Abstract
Background
Although echocardiography is the first-line imaging modality in the diagnosis of total anomalous pulmonary venous connection (TAPVC), multidetector CT (MDCT) could have advantages in the diagnosis of TAPVC in certain cases.
Objective
To compare MDCT with echocardiography in the evaluation of TAPVC.
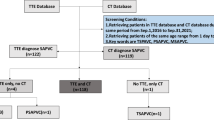
Materials and methods
Enrolled in the study were 23 patients with surgically proven TAPVC. The echocardiography and MDCT findings were independently interpreted by a paediatric cardiologist and cardiac radiologist in terms of: (1) the drainage site of the common pulmonary vein, (2) stenosis of the vertical vein, and (3) the course of the atypical vessel into the systemic vein in the case of vertical vein stenosis. The findings from both modalities were correlated with the results obtained at surgery (n=22) or autopsy (n=1).
Results
In all patients, MDCT correctly depicted the drainage site of the common pulmonary vein, stenosis of the vertical vein and the course of the atypical vessel into the systemic vein (sensitivity 100%, specificity 100%). The specificity of echocardiography was 100% for the three defined findings. The sensitivity of echocardiography, however, was 87%, 71% and 0%, respectively.
Conclusion
MDCT can facilitate the diagnosis of TAPVC in certain cases.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Delisle G, Ando M, Calder AL et al (1976) Total anomalous pulmonary venous connection: report of 93 autopsied cases with emphasis on diagnostic and surgical considerations. Am Heart J 91:99–122
Hancock Friesen CJ, Zurakowski D, Thiagarajan RR et al (2005) Total anomalous pulmonary venous connection: an analysis of current management strategies in a single institution. Ann Thorac Surg 79:596–606
Ritter S, Tani LY, Shaddy RE et al (2000) An unusual variant of total anomalous pulmonary venous connection with varices and multiple drainage sites. Pediatr Cardiol 21:289–291
Hastreiter AR, Paul MH, Molthan ME et al (1962) Total anomalous pulmonary venous connection with severe pulmonary venous obstruction; a clinical entity. Circulation 25:916–928
Chin AJ, Sanders SP, Sherman F et al (1987) Accuracy of subcostal echocardiography in prospective diagnosis of total anomalous pulmonary venous connection. Am Heart J 113:1153–1159
Kim TH, Kim YM, Suh CH et al (2000) Helical CT angiography and three-dimensional reconstruction of total anomalous pulmonary venous connections in neonates and infants. AJR 175:1381–1386
Goo HW (2005) Pediatric CT: understanding of radiation dose and optimization of imaging techniques. J Korean Radiol Soc 52:1–5
Yang DH, Goo HW (2008) Pediatric 16-slice CT protocols: radiation dose and image quality. J Korean Radiol Soc 59:333–347
Thomas KE, Wang B (2008) Age-specific effective doses for pediatric MSCT examinations at a large children's hospital using DLP conversion coefficients: a simple estimation method. Pediatr Radiol 38:645–656
Park JA, Choo KS, Lee HD et al (2008) Supracardiac type total anomalous pulmonary venous connection (TAPVC) with oesophageal varices. Pediatr Radiol 38:1138–1140
Hsu YH, Chen CT, Hwang M et al (1991) Magnetic resonance imaging of total anomalous pulmonary venous drainage. Am Heart J 125:1560–1565
Romero-Cardenas A, Vargas-Barron J, Rylaarsdam M et al (1991) Total anomalous pulmonary venous return: diagnosis by transesophageal echocardiography. Am Heart J 121:1831–1834
Sreeram N, Walsh K (1992) Diagnosis of total anomalous pulmonary venous drainage by Doppler color flow imaging. J Am Coll Cardiol 19:1577–1582
Huhta JC, Gutgesell HP, Nihill MR (1985) Cross sectional echocardiographic diagnosis of total anomalous pulmonary venous connection. Br Heart J 53:525–534
Simpson JM, Moore P, Teitel DF (2001) Cardiac catheterization of low birth weight infants. Am J Cardiol 87:1372–1377
Vitiello R, McCrindle BW, Nykanen D et al (1998) Complications associated with pediatric cardiac catheterization. J Am Coll Cardiol 32:1433–1440
Sanborn PA, Michna E, Zurakowski D et al (2005) Adverse cardiovascular and respiratory events during sedation of pediatric patients for imaging examinations. Radiology 237:288–294
Tsai IC, Chen MC, Jan SL et al (2008) Neonatal cardiac multidetector row CT: why and how we do it. Pediatr Radiol 38:438–451
Didier D, Higgins CB, Fisher MR et al (1986) Congenital heart disease: gated MR imaging in 72 patients. Radiology 158:227–235
Masui T, Seelos KC, Kersting-Sommerhoff BA et al (1991) Abnormalities of the pulmonary veins: evaluation with MR imaging and comparison with cardiac angiography and echocardiography. Radiology 181:645–649
Soongswang J, Nana A, Laohaprasitiporn D et al (2000) Limitation of transthoracic echocardiography in the diagnosis of congenital heart diseases. J Med Assoc Thai 83(Suppl 2):S111–S117
Gutgesell HP, Huhta JC, Latson LA et al (1985) Accuracy of two-dimensional echocardiography in the diagnosis of congenital heart disease. Am J Cardiol 55:514–518
Marek J, Skovranek J, Hucin B et al (1995) Seven-year experience of noninvasive preoperative diagnostics in children with congenital heart defects: comprehensive analysis of 2,788 consecutive patients. Cardiology 86:488–495
Theocharopoulos N, Perisinakis K, Damilakis J et al (2006) Dosimetric characteristics of a 16-slice computed tomography scanner. Eur Radiol 16:2575–2585
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Oh, K.H., Choo, K.S., Lim, S.J. et al. Multidetector CT evaluation of total anomalous pulmonary venous connections: comparison with echocardiography. Pediatr Radiol 39, 950–954 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00247-009-1309-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00247-009-1309-3