Abstract
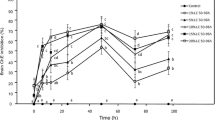
The use of various organophosphates to control mosquito populations is a common practice across the globe. We review the literature (LC50s) on dichlorvos, the primary breakdown product of Dibrom®, and use laboratory and field experiments to determine the lethal and sublethal (bioassays) effects of dichlorvos on two widely distributed and ecologically important estuarine invertebrate species, the marsh grass shrimp, Palaemonetes pugio and the Eastern oyster, Crassostrea virginica. Laboratory results based on LC50s and sublethal acetylcholinesterase (AChE) inhibition activity bioassays indicate that adult grass shrimp are more sensitive (∼ 500 × ) to dichlorvos than juvenile oysters. Although potentially an important factor for intertidal or shallow-dwelling estuarine organisms, the toxicity of dichlorvos was not enhanced in the presence of simulated sunlight for adult P. pugio. The most notable decreases in AChE activity were for grass shrimp and oysters exposed to dichlorvos concentrations above those considered ecologically relevant. In field experiments, both species were deployed in cages in unsprayed (n = 2) and sprayed (n = 3) sites and water samples collected pre- and post-spraying. Quantifiable dichlorvos levels were measured at the two narrowest creek treatment sites following mosquito spraying, suggesting that overspray can occur and there was evidence of a sublethal AChE response at these same sites. However, experiments at the widest creek revealed no measurable dichlorvos or sublethal responses. Results from this research suggest that adult grass shrimp are more sensitive to dichlorvos than juvenile oysters. Spraying near small tidal creeks may have measurable impacts on resident species, while larger (wider) creeks appear to be capable of buffering organisms from transient fluxes of mosquito control agents that may enter the system.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson G (1985) Species profiles: Life histories and environmental requirements of coastal fishes and invertebrates (Gulf of Mexico) -grass shrimp. U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service Biological Report. 82(11.35). U.S. Army Corps of Engineers TR EL-8-24, 19pp
Arnold GL, Luckenbach MW, Unger MA (2004) Runoff from tomato cultivation in the estuarine environment: biological effects of farm management practices. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 298:323–346
Boesch DF, Turner RE (1984) Dependence of fishery species on salt marshes; the role of food and refuge. Estuaries 7:460–468
Bolton-Warberg M (2005) Effects of the organophosphate insecticide dichlorvos on the daggerblade grass Shrimp, Palaemonetes pugio and the eastern oyster, Crassostrea virginica with reference to mosquito spraying. M.S. Thesis, College of Charleston, p 123
Calabrese EJ, Baldwin LA (1998) Hormesis as a biological hypothesis. Environ Health Perspect 106:357–362
Campbell GL, Marfin AA, Lanciotti RS, Gubler DJ (2002) West Nile Virus, Lancet Infect Dis 2:519–529
Chambers JR (1992) Coastal degradation and fish population losses. In: Stroud RH (ed) Stemming the tide of coastal fish habitat loss. National Coalition for Marine Conservation. Savannah, Georgia, p 285
Coen LD, Luckenbach MW, Breitburg DL (1999) The role of oyster reefs as essential fish habitat: a review of current knowledge and some new perspectives. In: Benaka LR (ed) Fish habitat: essential fish habitat and rehabilitation. American Fisheries Society, Symposium 22, Bethesda, MD. p 438–454
Coppage DL, Matthews E (1974) Short-term effects of OP pesticides on cholinesterases of estuarine fishes and pink shrimp. Bull Environ Contain Toxicol 11:483–488
Cusack R, Johnson G (1990) A study of dichlorvos (Nuvan; 2, 2 dichloroethenyl dimethyl phosphate), a therapeutic agent for the treatment of salmonids infected with sea lice (Lepeophtheirus salmonis). Aquaculture 90:101–112
Day JW, Hall CA, Kemp WM, Yanez-Arancibia A (1989) Estuarine ecology. John Wiley and Sons, New York, p 576
Dobson DP, Tack TJ (1991) Evaluation of the dispersion of treatment solutions of dichlorvos from marine salmon pens. Aquaculture 95:15–32
EPA (1995) Summary Report for Naled. Environmental Fate and Effects Division. Office of Prevention, Pesticides and Toxic Substances, p 26
Escartín E, Porte C (1997) The use of cholinesterase and carboxylesterase activities from Mytilus galloprovincialis in pollution monitoring. Environ Toxicol Chem 16:2090–2095
Eto E (1974) Organophosphorous pesticides and biological chemistry. CRC Press, Cleveland, OH, p 387
