Abstract
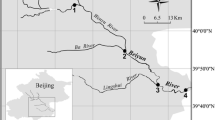
Natural occurring groundwater with abnormally high ammonium concentrations was discovered in the aquifer-aquitard system in the Pearl River Delta, South China. The community composition and abundance of aerobic/anaerobic ammonia/ammonium-oxidizing microorganisms (AOM) in the aquitard were investigated in this study. The alpha subunit of ammonia monooxygenase gene (amoA) was used as the biomarker for the detection of aerobic ammonia-oxidizing archaea (AOA) and bacteria (AOB), and also partial 16S rRNA gene for Plantomycetes and anaerobic ammonium-oxidizing (anammox) bacteria. Phylogenetic analysis showed that AOA in this aquitard were affiliated with those from water columns and wastewater treatment plants; and AOB were dominated by sequences among the Nitrosomonas marina/Nitrosomonas oligotropha lineage, which were affiliated with environmental sequences from coastal eutrophic bay and subtropical estuary. The richness and diversity of both AOA and AOB communities had very little variations with the depth. Candidatus Scalindua-related sequences dominated the anammox bacterial community. AOB amoA gene abundances were always higher than those of AOA at different depths in this aquitard. The Pearson moment correlation analysis showed that AOA amoA gene abundance positively correlated with pH and ammonium concentration, whereas AOB amoA gene abundance negatively correlated with C/N ratio. This is the first report that highlights the presence with low diversity of AOM communities in natural aquitard of rich ammonium.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Otte S, Schalk J, Kuenen J, Jetten M (1999) Hydroxylamine oxidation and subsequent nitrous oxide production by the heterotrophic ammonia oxidizer Alcaligenes faecalis. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 51(2):255–261
Kowalchuk GA, Stephen JR (2001) Ammonia-oxidizing bacteria: a model for molecular microbial ecology. Annu Rev Microbiol 55(1):485–529. doi:10.1146/annurev.micro.55.1.485
Nold SC, Zhou J, Devol AH, Tiedje JM (2000) Pacific Northwest marine sediments contain ammonia-oxidizing bacteria in the β subdivision of the Proteobacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol 66(10):4532–4535. doi:10.1128/aem.66.10.4532-4535.2000
Könneke M, Bernhard AE, de la Torre JR, Walker CB, Waterbury JB, Stahl DA (2005) Isolation of an autotrophic ammonia-oxidizing marine archaeon. Nature 437(7058):543–546
Strous M, Fuerst JA, Kramer EHM, Logemann S, Muyzer G, van de Pas-Schoonen KT, Webb R, Kuenen JG, Jetten MSM (1999) Missing lithotroph identified as new planctomycete. Nature 400(6743):446–449
Venter JC, Remington K, Heidelberg JF, Halpern AL, Rusch D, Eisen JA, Wu D, Paulsen I, Nelson KE, Nelson W, Fouts DE, Levy S, Knap AH, Lomas MW, Nealson K, White O, Peterson J, Hoffman J, Parsons R, Baden-Tillson H, Pfannkoch C, Rogers Y-H, Smith HO (2004) Environmental genome shotgun sequencing of the Sargasso Sea. Science 304(5667):66–74. doi:10.1126/science.1093857
Chen X-P, Zhu Y-G, Xia Y, Shen J-P, He J-Z (2008) Ammonia-oxidizing archaea: important players in paddy rhizosphere soil? Environ Microbiol 10(8):1978–1987
Jiang H, Dong H, Yu B, Lv G, Deng S, Berzins N, Dai M (2009) Diversity and abundance of ammonia-oxidizing archaea and bacteria in Qinghai Lake, Northwestern China. Geomicrobiol J 26(3):199–211
Wang Y-F, Gu J-D (2013) Higher diversity of ammonia/ammonium-oxidizing prokaryotes in constructed freshwater wetland than natural coastal marine wetland. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 97(15):7015–7033. doi:10.1007/s00253-012-4430-4
