microb Ecol 68:708–715
Sloan WT, Mary L, Stephen W, Head IM, Sean N, Curtis TP (2006) Quantifying the roles of immigration and chance in shaping prokaryote community structure. Environ Microbiol 8:732–740
Elzhov TV, Mullen KM, Spiess AN, Bolker B (2013) minpack.lm: R interface to the Levenberg-Marquardt nonlinear least-squares algorithm found in MINPACK, plus support for bounds. R package version 11-8 http://CRANR-project.org/package=minpacklm.
DasGupta A, Cai TT, Brown LD (2001) Interval estimation for a binomial proportion. Stat Sci 16:101–133
R Core Team (2012) R: a language and environment for statistical computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna. ISBN 3-900051-07-0
Östman Ö, Drakare S, Kritzberg ES, Langenheder S, Logue JB, Lindström ES (2010) Regional invariance among microbial communities. Ecol Lett 13:118–127
Sloan WT, Woodcock S, Lunn M, Head IM, Curtis TP (2007) Modeling taxa-abundance distributions in microbial communities using environmental sequence data. Microb Ecol 53:443–455
Kraft NJB, Comita LS, Chase JM, Sanders NJ, Swenson NG, Crist TO, Stegen JC, Mark V, Brad B, Anderson MJ (2011) Disentangling the drivers of β diversity along latitudinal and elevational gradients. Science 333:1755–1758
Zhou J, Deng Y, Zhang P, Xue K, Liang Y, Van Nostrand JD, Yang Y, He Z, Wu L, Stahl DA, Hazen TC, Tiedje JM, Arkin AP (2014) Stochasticity, succession, and environmental perturbations in a fluidic ecosystem. Proc Nat Acad Sci USA 111:836–845
Deng Y, Jiang Y, Yang Y, He Z, Luo F, Zhou J (2012) Molecular ecological network analyses. BMC Bioinformatics 13:113
Newman MEJ (2003) The structure and function of complex networks. SIAM Rev 45:167–256
Shannon P, Markiel A, Ozier O, Baliga NS, Wang J, Ramage D, Amin N, Schwikowski B, Ideker T (2003) Cytoscape: a software environment for integrated models of biomolecular interaction networks. Genome Res 13:2498–2504
McMurdie PJ, Holmes S (2014) Waste not, want not: why rarefying microbiome data is inadmissible. PLoS Comput Biol 14:e1003531
Williams RJ, Howe A, Hofmockel KS (2014) Demonstrating microbial co-occurrence pattern analyses within and between ecosystems. Front Microbiol 5:358
Montoya JM, Pimm SL, Solé RV (2006) Ecological networks and their fragility. Nature 442:259–264
Jiang L, Morin PJ (2004) Productivity gradients cause positive diversity-invasibility relationships in microbial communities. J Appl Psychol 7:1047–1057
De Roy K, Marzorati M, Negroni A, Thas O, Balloi A, Fava F, Verstraete W, Daffonchio D, Boon N (2013) Environmental conditions and community evenness determine the outcome of biological invasion. Nat Commun 4:1383
Bailey MT (2012) The contributing role of the intestinal microbiota in stressor-induced increases in susceptibility to enteric infection and systemic immunomodulation. Horm Behav 62:286–294
Sekirov I, Tam NM, Jogova M, Robertson ML, Li Y, Lupp C, Finlay BB (2008) Antibiotic-induced perturbations of the intestinal microbiota alter host susceptibility to enteric infection. Infect Immun 76:4726–4736
Ninawe A, Selvin J (2009) Probiotics in shrimp aquaculture: avenues and challenges. Crit Rev Microbiol 35:43–66
Mugnier C, Justou C, Lemonnier H, Patrois J, Ansquer D, Goarant C, Lecoz JR (2013) Biological, physiological, immunological and nutritional assessment of farm-reared Litopenaeus stylirostris shrimp affected or unaffected by vibriosis. Aquaculture 388–391:105–114
Scheuring I, Yu DW (2012) How to assemble a beneficial microbiome in three easy steps. Ecol Lett 15:1300–1307
Wen C, Xue M, Liang H, Zhou S (2014) Evaluating the potential of marine Bacteriovorax sp. DA5 as a biocontrol agent against vibriosis in Litopenaeus vannamei larvae. Vet Microbiol 173:84–91
Fuhrman JA (2009) Microbial community structure and its functional implications. Nature 459:193–199
Mahajan GB, Balachandran L (2012) Antibacterial agents from actinomycetes—a review. Front Biosci 4:240–253
Stecher B, Hardt WD (2011) Mechanisms controlling pathogen colonization of the gut. Curr Opin Microbiol 14:82–91
Moya A, Ferrer M (2016) Functional redundancy-induced stability of gut microbiota subjected to disturbance. Trends Microbiol 24:402–413
Knelman JE, Nemergut DR (2014) Changes in community assembly may shift the relationship between biodiversity and ecosystem function. Front Microbiol 5:424
Claud EC, Keegan KP, Brulc JM, Lu L, Bartels D, Glass E, Chang EB, Meyer F, Antonopoulos DA (2013) Bacterial community structure and functional contributions to emergence of health or necrotizing enterocolitis in preterm infants. Microbiome 1:20
Bell T, Newman JA, Silverman BW, Turner SL, Lilley AK (2005) The contribution of species richness and composition to bacterial services. Nature 436:1157–1160
Vigne JD, Lefèvre C, Patoumathis M (2013) Longitudinal analyses of gut mucosal microbiotas in ulcerative colitis in relation to patient age and disease severity and duration. J Clin Microbiol 51:849–856
Kline KA, Fälker S, Dahlberg S, Normark S, Henriques-Normark B (2009) Bacterial adhesins in host-microbe interactions. Cell Host Microbe 5:580–592
Settembre C, Fraldi A, Medina DL, Ballabio A (2013) Signals from the lysosome: a control centre for cellular clearance and energy metabolism. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 14:283–296
Guimera R, Sales-Pardo M, Amaral LA (2007) Classes of complex networks defined by role-to-role connectivity profiles. Nat Physcis 3:63–69
Newman ME (2006) Modularity and community structure in networks. Proc Nat Acad Sci USA 103:8577–8582
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Zhejiang Province Public Welfare Technology Application Research Project (2016C32063); the Spark Program of China (2015GA701024); the Open Fund of Key Laboratory of Marine Biogenetic Resources, Third Institute of Oceanography (HY201601); and the KC Wong Magna Fund of Ningbo University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhu, J., Dai, W., Qiu, Q. et al. Contrasting Ecological Processes and Functional Compositions Between Intestinal Bacterial Community in Healthy and Diseased Shrimp. Microb Ecol 72, 975–985 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00248-016-0831-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00248-016-0831-8