Finley DB, Scott GI, Daugomah JW, Layman SL, Reed LA, Sanders M, Sivertsen SK, Strozier ED (1999) Case study: Ecotoxicological assessment of urban and agricultural nonpoint source runoff effects on the grass shrimp, Palaemonetes pugio. In: Ecotoxicology and risk assessment for wetlands. Lewis MA, Mayer FL, Powell RL, Nelson MK, Klaine SJ, Henry MG, Dickson GW (eds). SETAC Press, USA, pp 243–274
Forget J, Pavilion JF, Menasria MR, Bocquene G (1998) Mortality and LC50 values for several stages of the marine copepod Tigriopus brevicornis (Müller) exposed to the metals arsenic and cadmium and the pesticides atrazine, carbofuran, dichlorvos and malathion. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 40:239–244
Fulton MH, Scott GI, Fortner A, Bidleman TF, Ngabe B (1993) The effects of urbanization on small high-salinity estuaries of the southeastern United States. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 25:476–484
Hennessey MK, Nigg HN, Habeck DH (1992) Mosquito (Diptera: Culicidae) adulticide drift into wildlife refuges of the Florida Keys. Environ Entomol 21:714–721
Holland AF, Sanger DM, Gawle CP, Lerberg SB, Santiago MS, Riekerk GHM, Zimmerman LE, Scott GI (2004) Linkages between tidal creek ecosystems and the landscape and demographic attributes of their watersheds. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 298:151–178
Jones CG, Lawton JH, Shachak M (1994) Organisms as ecosystem engineers. Oikos 69:373–386
Kennedy VS, Newell RIE, Eble AF (1996) The Eastern Oyster: Crassostrea virginica. Maryland Sea Grant, College Park, Maryland, p 734
Key PB, Fulton MH (1993) Lethal and sub-lethal effects of chlorpyrifos exposure on adult and larval stages of the grass shrimp, Palaemonetes pugio. J Environ Sci Health 28:621–640
Key PB, Fulton MH, Layman SL, Scott GI (1998a) Azinphosmethyl exposure to grass shrimp (Palaemonetes pugio) life stages with emphasis on larval acetylcholinesterase activity. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 60:645–650
Key PB, Fulton MH, Scott GI, Layman SL, Wirth EF (1998) Lethal and sub-lethal effects of malathion on three life stages of the grass shrimp, Palaemonetes pugio. Aquat Toxicol 40:311–322
Kirby MX (2004) Fishing down the coast: historical expansion and collapse of oyster fisheries along coastal margins. Proc Natl Acad Sci 101:13096–13099
Kneib RT (1985) Predation and disturbance by grass shrimp, Palaemonetes pugio Holthius in soft-substratum benthic invertebrate assemblages. J Exp Mar Bio Ecol 93:215–223
Kneib RT (1997) Early life stages of resident nekton in intertidal marshes. Estuaries 20:214–230
Lartiges SB, Garrigues PP (1995) Degradation kinetics of organophosphorous and organonitrogen pesticides in different waters under various environmental conditions. Environ Sci Technol 29:1246–1254
Le Bris H, Maffart P, Bocquené G, Buchet V, Galgani F, Blanc G (1995) Laboratory study on the effect of dichlorvos on two commercial bivalves. Aquaculture 138:139–144
Lehotay SJ, Harman-Fetcho JA, McConnell LL (1999) Agricultural pesticide residues in oysters and water from two Chesapeake Bay tributaries. Mar Pollut Bull 37:32–44
Leight AK, Scott GI, Fulton MH, Daugomah JW (2005) Long term monitoring of grass shrimp Palaemontes spp. population metrics at sites with agricultrual runoff influences. Integr Comp Biol 45:143–150
Lerberg SB, Holland AF, Sanger DM (2000) Responses of tidal creek macrobenthic communities to the effects of watershed development. Estuaries 23:838–853
Lundebye AK, Curtis T, Braven J, Depledge M (1997) Comparative properties of channel catfish (Ictalurus punctatus) and blue crab (Callinectes sapidus) acetylcholinesterase. Comp Biochem Physiol, Part C: Toxicol Pharmacol 91:293–300
Mallin MA, Burkholder JM, Cahoon LB, Posey MH (2000) North and South Carolina coasts. Mar Pollut Bull 41:56–75
Mayer FL Jr, Ellersieck, MR (1986) Manual of Acute Toxicity: Interpretation and Data Base for 410 Chemicals and 66 Species of Freshwater Animals. Resour Publ No. 160, U.S. Dept. Interior, Fish Wildl. Serv. Washington, DC, 505pp
McHenery JG, Francis C (1990) Toxicity of dichlorvos to stage 4 Homarus gammarus larvae. Scottish Fisheries Working Paper 8/90
McHenery JG, Saward D, Seaton DD (1991) Lethal and sub-lethal effects of the salmon debusing agent dichlorvos on the larvae of the lobster (Homarus gammarus L.) and herring (Clupea harengus L.). Aquaculture 98:331–347
Mitsch WJ, Gosselink JG (1993) Wetlands, 2nd edition. Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York p 72
National Research Council (2004) Nonnative oysters in Chesapeake Bay. National Academies Press. Washington, DC, p 325
Payne NJ, Helson BV, Sundaram KMS, Fleming RA (1988) Estimating buffer zone widths for pesticide applications. Pestic Sci 24:147–161
