Abstract
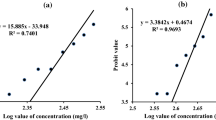
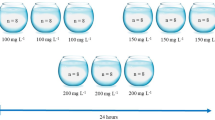
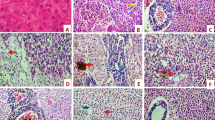
Laboratory experiments were performed to examine the toxic effects of fluoride (F–) on the survival and behavior of white-clawed crayfish (Austropotamobius pallipes). Body fluoride contents (bioaccumulation) of test crayfish were also examined. No significant differences between male and female crayfish regarding mortality, escape (tail-flip) response, and fluoride bioaccumulation were detected. For mortality, 48-, 72-, 96-, 120-, 144-, 168-, and 192-h median lethal concentrations (LC50) were estimated to be 93.0, 55.3, 42.7, 36.5, 32.9, 30.6, and 28.9 mg F–/l, respectively. For the escape response, 48-, 72-, 96-, 120-, 144-, 168- and 192-h median effective concentrations (EC50) were estimated to be 18.4, 11.1, 8.6, 7.4, 6.7, 6.2 and 5.9 mg F–/l, respectively. Average food consumption in test crayfish tended to decrease with increasing water fluoride concentration with a 192-h lowest–observed effect concentration of 10.7 mg F–/l. These results indicate that the escape response was the most sensitive end point to fluoride toxicity followed by food consumption and mortality. Fluoride bioaccumulation in test crayfish increased with increasing water fluoride concentration and exposure time. The exoskeleton accumulated more fluoride than muscle. A comparison of the obtained results with previous data for other freshwater invertebrates shows that white-clawed crayfish are relatively tolerant to fluoride toxicity. We conclude that fluoride pollution in freshwater ecosystems should not be viewed as an important risk factor contributing to the catastrophic decrease of A. pallipes in many European countries. Our results indicate that fluoride bioaccumulation in A. pallipes might be used as a bioindicator of fluoride pollution in freshwater ecosystems where it is present.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aguirre-Sierra A, Alonso A, Camargo JA (2011) Contrasting sensitivities to fluoride toxicity between juveniles and adults of the aquatic snail Potamopyrgus antipodarum (Hydrobiidae, Mollusca). Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 86:476–479
Alonso A, Camargo JA (2004) Toxic effects of unionized ammonia on survival and feeding activity of the freshwater amphipod Eulimnogammarus toletanus (Gammaridae, Crustacea). Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 72:1052–1058
Alonso A, Camargo JA (2011) Subchronic toxic effects of fluoride ion on the survival and behavior of the aquatic snail Potamopyrgus antipodarum (Hydrobiidae, Mollusca). Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 60:511–517
American Public Health Association (1998) Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater (20th ed). APHA-AWWA-WPCF, Washington DC
Camargo JA (1991) Ecotoxicological study of the influence of an industrial effluent on a net-spinning caddisfly assemblage in a regulated river. Water Air Soil Pollut 60:263–277
Camargo JA (2003) Fluoride toxicity to aquatic organisms: a review. Chemosphere 50:251–264
Camargo JA, Tarazona JV (1990) Acute toxicity to freshwater macroinvertebrates of fluoride ion (F–) in soft water. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 45:883–887
Camargo JA, Ward JV, Martin KL (1992) The relative sensitivity of competing hydropsychid species to fluoride toxicity in the Cache la Poudre River (Colorado). Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 22:107–113
Dave G (1984) Effects of fluoride on growth, reproduction and survival in Daphnia magna. Comp Biochem Physiol C 78:425–431
Demers A, Reynolds JD (2002) A survey of the whiteclawed crayfish, Austropotamobius pallipes (Lereboullet), and of water quality in two catchments of eastern Ireland. Bulletin Français de la Peche et de la Pisciculture 367:729–740
Demers A, Souty-Grosset C, Trouilhé MC, Füreder L, Renai B, Gherardi F (2006) Tolerance of three European native species of crayfish to hypoxia. Hydrobiologia 560:425–432
Gonzalo C, Camargo JA (2012) Fluoride bioaccumulation in the signal crayfish Pacifastacus leniusculus (Dana) as suitable bioindicator of fluoride pollution in freshwater ecosystems. Ecol Indic 20:244–251
Gonzalo C, Camargo JA, Masiero L, Casellato S (2010) Fluoride toxicity and bioaccumulation in the invasive amphipod Dikerogammarus villosus (Sowinsky, 1894): a laboratory study. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 85:472–475