Wang Y-F, Feng Y-Y, Ma X, Gu J-D (2013) Seasonal dynamics of ammonia/ammonium-oxidizing prokaryotes in oxic and anoxic wetland sediments of subtropical coastal mangrove. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 97(17):7919–7934. doi:10.1007/s00253-012-4510-5
Laverock B, Tait K, Gilbert JA, Osborn AM, Widdicombe S (2014) Impacts of bioturbation on temporal variation in bacterial and archaeal nitrogen-cycling gene abundance in coastal sediments. Environ Microbiol Rep 6(1):113–121. doi:10.1111/1758-2229.12115
Restrepo-Ortiz CX, Auguet J-C, Casamayor EO (2014) Targeting spatiotemporal dynamics of planktonic SAGMGC-1 and segregation of ammonia-oxidizing thaumarchaeota ecotypes by newly designed primers and quantitative polymerase chain reaction. Environ Microbiol 16(3):689–700
Francis CA, Roberts KJ, Beman JM, Alyson ES, Oakley BB (2005) Ubiquity and diversity of ammonia-oxidizing archaea in water columns and sediments of the ocean. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 102(41):14683–14688
Zheng Y, Hou L, Liu M, Lu M, Zhao H, Yin G, Zhou J (2013) Diversity, abundance, and activity of ammonia-oxidizing bacteria and archaea in Chongming eastern intertidal sediments. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 97(18):8351–8363. doi:10.1007/s00253-012-4512-3
Wang J, Wang W, Gu J-D (2014) Conversion from soybean to rice paddy cultivation on community structure and abundance of ammonia-oxidizing archaea and bacteria in Baijiang soil of Northern China. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 98(6):2765–2778. doi:10.1007/s00253-013-5213-2
Sher Y, Zaady E, Nejidat A (2013) Spatial and temporal diversity and abundance of ammonia oxidizers in semi-arid and arid soils: indications for a differential seasonal effect on archaeal and bacterial ammonia oxidizers. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 86(3):544–556. doi:10.1111/1574-6941.12180
Qin H, Yuan H, Zhang H, Zhu Y, Yin C, Tan Z, Wu J, Wei W (2013) Ammonia-oxidizing archaea are more important than ammonia-oxidizing bacteria in nitrification and NO3 −-N loss in acidic soil of sloped land. Biol Fertil Soils 49(6):767–776. doi:10.1007/s00374-012-0767-1
Cao H, Auguet J-C, Gu J-D (2013) Global ecological pattern of ammonia-oxidizing archaea. PLoS One 8(2), e52853
Alves RJE, Wanek W, Zappe A, Richter A, Svenning MM, Schleper C, Urich T (2013) Nitrification rates in Arctic soils are associated with functionally distinct populations of ammonia-oxidizing archaea. ISME J 7:1620–1631. doi:10.1038/ismej.2013.35
Zhang L-M, Hu H-W, Shen J-P, He J-Z (2012) Ammonia-oxidizing archaea have more important role than ammonia-oxidizing bacteria in ammonia oxidation of strongly acidic soils. ISME J 6(5):1032–1045
Sauder LA, Peterse F, Schouten S, Neufeld JD (2012) Low-ammonia niche of ammonia-oxidizing archaea in rotating biological contactors of a municipal wastewater treatment plant. Environ Microbiol 14(9):2589–2600. doi:10.1111/j.1462-2920.2012.02786.x
Zhang F-Q, Pan W, Gu J-D, Xu B, Zhang W-H, Zhu B-Z, Wang Y-X, Wang Y-F (2016) Dominance of ammonia-oxidizing archaea community induced by land use change from Masson pine to eucalypt plantation in subtropical China. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. doi:10.1007/s00253-016-7506-8
Gan X-H, Zhang F-Q, Gu J-D, Guo Y-D, Li Z-Q, Zhang W-Q, Xu X-Y, Zhou Y, Wen X-Y, Xie G-G, Wang Y-F (2016) Differential distribution patterns of ammonia-oxidizing archaea and bacteria in acidic soils of Nanling National Nature Reserve forests in subtropical China. Anton Leeuw 109(2):237–251
Hanks JH, Weintraub RL (1936) The pure culture isolation of ammonia-oxidizing bacteria. J Bacteriol 32(6):653