Pierce RH (1998) Effects of mosquito control measures on non-targeted organisms in the Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary. Mote Marine Laboratory Technical Report No 609
Scott GI, Fulton MH, Crosby MC, Key PB, Daugomah JW, Walden JT, Strozier ED, Louden CJ, Chandler GT, Fidleman TF, Jackson KL, Hampton TW, Hoffman T, Shultz A, Bradford M (1992) Agricultural nonpoint runoff effects on estuarine organisms: correlating laboratory and field bioassays and ecotoxicological biomomtoring. Final Report. U.S. EPA, Gulf Breeze, FL, p 281
Scott GI, Fulton MH, Moore DW, Wirth EF, Chandler GT, Key PB, Daugomah JW, Strozier ED, Devane J, Clark JR, Lewis MA, Finley DB, Ellenberg W, Karnaky JJ Jr (1999) Assessment of risk reduction strategies for the management of agricultural nonpoint source pesticide runoff in estuarine ecosystems. Toxicol and Ind Health 15:200–213
Snoo GR, de Wit PJ (1998) Buffer zones for reducing pesticides drift to ditches and risks to aquatic organisms. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 41:112–118
Spiehnan A, D’Antonio M (2001) Mosquito: a natural history of our most persistent and deadly foe. Hyperion. New York, p 247
Stanley DW, Sellers MA (1986) Species profile: life histories and environmental requirements of coastal fishes and invertebrates (Gulf of Mexico)-American Oyster. U.S. Fish Wildl Serv Biol Rep 82(11.64) U.S. Army Corps of Engineers, TR EL-82-4, p 25
Stebbing ARD (1982) Hormesis- the stimulation of growth by low levels of inhibitors. Sci Total Environ 22:213–234
Sturm A, da Silva de Assis HC, Hansen PD (1999) Cholinesterases of marine teleost fish: Enzymological characterization and potential use in biomonitoring of neurotoxic contamination. Mar Environ Res 47:389–398
Tietze NS, Hester PG, Shaffer KR (1994) Mass recovery of malathion in simulated open field mosquito adulticides tests. Arch Environ Contain Toxicol 26:473–477
Tietze NS, Hester PG, Shaffer KR (1995) Acute effects of Permanone registered 31–66 (permethrin-piperonyl butoxide) on nontarget minnows and grass shrimp. J Am Mosq Control Assoc 11 476–479
U.S. Department of Interior, Fish and Wildlife Service (1980) Handbook of Acute Toxicity of Chemicals to Fish and Aquatic Invertebrates. Resource Publication No.137. Washington, DC: U.S. Government Printing Office
US Public Health Service (1995) Hazardous Substance Data Bank. Washington, D.C
Vernberg FJ, Vernberg WB, Blood E, Fortner A, Fulton MH, McKellar H, Mitchner W, Scott GI, El-Fiji K (1992) Impacts of urbanization on high salinity estuaries of the Southeastern U.S. Netherlands. J Deep Sea Res 30:239–248
Verschueren K (1983) Handbook of environmental data on organic chemicals, 2nd ed., Van Nostrand Reinhold Company, New York, NY, 839pp
Wang TC, Lenahan RA, Tucker Jr JW (1987) Deposition and persistence of aerially-applied fenthion in a Florida estuary. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 38:226–231
Weinstein MP, Kreeger DA (2000) Concepts and controversies in tidal marsh ecology. Kluwere Academic Publishers, Boston, p 875
Wells DE, Robson JN, Finlayson DM (1990) Fate of dichlorvos (DDVP) in sea water following treatment for salmon louse, Lepeophtheirus salmonis, infestations in Scottish fish farms. Scottish Fisheries Working Paper 13/90
Wiegert RG, Freeman BJ (1990) Tidal salt marshes of the southeast Atlantic Coast: A community profile. U.S. Fish Wildl Serv Biol Rep 85:1–67
Acknowledgments
We wish to acknowledge Amy Ringwood for technical assistance and Keith Walters for statistical advice throughout this study. Special thanks to Pete Key, Marie DeLorenzo, Jen Hoguet, Chuck Keppler, Kevin Crawford, Martin Hyatt, Ed Harne, staff at the Center for Coastal Environmental Health and Biomolecular Research Lab (CCEHBR) and the Shellfish Research Section, Marine Resources Research Institute, SCDNR, for their laboratory and field assistance. This research was made possible through grant funds to L.D.C. from the SC Maine Recreational Fisheries Stamp Program, CICEET (NA17OZ2507), and the South Carolina Sea Grant Consortium (nos. NA86RG0052 and NA16RG2250) and to J.E.W. through The Citadel Foundation. This is contribution no. 294 from the Grice Marine Laboratory, College of Charleston, and from SCDNR no. 591.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bolton-Warberg, M., Coen, L.D. & Weinstein, J.E. Acute Toxicity and Acetylcholinesterase Inhibition in Grass Shrimp (Palaemonetes pugio) and Oysters (Crassostrea virginica) Exposed to the Organophosphate Dichlorvos: Laboratory and Field Studies. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 52, 207–216 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00244-005-0325-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00244-005-0325-z