Holdich DM (2002) Distribution of crayfish in Europe and some adjoining countries. Bulletin Français de la Peche et de la Pisciculture 367:611–650
Holdich DM, Reynolds JD, Souty-Grosset C, Sibley PJ (2009) A review of the ever increasing threat to European crayfish from non-indigenous crayfish species. Knowl Manag Aquatic Ecosyst 394–395:11–46
Kessabi M (1984) Métabolisme et biochimie toxicologique du fluor: une revue [in French]. Rev Méd Vét 135:497–510
Kouba A, Buřič M, Kozák P (2010) Bioaccumulation and effects of heavy metals in crayfish: a review. Water Air Soil Pollut 211:5–16
Longshaw M (2011) Deseases of crayfish: a review. J Invertebr Pathol 106:54–70
Metcalfe-Smith JL, Holtze KE, Sirota GR, Reid JJ, de Solla SR (2003) Toxicity of aqueous and sediment-associated fluoride to freshwater organisms. Environ Toxicol Chem 22:161–166
Newman MC (2010) Fundamentals of ecotoxicology (3rd ed). CRC and Taylor & Francis Group, Boca Raton
Reddy SLN, Venugopal NBRK (1990) Effect of fluoride on acetylcholinesterase activity and oxygen consumption in a freshwater field crab, Barytelphusa guerini. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 45:760–766
Reddy SLN, Gopal N, Reddy A, Rao J (1989) Fluoride-induced changes in carbohydrate metabolism in the tissue of freshwater crab Barytelphusa guereni. Ecotoxicol Environ Safe 18:59–67
Sands M, Nicol S, McMinn A (1998) Fluorine in Antarctic marine crustaceans. Mar Biol 132:591–598
Shi X, Zhuang P, Zhang L, Feng G, Chen L, Liu J, Qu L, Wang R (2009) The bioaccumulation of fluoride ion (F–) in Siberian sturgeon (Acipenser baerii) under laboratory conditions. Chemosphere 75:376–380
Sigler WF, Neuhold JM (1972) Fluoride intoxication in fish: a review. J Wildlife Dis 8:252–254
Sokal RR, Rohlf FJ (1995) Biometry: the principles and practice of statistics in biological research (3rd ed). Freeman, New York
Souty-Grosset C, Holdich DM, Noël PY, Reynolds JD, Haffner P (eds) (2006) Atlas of crayfish in Europe. Museum National d’Histoire Naturelle, Paris
Thorp JH, Covich AP (eds) (2010) Ecology and classification of North American freshwater invertebrates, 3rd edn. Academic, San Diego
United States Environmental Protection Agency (1991) Multifactor probit analysis. USEPA 600/X-91-101, Washington, DC
Walker CH, Hopkin SP, Sibly RM, Peakall DB (2005) Principles of ecotoxicology (3rd ed). CRC, Boca Raton
Weinstein LH, Davison AW (2004) Fluorides in the environment: effects on plants and animals. CABI, Cambridge
Wigginton AJ, Cooper RL, Fryman-Gripshover EM, Birge WJ (2010) Effects of cadmium and body mass on two anti-predator behaviours of five species of crayfish. Int J Zool Res 6:92–104
World Health Organization (2002) Environmental health criteria 227. Fluorides, WHO, Geneva
Zhang H, Xianhao C, Jianming P, Weiping X (1993) Biogeochemistry research of fluoride in Antarctic Ocean: I. The study of fluoride anomaly in krill. Antarctic Res 4:55–61
Acknowledgments
Funds for this research came from the former Spanish Ministry of Science and Innovation and the current Spanish Ministry of Economy and Competitiveness (Research Projects No. CGL2006-06804 and CGL2011-28585). The University of Alcala provided logistical support for carrying out laboratory experiments. Arantxa Aguirre-Sierra was supported by a Research Grant from the University of Alcala. We are grateful to Cristina Gonzalo for collaboration in bioaccumulation analyses. We also thank Dirección General de Montes y Espacios Naturales of Junta de Castilla-La Mancha for giving us official authorization to obtain white-clawed crayfish from the Rillo de Gallo crayfish farm in Guadalajara province. Last, we are grateful to three anonymous reviewers for their comments and suggestions, which contributed to improve the writing and scientific quality of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Aguirre-Sierra, A., Alonso, Á. & Camargo, J.A. Fluoride Bioaccumulation and Toxic Effects on the Survival and Behavior of the Endangered White-Clawed Crayfish Austropotamobius pallipes (Lereboullet). Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 65, 244–250 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00244-013-9892-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00244-013-9892-6