Abstract
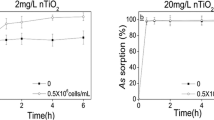
The environmental factors are expected to affect the ecotoxicity of heavy metals in the presence of engineered nanoparticles (NPs) in aquatic ecosystems. However, in sediment scenario, little is known regarding their impacts on the ecotoxicity of co-exposure of sediment-associated heavy metals and NPs. This study evaluated the impacts of different levels of organic matter (OM) (4.8–11.6%) and pH (6–9) on the ecotoxicological effects of co-exposure of sediment-associated titanium dioxide nanoparticles (TiO2-NPs) and cadmium (Cd) to a freshwater gastropod Bellamya aeruginosa. The burdens of Ti and Cd and biomarkers of DNA damage, Na+/K+-ATPase, lipid peroxidation (LPO), and protein carbonylation (PC) in the hepatopancreas were determined following 21 days of exposure. At background level of OM (4.8%) in sediments, TiO2-NPs significantly promoted Cd accumulation in low-Cd treatments (5 mg/kg) but did not promote Cd accumulation in high-Cd treatments (25 mg/kg). At the relatively higher OM levels (7.1 and 11.6%), TiO2-NPs significantly enhanced Cd accumulation and toxicity as evidenced by aggravated DNA damage, decreased Na+/K+-ATPase activities, and increased LPO and PC levels. Moreover, Cd burdens in both low-Cd and high-Cd treatment were positively correlated with corresponding Ti burdens, indicating TiO2-NPs partially acted as carrier of Cd. At all pH levels, in low-Cd treatments, TiO2-NPs did not affect Cd accumulation, LPO, and PC levels but significantly enhanced DNA damage and slightly facilitated the inhibition of Na+/K+-ATPase activities. In high-Cd treatments, only at pH 9, TiO2-NPs significantly enhanced Cd accumulation and toxicity. Our results implied that interaction between TiO2-NPs and OM or pH significantly affected the accumulation and toxicity of Cd in B. aeruginosa, but the underlying mechanisms need further investigation. Additionally, it should be noted that the potential ecological risk of co-exposure of NPs and coexisting pollutants might be closely species-specific and related to environmental media.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254
Chen Q, Song B (1975) A preliminary study on reproduction and growth of the snail Bellamya aeruginosa (Veeve). Acta Hydrobiol Sin 5:519–534 (in Chinese)
Chen H, Gao B, Li H (2014) Functionalization, pH, and ionic strength influenced sorption of sulfamethoxazole on graphene. J Environ Chem Eng 2:310–315
Christian P, Von der Kammer F, Baalousha M, Hofmann T (2008) Nanoparticles: structure, properties, preparation and behavior in environmental media. Ecotoxicology 17:326–343
Domingos RF, Tufenkji N, Wilkinson KJ (2009) Aggregation of titanium dioxide nanoparticles: role of a fulvic acid. Environ Sci Technol 43:1282–1286
Dunphy Guzman KA, Finnegan MP, Banfield JF (2006) Influence of surface potential on aggregation and transport of titania nanoparticles. Environ Sci Technol 40:7688–7693
Farre M, Gajda-Schrantz K, Kantiani L, Barcelo D (2009) Ecotoxicity and analysis of nanomaterials in the aquatic environment. Anal Bioanal Chem 393:81–95
Finnegan MP, Zhang H, Banfield JF (2007) Phase stability and transformation in titania nanoparticles in aqueous solutions dominated by surface energy. J Phys Chem C 111:1962–1968
Grillo R, Rosa AH, Fraceto LF (2015) Engineered nanoparticles and organic matter: a review of the state-of-the-art. Chemosphere 119:608–619
Hartmann NB, Legros S, Von der Kammer F (2012) The potential of TiO2 nanoparticles as carriers for cadmium uptake in Lumbriculus variegatus and Daphnia magna. Aquat Toxicol 118–119:1–8
Hu C, Li M, Cui YB, Li DS, Chen J, Yang LY (2010) Toxicological effects of TiO2 and ZnO nanoparticles in soil on earthworm Eisenia fetida. Soil Biol Biochem 42:586–591