Adair KL, Schwartz E (2008) Evidence that ammonia-oxidizing archaea are more abundant than ammonia-oxidizing bacteria in semiarid soils of northern Arizona, USA. Microb Ecol 56(3):420–426. doi:10.1007/s00248-007-9360-9
Santoro AE, Francis CA, de Sieyes NR, Boehm AB (2008) Shifts in the relative abundance of ammonia-oxidizing bacteria and archaea across physicochemical gradients in a subterranean estuary. Environ Microbiol 10(4):1068–1079
Shen J-p, L-m Z, Zhu Y-g, J-b Z, He J-z (2008) Abundance and composition of ammonia-oxidizing bacteria and ammonia-oxidizing archaea communities of an alkaline sandy loam. Environ Microbiol 10(6):1601–1611
Leininger S, Urich T, Schloter M, Schwark L, Qi J, Nicol GW, Prosser JI, Schuster SC, Schleper C (2006) Archaea predominate among ammonia-oxidizing prokaryotes in soils. Nature 442(7104):806–809
Strauss SL, Reardon CL, Mazzola M (2014) The response of ammonia-oxidizer activity and community structure to fertilizer amendment of orchard soils. Soil Biol Biochem 68:410–418
Hernández M, Dumont MG, Calabi M, Basualto D, Conrad R (2014) Ammonia oxidizers are pioneer microorganisms in the colonization of new acidic volcanic soils from South of Chile. Environ Microbiol Rep 6(1):70–79. doi:10.1111/1758-2229.12109
Wells GF, Park H-D, Yeung C-H, Eggleston B, Francis CA, Criddle CS (2009) Ammonia-oxidizing communities in a highly aerated full-scale activated sludge bioreactor: betaproteobacterial dynamics and low relative abundance of Crenarchaea. Environ Microbiol 11(9):2310–2328
Mosier AC, Francis CA (2008) Relative abundance and diversity of ammonia-oxidizing archaea and bacteria in the San Francisco Bay estuary. Environ Microbiol 10(11):3002–3016
Boyle-Yarwood SA, Bottomley PJ, Myrold DD (2008) Community composition of ammonia-oxidizing bacteria and archaea in soils under stands of red alder and Douglas fir in Oregon. Environ Microbiol 10(11):2956–2965
Mulder A, van de Graaf AA, Robertson LA, Kuenen JG (1995) Anaerobic ammonium oxidation discovered in a denitrifying fluidized bed reactor. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 16(3):177–183
van de Graaf A, Mulder A, de Bruijn P, Jetten M, Robertson L, Kuenen J (1995) Anaerobic oxidation of ammonium is a biologically mediated process. Appl Environ Microbiol 61(4):1246–1251
Broda E (1977) Two kinds of lithotrophs missing in nature. Z Allg Mikrobiol 17(6):491–493
Schmid M, Twachtmann U, Klein M, Strous M, Juretschko S, Jetten M, Metzger JW, Schleifer K-H, Wagner M (2000) Molecular evidence for genus level diversity of bacteria capable of catalyzing anaerobic ammonium oxidation. Syst Appl Microbiol 23(1):93–106. doi:10.1016/s0723-2020(00)80050-8
Schmid M, Walsh K, Webb R, Rijpstra WI, van de Pas-Schoonen K, Verbruggen MJ, Hill T, Moffett B, Fuerst J, Schouten S, Damsté JSS, Harris J, Shaw P, Jetten M, Strous M (2003) Candidatus “Scalindua brodae”, sp. nov., Candidatus “Scalindua wagneri”, sp. nov., two new species of anaerobic ammonium oxidizing bacteria. Syst Appl Microbiol 26(4):529–538
Kartal B, Rattray J, van Niftrik LA, van de Vossenberg J, Schmid MC, Webb RI, Schouten S, Fuerst JA, Damsté Jaap S, Jetten MSM, Strous M (2007) Candidatus “Anammoxoglobus propionicus” a new propionate oxidizing species of anaerobic ammonium oxidizing bacteria. Syst Appl Microbiol 30(1):39–49
Quan Z-X, Rhee S-K, Zuo J-E, Yang Y, Bae J-W, Park JR, Lee S-T, Park Y-H (2008) Diversity of ammonium-oxidizing bacteria in a granular sludge anaerobic ammonium-oxidizing (anammox) reactor. Environ Microbiol 10(11):3130–3139
Song B, Buckner CT, Hembury DJ, Mills RA, Palmer MR (2014) Impact of volcanic ash on anammox communities in deep sea sediments. Environ Microbiol Rep 6(2):159–166. doi:10.1111/1758-2229.12137
