Abstract
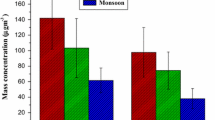
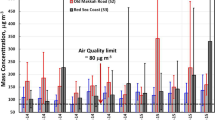
Exposures to airborne metals are known to cause physiological responses in organisms and wide-ranging health effects in humans. Hence determination of metals in particulate matter is important from a toxicological perspective. In the current study heavy metals associated with respirable (RSPM) and nonrespirable (NRSPM) fractions of suspended particulate matter were estimated in air samples from six stations in Coimbatore, India, during March 1999 to February 2001. The mean quantity of heavy metals in RSPM was in the order Zn > Cu > Pb > Ni > Cr > Cd. Concentrations of these heavy metals were in the range of BDL (below detectable level) to 2147 ng/m3 in RSPM. The highest level of lead (2147 ng/m3) was recorded at an industrial station. The station also had the highest mean value (481 ± 544.3 ng/m3), suggesting the importance of industrial operations in determining the ambient concentrations of lead. Significant positive correlation among metals excepting lead and copper suggests that they originate mostly from a common source. Air samples of urban and industrial areas showed higher concentrations than residential (Urban) and suburban areas.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mohanraj, R., Azeez, P. & Priscilla, T. Heavy Metals in Airborne Particulate Matter of Urban Coimbatore. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 47, 162–167 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00244-004-3054-9
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00244-004-3054-9