Abstract
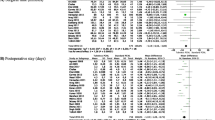
The objective of this study was to conduct a systematic review and meta-analysis to evaluate the efficacy and safety of tubeless versus standard percutaneous nephrolithotomy (PCNL). Relevant randomized or quasi-randomized controlled trials studies were identified from electronic database (Cochrane CENTRAL, Medline and EMBASE et al.). The retrieval time ended in August 2010. The quality of the included trials was assessed and the data were extracted independently by two reviewers. We divided the participants who received standard PCNL into two subgroups: small tube (4–10 F) group and big tube (14–24 F) group to reduce heterogeneity and bias. Efficacy (hospital stay time, operative time, stone-free rate) and safety (postoperative pain and analgesia requirement, postoperative fever, blood transfusion, urine leakage) were explored by using review manager v5.0. Fourteen randomized controlled trials comprising 776 subjects met the inclusion criteria. Our meta-analysis showed that there were statistically significant differences in hospital stay, postoperative analgesic requirement and urine leakage between tubeless and standard PCNL. In operative time, significant difference was found between tubeless and big tube group. No statistically significant differences were found in stone-free rate, postoperative fever, and blood transfusion between tubeless and standard PCNL. In conclusion, Tubeless PCNL was an effective and safe procedure for treatment of renal stones in selected patients, with shorter hospital stay, less analgesic requirement, lower urine leakage and without increased complications. Patients can receive great benefit from tubeless PCNL and it will become more palatable to patients as well as more cost-effective than standard PCNL in the future.









Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- PCNL:
-
Percutaneous nephrolithotomy
- VAS:
-
Visual analog scale
- CI:
-
Confidence interval
- SD:
-
Standard deviation
- OR:
-
Odds ratio
- MD:
-
Mean difference
References
Fernstrom I, Johannson B (1976) Percutaneous pyelolithotomy: A new extraction technique. Scand J Urol Nephrol 10:257–259
Winfield HN, Weyman P, Clayman RV (1986) Percutaneous nephrostolithotomy: complications of premature nephrostomy tube removal. J Urol 136:77–79
Jackman SV, Docimo SG, Cadeddu JA et al (1998) The “miniperc” technique: a less invasive alternative to percutaneous nephrolithotomy. World J Urol 16:371–374
Bellman GC, Davdoff R, Candela J, Gerspach J, Kurtz S, Stout L (1997) Tubeless percutaneous renal surgery. J Urol 157:1578–1582
Shah HN, Sodha HS, Khandkar AA et al (2008) A randomized trial evaluating type of nephrostomy drainage after percutaneous nephrolithotomy: small bore v tubeless. J Endourol 22:1433–1439
Jadad AR, Moore RA, Carroll D, Jenkinson C, Reynolds DJM, Gavaghan DJ, McQuay HJ (1996) Assessing the quality of reports of randomized clinical trials: is blinding necessary? Controlled Clin Trials 17:1–12
Higgins JPT, Green S (2009) Cochrane handbook for systematic reviews of interventions, Version 5.0.2 updated September 2009. The Cochrane Collaboration
Desai MR, Kukreja RA, Desai MM, Mhaskar SS, Wani KA, Patel SH, Bapat SD (2004) A prospective randomized comparison of type of nephrostomy drainage following percutaneous nephrostolithotomy: large bore versus small bore versus tubeless. J Urol 172:565–567
Feng MI, Tamaddon K, Mikhail A, Kaptein JS, Bellman GC (2001) Prospective randomized study of various techniques of percutaneous nephrolithotomy. Urology 58:345–350