Hou L, Zheng Y, Liu M, Gong J, Zhang X, Yin G, You L (2013) Anaerobic ammonium oxidation (anammox) bacterial diversity, abundance, and activity in marsh sediments of the Yangtze Estuary. J Geophys Res Biogeosci 118(3):1237–1246. doi:10.1002/jgrg.20108
Wang Y-F, Li X-Y, Gu J-D (2014) Differential responses of ammonia/ammonium-oxidizing prokaryotes in mangrove sediment to amendment of acetate and leaf litter. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 98(7):3165–3180. doi:10.1007/s00253-013-5318-7
Wang Y-F, Gu J-D (2014) Effects of allylthiourea, salinity and pH on ammonia/ammonium-oxidizing prokaryotes in mangrove sediment incubated in laboratory microcosms. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 98(7):3257–3274. doi:10.1007/s00253-013-5399-3
Penton CR, Devol AH, Tiedje JM (2006) Molecular evidence for the broad distribution of anaerobic ammonium-oxidizing bacteria in freshwater and marine sediments. Appl Environ Microbiol 72(10):6829–6832. doi:10.1128/aem.01254-06
Kuypers MMM, Sliekers AO, Lavik G, Schmid M, Jorgensen BB, Kuenen JG, Sinninghe Damsté JS, Strous M, Jetten MSM (2003) Anaerobic ammonium oxidation by anammox bacteria in the Black Sea. Nature 422(6932):608–611
Rysgaard S, Glud RN (2004) Anaerobic N2 production in Arctic sea ice. Limnol Oceanogr 49(1):86–94
Schubert CJ, Durisch-Kaiser E, Wehrli B, Thamdrup B, Lam P, Kuypers MM (2006) Anaerobic ammonium oxidation in a tropical freshwater system (Lake Tanganyika). Environ Microbiol 8(10):1857–1863
Sun W, Xu MY, Wu WM, Guo J, Xia CY, Sun GP, Wang AJ (2014) Molecular diversity and distribution of anammox community in sediments of the Dongjiang River, a drinking water source of Hong Kong. J Appl Microbiol 116(2):464–476. doi:10.1111/jam.12367
Long A, Heitman J, Tobias C, Philips R, Song B (2013) Co-occurring anammox, denitrification, and codenitrification in agricultural soils. Appl Environ Microbiol 79(1):168–176. doi:10.1128/aem.02520-12
Dai M, Wang L, Guo X, Zhai W, Li Q, He B, Kao S-J (2008) Nitrification and inorganic nitrogen distribution in a large perturbed river/estuarine system: the Pearl River Estuary, China. Biogeosci Disc 5 (2)
Harrison PJ, Yin K, Lee J, Gan J, Liu H (2008) Physical–biological coupling in the Pearl River Estuary. Cont Shelf Res 28(12):1405–1415
Li P, Qiao P (1982) The model of evolution of the Pearl River Delta duing last 6,000 years. J Sediment Res 3:3
Wu C, BAO Y, REN J, Shi H, LEI Y A study on the Pearl Rive Delta in the last 6000 years-a long-term modeling approach. In: International conference on tidal dynamics and environment (TIDALITE 2002), 2002. Hangzhou
Jiao JJ, Wang Y, Cherry JA, Wang X, Zhi B, Du H, Wen D (2010) Abnormally high ammonium of natural origin in a coastal aquifer-aquitard system in the Pearl River Delta, China. Environ Sci Technol 44(19):7470–7475. doi:10.1021/es1021697
Conkling B, Blanchar R (1989) Glass microelectrode techniques for in situ pH measurements. Soil Sci Soc Am J 53(1):58–62
Neef A, Amann R, Schlesner H, Schleifer K-H (1998) Monitoring a widespread bacterial group: in situ detection of planctomycetes with 16S rRNA-targeted probes. Microbiology 144(12):3257–3266. doi:10.1099/00221287-144-12-3257
Francis CA, Beman JM, Kuypers MMM (2007) New processes and players in the nitrogen cycle: the microbial ecology of anaerobic and archaeal ammonia oxidation. ISME J 1(1):19–27
Okano Y, Hristova KR, Leutenegger CM, Jackson LE, Denison RF, Gebreyesus B, Lebauer D, Scow KM (2004) Application of real-time PCR to study effects of ammonium on population size of ammonia-oxidizing bacteria in soil. Appl Environ Microbiol 70(2):1008–1016. doi:10.1128/aem.70.2.1008-1016.2004