Jiang J, Oberdörster G, Biswas P (2008) Characterization of size, surface charge, and agglomeration state of nanoparticle dispersions for toxicological studies. J Nanoparticle Res 11:77–89
Li Y, Ma T, Guo X, Yang C, Zhi Dang (2014) Sorption of phenanthrene on nano-TiO2 coated with humic acid. J Agro-Environ Sci 33:2247–2253 (in Chinese)
Lionetto MG, Maffia M, Cappello MS, Giordano ME, Storelli C, Schettino T (1998) Effect of cadmium on carbonic anhydrase and Na+-K+-ATPase in eel, Anguilla anguilla, intestine and gills. Comp Biochem Physiol Part A 120:89–91
Ma T, Zhou K, Zhu C, Liu J, Wang Z (2009) Biomarker responses of Bellamya aeruginosa to the chronic stress of cadmium-contaminated sediment. Acta Sci Circum 29:1750–1756 (in Chinese)
Ma T, Gong S, Zhou K, Zhu C, Deng K, Luo Q, Wang Z (2010) Laboratory culture of the freshwater benthic gastropod Bellamya aeruginosa (Reeve) and its utility as a test species for sediment toxicity. J Environ Sci 22:304–313
MacDonald DD, Ingersoll CG, Berger TA (2000) Development and evaluation of consensus-based sediment quality guidelines for freshwater ecosystems. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 39:20–31
Maria VL, Ribeiro MJ, Amorim MJ (2014) Oxidative stress biomarkers and metallothionein in Folsomia candida—responses to Cu and Cd. Environ Res 133:164–169
Menard A, Drobne D, Jemec A (2011) Ecotoxicity of nanosized TiO2. Review of in vivo data. Environ Pollut 159:677–684
Musee N, Oberholster PJ, Sikhwivhilu L, Botha AM (2010) The effects of engineered nanoparticles on survival, reproduction, and behavior of freshwater snail, Physa acuta (draparnaud, 1805). Chemosphere 81:1196–1203
Nigro M, Bernardeschi M, Costagliola D, Della Torre C, Frenzilli G, Guidi P, Lucchesi P, Mottola F, Santonastaso M, Scarcelli V, Monaci F, Corsi I, Stingo V, Rocco L (2015) n-TiO2 and CdCl2 co-exposure to titanium dioxide nanoparticles and cadmium: genomic, DNA and chromosomal damage evaluation in the marine fish European sea bass (Dicentrarchus labrax). Aquat Toxicol 168:72–77
Petersen EJ, Zhang L, Mattison NT, O’Carroll DM, Whelton AJ, Uddin N, Nguyen T, Huang QG, Henry TB, Holbrook RD, Chen KL (2011) Potential release pathways, environmental fate, and ecological risks of carbon nanotubes. Environ Sci Technol 45:9837–9856
Petosa AR, Jaisi DP, Quevedo IR, Elimelech M, Tufenkji N (2010) Aggregation and deposition of engineered nanomaterials in aquatic environments: role of physicochemical interactions. Environ Sci Technol 44:6532–6549
Pettibone JM, Cwiertny DM, Scherer M, Grassian VH (2008) Adsorption of organic acids on TiO2 nanoparticles: effects of pH, nanoparticle size, and nanoparticle aggregation. Langmuir 24:6659–6667
Pourrut B, Jean S, Silvestre J, Pinelli E (2011) Lead-induced DNA damage in Vicia faba root cells: potential involvement of oxidative stress. Mutat Res 726:123–128
Praetorius A, Labille J, Scheringer M, Thill A, Hungerbühler K, Bottero J-Y (2014) Heteroaggregation of titanium dioxide nanoparticles with model natural colloids under environmentally relevant conditions. Environ Sci Technol 48:10690–10698
Rosenfeldt RR, Seitz F, Senn L, Schilde C, Schulz R, Bundschuh M (2015) Nanosized titanium dioxide reduces copper toxicity—the role of organic material and the crystalline phase. Environ Sci Technol 49:1815–1822
Savolainen K, Alenius H, Norppa H, Pylkkänen L, Tuomi T, Kasper G (2010) Risk assessment of engineered nanomaterials and nanotechnologies: a review. Toxicology 269:92–104
Scown TM, van Aerle R, Tyler CR (2010) Review: do engineered nanoparticles pose a significant threat to the aquatic environment? Crit Rev Toxicol 40:653–670
Simpson SL, Angel BM, Jolley DF (2004) Metal equilibration in laboratory-contaminated (spiked) sediments used for the development of whole-sediment toxicity tests. Chemosphere 54:597–609
