Abstract
Background
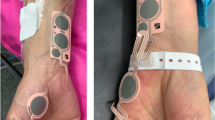
Perforator flaps surgery barely damages underlying muscle function, but only clinical qualitative evidences exist about muscle preservation after surgical dissection. We have employed for the first time electromyography and nerve conduction studies in evaluating the latissimus dorsi electrical muscle function after thoraco-dorsal artery perforator flap dissection in a retrospective cohort study.
Methods
We included ten consecutive patients requiring axillary reconstruction with thoraco-dorsal artery perforator flap, from June 2017 to June 2018. All patients were suffering from hidradenitis suppurativa. Electromyography (EMG) and nerve conduction study (NCS) were conducted on each patient, both before and after the operation. Differences between pre- and postoperative amplitude and latency values were calculated.
Results
Postoperative signal amplitude and latency means did not differ significantly from the preoperative one. Operative time and area of excision did not correlate with changes of electrical function.
Conclusions
This is the first quantitative analysis performed for the evaluation of muscle electrical activity after perforator flap surgery. Perforator pedicle intra-muscular dissection does not cause any injury to the muscle fibers. TDAP flap confirms to be a safe procedure for latissimus dorsi muscle function.
Level of evidence: Level III, therapeutic study.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Angrigiani C, Grilli D, Siebert J (1995) Latissimus dorsi musculocutaneous flap without muscle. Plast Reconstr Surg. https://doi.org/10.1097/00006534-199512000-00014
Rindom MB, Gunnarsson GL, Lautrup MD, Christensen RD, Sørensen JA, Thomsen JB (2018) Shoulder-related donor site morbidity and patient-reported satisfaction after delayed breast reconstruction with pedicled flaps from the back: a comparative analysis. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bjps.2018.04.009
Russell RC, Pribaz J, Zook EG, Leighton WD, Eriksson E, Smith CJ (1986) Functional evaluation of latissimus dorsi donor site. Plast Reconstr Surg. https://doi.org/10.1097/00006534-198609000-00009
Hamdi M, Van Landuyt K, Hijjawi JB, Roche N, Blondeel P, Monstrey S (2008) Surgical technique in pedicled thoracodorsal artery perforator flaps: a clinical experience with 99 patients. Plast Reconstr Surg 121(5):1632–1641
Nail-Barthelemy R, Stroumza N, Qassemyar Q, Delage M, Nassif A, Atlan M (2018) Evaluation of the mobility of the shoulder and quality of life after perforator flaps for recalcitrant axillary hidradenitis. Ann Chir Plast Esthet. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.anplas.2018.01.003
Beaton DE, Wright JG, Katz JN et al (2005) Development of the QuickDASH: comparison of three item-reduction approaches. J Bone Jt Surg Ser A. https://doi.org/10.2106/JBJS.D.02060
Bottero L, Lefaucheur JP, Fadhul S, Raulo Y, Collins ED, Lantieri L (2004) Electromyographic assessment of rectus abdominis muscle function after deep inferior epigastric perforator flap surgery. Plast Reconstr Surg. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.PRS.0000095941.86060.8E
Wormald JCR, Balzano A, Clibbon JJ, Figus A (2014) Surgical treatment of severe hidradenitis suppurativa of the axilla: thoracodorsal artery perforator (TDAP) flap versus split skin graft. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg 67(8):1118–1124
Marchesi A, Parodi PC, Brioschi M et al (2016) Soft-tissue defects of the Achilles tendon region: Management and reconstructive ladder. Review of the literature. Injury. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.injury.2016.07.053
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation, data collection and analysis were performed by Francesco Bordone, Michele Sterlicchio, Giovanna Zaccaria, Veronica Ponti, Stefano Marcelli. The first draft of the manuscript was written by Andrea Marchesi and Francesco Amendola, and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. Daniele Tosi independently reviewed the manuscript and the references. Luca Vaienti eventually reviewed all the study and personally guaranteed for the correct execution of all study phases. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Marchesi Andrea, Amendola Francesco, Bordone Francesco, Sterlicchio Michele, Ponti Veronica, Marcelli Stefano, Daniele Tosi, Giovanna Zaccaria, Vaienti Luca declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Human rights
The study has been performed in accordance with the ethical standards as laid down in the 1964 Declaration of Helsinki and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Ethical approval
Complying with the specific requirements of our country, Ethical approval was not needed, due to minor invasiveness of the electromyography.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Marchesi, A., Amendola, F., Bordone, F. et al. Muscle electrical activity after perforator flap surgery: a pilot cohort study. Eur J Plast Surg 43, 165–168 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00238-019-01581-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00238-019-01581-3