Abstract
Background
Gadoxetate disodium, utilized in hepatobiliary magnetic resonance (MR) imaging, has been associated with transient respiratory motion during the arterial phase in adults.
Objective
The purpose of this study was to determine the presence and severity of this phenomenon in children imaged awake versus under general anesthesia.
Materials and methods
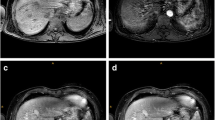
This retrospective cohort study was approved by the institutional review board; informed consent was waived. One hundred thirty exams of children ≤18 years old who underwent dynamic liver MR imaging with gadoxetate disodium between October 2010 and January 2018 were reviewed. Three pediatric radiologists scored respiratory motion artifacts on all imaging phases using a 5-point Likert scale. Differences in mean motion scores were assessed with analysis of variance and Tukey’s multiple comparisons test, and multivariable regression was used to identify predictors of arterial phase motion in awake patients.
Results
One hundred thirty patients (50% [n=65] female; mean age: 9.8±3.7 years, 48.5% [n=63] awake) were included. There were significant differences in mean motion scores between phases in the awake cohort (P<0.0001) but not in the general anesthesia cohort (P=0.051). In the awake cohort, arterial phase motion score (mean: 3.52±0.83) was significantly higher than mean motion score in all other phases (P≤0.0003). There were no significant patient-specific predictors of arterial phase motion score in the awake cohort.
Conclusion
Significantly increased arterial phase respiratory motion artifact in awake children undergoing dynamic liver MR imaging with gadoxetate disodium suggests that transient respiratory motion occurs in children. General anesthesia may suppress this phenomenon.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Frydrychowicz A, Lubner MG, Brown JJ et al (2012) Hepatobiliary MR imaging with gadolinium-based contrast agents. J Magn Reson Imaging 35:492–511
Balci NC, Semelka RC (2005) Contrast agents for MR imaging of the liver. Radiol Clin North Am 43:887–898
Dahlstrom N, Persson A, Albiin N et al (2007) Contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance cholangiography with Gd-BOPTA and Gd-EOB-DTPA in healthy subjects. Acta Radiol 48:362–368
Lee NK, Kim S, Lee JW et al (2009) Biliary MR imaging with Gd-EOB-DTPA and its clinical applications. Radiographics 29:1707–1724
Geller J, Kasahara M, Martinez M et al (2016) Safety and efficacy of gadoxetate disodium-enhanced liver MRI in pediatric patients aged >2 months to <18 years--results of a retrospective, multicenter study. Magn Reson Insights 9:21–28
Kolbe AB, Podberesky DJ, Zhang B, Towbin AJ (2015) The impact of hepatocyte phase imaging from infancy to young adulthood in patients with a known or suspected liver lesion. Pediatr Radiol 45:354–365
Tamrazi A, Vasanawala SS (2011) Functional hepatobiliary MR imaging in children. Pediatr Radiol 41:1250–1258
Meyers AB, Towbin AJ, Serai S et al (2011) Characterization of pediatric liver lesions with gadoxetate disodium. Pediatr Radiol 41:1183–1197
Davenport MS, Viglianti BL, Al-Hawary MM et al (2013) Comparison of acute transient dyspnea after intravenous administration of gadoxetate disodium and gadobenate dimeglumine: effect on arterial phase image quality. Radiology 266:452–461
Davenport MS, Caoili EM, Kaza RK, Hussain HK (2014) Matched within-patient cohort study of transient arterial phase respiratory motion-related artifact in MR imaging of the liver: gadoxetate disodium versus gadobenate dimeglumine. Radiology 272:123–131
Motosugi U, Bannas P, Bookwalter CA et al (2016) An investigation of transient severe motion related to gadoxetic acid-enhanced MR imaging. Radiology 279:93–102
Davenport MS, Malyarenko DI, Pang Y et al (2017) Effect of gadoxetate disodium on arterial phase respiratory waveforms using a quantitative fast Fourier transformation-based analysis. AJR Am J Roentgenol 208:328–336
McClellan TR, Motosugi U, Middleton MS et al (2017) Intravenous gadoxetate disodium administration reduces breath-holding capacity in the hepatic arterial phase: a multi-center randomized placebo-controlled trial. Radiology 282:361–368
Shah MR, Flusberg M, Paroder V et al (2017) Transient arterial phase respiratory motion-related artifact in MR imaging of the liver: an analysis of four different gadolinium-based contrast agents. Clin Imaging 41:23–27
Jaimes C, Kirsch JE, Gee MS (2018) Fast, free-breathing and motion-minimized techniques for pediatric body magnetic resonance imaging. Pediatr Radiol 48:1197–1208
Davenport MS, Bashir MR, Pietryga JA et al (2014) Dose-toxicity relationship of gadoxetate disodium and transient severe respiratory motion artifact. AJR Am J Roentgenol 203:796–802
Endrikat J, Kim SY, Sakaguchi T et al (2016) Safety of gadoxetate disodium: results from six clinical phase IV studies in 8194 patients. Acta Radiol 57:1326–1333
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
Dr. Trout is a consultant for Guerbet Group, is part of the Speakers Bureau for Applied Radiology, and receives honoraria for authorship from Reed Elsevier and Wolters Kluwer. Dr. Dillman and Dr. Towbin receive grant funding from Guerbet Group.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gilligan, L.A., Trout, A.T., Anton, C.G. et al. Respiratory motion in children and young adults undergoing liver magnetic resonance imaging with intravenous gadoxetate disodium contrast material. Pediatr Radiol 49, 1171–1176 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00247-019-04437-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00247-019-04437-x