Marcovich R, Jacobson AI, Singh J, Shah D, El-Hakim A, Lee BR, Smith AD (2004) No panacea for drainage after percutaneous nephrolithotomy. J Endourol 18:743–747
Tefekli A, Altunrende F, Tepeler K, Tas A, Aydin S, Muslumanoglu AY (2006) Tubeless percutaneous nephrolithotomy in selected patients: a prospective randomized comparison. Int Urol Nephrol 39:57–63
Agrawal MS, Agrawal M, Gupta A et al (2008) A randomized comparison of tubeless and standard percutaneous nephrolithotomy. J Endourol 22:439–442
Choi M, Brusky J, Weaver J et al (2006) Randomized trial comparing modified tubeless percutaneous nephrolithotomy with tailed stent with percutaneous nephrostomy with small bore tube. J Endourol 20:766–770
Sofikerim M, Demirci D, Huri E et al (2007) Tubeless percutaneous nephrolithotomy: Safe even in supracostal access. J Endourol 21:967–972
Singh I, Singh A, Mittal G (2008) Tubeless percutaneous nephrolithotomy: is it really less morbid? J Endourol 22:427–434
Kara C, Resorlu B, Bayindir M, Unsal A (2010) A randomized comparison of totally tubeless and standard percutaneous nephrolithotomy in elderly patients. Urology 76:289–294
Mishra S, Sabnis RB, Kurien A et al (2010) Questioning the wisdom of tubeless percutaneous nephrolithotomy (PCNL): a prospective randomized controlled study of early tube removal vs tubeless PCNL. BJU Int 106:1045–1048
Istanbulluoglu MO, Ozturk B, Gonen M, Cicek T, Ozkardes H (2009) Effectiveness of totally tubeless percutaneous nephrolithotomy in selected patients: a prospective randomized study. Int Urol Nephrol 41:541–545
Weiland D, Pedro RN, Anderson JK, Best SL, Lee C, Hendlin K, Kim J, Monga M (2007) Randomized prospective evaluation of nephrostomy tube configuration: impact on postoperative pain. Int Braz J Urol 33:313–322
Falahatkar S, Khosropanah I, Roshani A, Niroumand H, Nikpour S (2008) Safety and efficacy of tubeless percutaneous nephrolithotomy. Acta Medica Iranica 46:383–385
Jou YC, Cheng MC, Sheen JH, Lin CT, Chen PC (2004) Cauterization of access tract for nephrostomy tube-free percutaneous nephrolithotomy. J Endourol 18:547–549
Al-Ba’adani TH, Al-Kohlany KM, Al-Adimi A, Al-Towaity M, Al-Baadani T, Alwan M, Al-Hussieni M, Al-Germozi S, Al-Masani M, Al-Badwy K, El-Nono IH (2008) Tubeless percutaneous neprolithotomy: the new gold standard, Int Urol Nephrol 40:603–608
Lee DI, Uribe C, Eichel L, Khonsari S, Basillote J, Park HK, Li CC, McDougall EM, Clayman RV (2004) Sealing percutaneous nephrolithotomy tracts with gelatin matrix hemostatic sealant: initial clinical use. J Urol 171:575–578
DavidoV R, Bellman GC (1997) Influence of technique of percutaneous tract creation on incidence of renal hemorrhage. J Urol 157:1229–1231
Salem HK, Morsi HA, Omran A, Daw MA (2007) Tubeless percutaneous nephrolithotomy in children. J Pediatr Urol 3:235–238
Yang RM, Bellman GC (2004) Tubeless percutaneous renal surgery in obese patients. Urology 63:1036–1041
Lojanapiwat B (2010) Does previous open nephrolithotomy affect the efficacy and safety of tubeless percutaneous nephrolithotomy? Urol Int 85:42–46
Beiko D, Lee L (2010) Outpatient tubeless percutaneous nephrolithotomy: the initial case series. Can Urol Assoc J 4:E86–E90
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank the staff and colleagues in the Chinese Cochrane Centre for their help and support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yuan, H., Zheng, S., Liu, L. et al. The efficacy and safety of tubeless percutaneous nephrolithotomy: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Urol Res 39, 401–410 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00240-010-0355-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00240-010-0355-5