Singh NP, McCoy MT, Tice RR, Schneider EL (1988) A simple technique for quantitation of low levels of DNA damage in individual cells. Exp Cell Res 175:184–191
Stone V, Nowack B, Baun A, van den Brink N, von der Kammer F, Dusinska M, Handy R, Hankin S, Hassellöv M, Joner E, Fernandes TF (2010) Nanomaterials for environmental studies: classification, reference material issues, and strategies for physico-chemical characterization. Sci Total Environ 408:1745–1754
Sun H, Zhang X, Niu Q, Chen Y, Crittenden JC (2007) Enhanced accumulation of arsenate in carp in the presence of titanium dioxide nanoparticles. Water Air Soil Pollut 178:245–254
Tan C, Wang WX (2014) Modification of metal bioaccumulation and toxicity in Daphnia magna by titanium dioxide nanoparticles. Environ Pollut 186:36–42
Tan C, Fan WH, Wang WX (2011) Role of titanium dioxide nanoparticles in the elevated uptake and retention of cadmium and zinc in Daphnia magna. Environ Sci Technol 46:469–476
Thio BJR, Zhou DX, Keller AA (2011) Influence of natural organic matter on the aggregation and deposition of titanium dioxide nanoparticles. J Hazard Mater 189:556–563
Tice RR, Agurell E, Anderson D (2000) Single cell gel/comet assay: guidelines for in vitro and in vivo genetic toxicology testing. Environ Mol Mutagen 35:206–221
Tsyusko OV, Hardas SS, Shoults-Wilson WA, Starnes CP, Joice G, Butterfield DA, Unrine JM (2012) Short-term molecular-level effects of silver nanoparticle exposure on the earthworm, Eisenia fetida. Environ Pollut 171:249–255
Vale G, Franco C, Diniz MS, Santos MMC, Domingos RF (2014) Bioavailability of cadmium and biochemical responses on the freshwater bivalve Corbicula fluminea—the role of TiO2 nanoparticles. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 109:161–168
Vance ME, Kuiken T, Vejerano EP, McGinnis SP, Hochella MF Jr, Rejeski D, Hull MS (2015) Nanotechnology in the real world: redeveloping the nanomaterial consumer products inventory. Beilstein J Nanotechnol 6:1769–1780
Wang X, Lu J, Xu M, Xing B (2008) Sorption of pyrene by regular and nanoscaled metal oxide particles: influence of adsorbed organic matter. Environ Sci Technol 42:7267–7272
Xu D, Li C, Wen Y, Liu W (2013) Antioxidant defense system responses and DNA damage of earthworms exposed to perfluorooctane sulfonate (PFOS). Environ Pollut 174:121–127
Yang K, Xing B (2009) Sorption of phenanthrene by humic acid-coated nanosized TiO2 and ZnO. Environ Sci Technol 43:1845–1851
Yang WW, Wang Y, Huang B (2014) TiO2 nanoparticles act as a carrier of Cd bioaccumulation in the ciliate Tetrahymena thermophila. Environ Sci Technol 48:7568–7575
Zhang X, Sun H, Zhang Z, Niu Q, Chen Y, Crittenden JC (2007) Enhanced bioaccumulation of cadmium in carp in the presence of titanium dioxide nanoparticles. Chemosphere 67:160–166
Zheng S, Wang Y, Zhou Q, Chen C (2013) Responses of oxidative stress biomarkers and DNA damage on a freshwater snail (Bellamya aeruginosa) stressed by ethylbenzene. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 65:251–259
Zhu C, Ma T, Zhou K, Liu J, Peng J, Ren B (2010) Pollution characteristics and potential ecotoxicity risk of heavy metals in surface river sediments of western Hunan. Acta Ecol Sin 30:3982–3993 (in Chinese)
Acknowledgments
The work was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 41171383) and Open Foundation of Key laboratory for Ecotourism of Hunan Province, China (No. JDSTLY1409).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ma, T., Wang, M., Gong, S. et al. Impacts of Sediment Organic Matter Content and pH on Ecotoxicity of Coexposure of TiO2 Nanoparticles and Cadmium to Freshwater Snails Bellamya aeruginosa . Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 72, 153–165 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00244-016-0338-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00244-016-0338-9