Tamura K, Peterson D, Peterson N, Stecher G, Nei M, Kumar S (2011) MEGA5: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis using maximum likelihood, evolutionary distance, and maximum parsimony methods. Mol Biol Evol 28(10):2731–2739. doi:10.1093/molbev/msr121
Felsenstein J (1985) Confidence limits on phylogenies: an approach using the bootstrap. Evolution 39(4):783–791
Schloss PD, Handelsman J (2005) Introducing DOTUR, a computer program for defining operational taxonomic units and estimating species richness. Appl Environ Microbiol 71(3):1501–1506. doi:10.1128/aem.71.3.1501-1506.2005
Beman JM, Francis CA (2006) Diversity of ammonia-oxidizing archaea and bacteria in the sediments of a hypernutrified subtropical estuary: Bahía del Tóbari, Mexico. Appl Environ Microbiol 72(12):7767–7777. doi:10.1128/aem.00946-06
Dong L-h, Yang J-s, Yuan H-l (2008) Research advances in molecular ecology of ammonia oxidizing bacteria. Chin J Appl Ecol 19(6):1381–1388
Mullins TD, Britschgi TB, Krest RL, Giovannoni SJ (1995) Genetic comparisons reveal the same unknown bacterial lineages in Atlantic and Pacific bacterioplankton communities. Limnol Oceanogr 40(1):148–158
Herrmann M, Saunders AM, Schramm A (2008) Archaea dominate the ammonia-oxidizing community in the rhizosphere of the freshwater macrophyte Littorella uniflora. Appl Environ Microbiol 74(10):3279–3283. doi:10.1128/aem.02802-07
Herrmann M, Saunders AM, Schramm A (2009) Effect of lake trophic status and rooted macrophytes on community composition and abundance of ammonia-oxidizing prokaryotes in freshwater sediments. Appl Environ Microbiol 75(10):3127–3136. doi:10.1128/aem.02806-08
Zhang T, Jin T, Yan Q, Shao M, Wells G, Criddle C, P Fang H (2009) Occurrence of ammonia‐oxidizing Archaea in activated sludges of a laboratory scale reactor and two wastewater treatment plants. J Appl Microbiol 107(3):970–977
Purkhold U, Wagner M, Timmermann G, Pommerening-Röser A, Koops H-P (2003) 16S rRNA and amoA-based phylogeny of 12 novel betaproteobacterial ammonia-oxidizing isolates: extension of the dataset and proposal of a new lineage within the nitrosomonads. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 53(5):1485–1494
Purkhold U, Pommerening-Röser A, Juretschko S, Schmid MC, Koops H-P, Wagner M (2000) Phylogeny of all recognized species of ammonia oxidizers based on comparative 16S rRNA and amoA sequence analysis: implications for molecular diversity surveys. Appl Environ Microbiol 66(12):5368–5382. doi:10.1128/aem.66.12.5368-5382.2000
Koops H-P, Pommerening-Röser A (2001) Distribution and ecophysiology of the nitrifying bacteria emphasizing cultured species. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 37(1):1–9
Hallin S, Lydmark P, Kokalj S, Hermansson M, Sörensson F, Jarvis Å, Lindgren PE (2005) Community survey of ammonia‐oxidizing bacteria in full‐scale activated sludge processes with different solids retention time. J Appl Microbiol 99(3):629–640
Dionisi HM, Layton AC, Harms G, Gregory IR, Robinson KG, Sayler GS (2002) Quantification of Nitrosomonas oligotropha-like ammonia-oxidizing bacteria and Nitrospira spp. from full-scale wastewater treatment plants by competitive PCR. Appl Environ Microbiol 68(1):245–253
Whang L-M, Chien I, Yuan S-L, Wu Y-J (2009) Nitrifying community structures and nitrification performance of full-scale municipal and swine wastewater treatment plants. Chemosphere 75(2):234–242
Cébron A, Berthe T, Garnier J (2003) Nitrification and nitrifying bacteria in the lower Seine River and estuary (France). Appl Environ Microbiol 69(12):7091–7100
Burrell PC, Phalen CM, Hovanec TA (2001) Identification of bacteria responsible for ammonia oxidation in freshwater aquaria. Appl Environ Microbiol 67(12):5791–5800. doi:10.1128/aem.67.12.5791-5800.2001
Koops H, Böttcher B, Möller U, Pommerening-Röser A, Stehr G (1991) Classification of eight new species of ammonia-oxidizing bacteria: Nitrosomonas communis sp. nov., Nitrosomonas ureae sp. nov., Nitrosomonas aestuarii sp. nov., Nitrosomonas marina sp. nov., Nitrosomonas nitrosa sp. nov., Nitrosomonas eutropha sp. nov., Nitrosomonas oligotropha sp. nov. and Nitrosomonas halophila sp. nov. J Gen Microbiol 137(7):1689–1699
Regan JM, Harrington GW, Noguera DR (2002) Ammonia- and nitrite-oxidizing bacterial communities in a pilot-scale chloraminated drinking water distribution system. Appl Environ Microbiol 68(1):73–81. doi:10.1128/aem.68.1.73-81.2002
Stehr G, Böttcher B, Dittberner P, Rath G, Koops H-P (1995) The ammonia-oxidizing nitrifying population of the River Elbe estuary. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 17(3):177–186
Bollmann A, Schmidt I, Saunders AM, Nicolaisen MH (2005) Influence of starvation on potential ammonia-oxidizing activity and amoA mRNA levels of Nitrosospira briensis. Appl Environ Microbiol 71(3):1276–1282
Bollmann A, Bär-Gilissen M-J, Laanbroek HJ (2002) Growth at low ammonium concentrations and starvation response as potential factors involved in niche differentiation among ammonia-oxidizing bacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol 68(10):4751–4757. doi:10.1128/aem.68.10.4751-4757.2002
Lam P, Jensen MM, Lavik G, McGinnis DF, Müller B, Schubert CJ, Amann R, Thamdrup B, Kuypers MMM (2007) Linking crenarchaeal and bacterial nitrification to anammox in the Black Sea. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 104(17):7104–7109. doi:10.1073/pnas.0611081104
Watson S, Bock E, Harms H, Koops H-P, Hooper A (1989) Nitrifying bacteria. In: Staley J, Bryant M, Pfennif N, Holt J (eds) Bergey’s manual of systematic microbiology, 3rd edn. Williams & Wilkins, Baltimore, pp 1808–1834
Casciotti KL, Ward BB (2001) Dissimilatory nitrite reductase genes from autotrophic ammonia-oxidizing bacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol 67(5):2213–2221. doi:10.1128/aem.67.5.2213-2221.2001
Diab S, Kochba M, Mires D, Avnimelech Y (1992) Combined intensive-extensive (CIE) pond system A: inorganic nitrogen transformations. Aquaculture 101(1):33–39
You J, Das A, Dolan EM, Hu Z (2009) Ammonia-oxidizing archaea involved in nitrogen removal. Water Res 43(7):1801–1809
Wang Y, Ke X, Wu L, Lu Y (2009) Community composition of ammonia-oxidizing bacteria and archaea in rice field soil as affected by nitrogen fertilization. Syst Appl Microbiol 32(1):27–36
Stein LY, Arp DJ (1998) Loss of ammonia monooxygenase activity in Nitrosomonas europaea upon exposure to nitrite. Appl Environ Microbiol 64(10):4098–4102
Anthonisen AC, Loehr RC, Prakasam TBS, Srinath EG (1976) Inhibition of nitrification by ammonia and nitrous acid. J Water Pollut Control Fed 48(5):835–852
Acknowledgments
This study was supported financially by the General Research Fund of the Research Grants Council, the Hong Kong Special Administrative Region, China (HKU 702707P) and Guangdong Geological Survey.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Kwok-Ho Lee and Yong-Feng Wang contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, KH., Wang, YF., Wang, Y. et al. Abundance and Diversity of Aerobic/Anaerobic Ammonia/Ammonium-Oxidizing Microorganisms in an Ammonium-Rich Aquitard in the Pearl River Delta of South China. Microb Ecol 76, 81–91 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00248-016-0815-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00248-016-0815-8