Abstract
Background
Lower face dimensions have a great impact on the perception of nasal beauty. For this reason, evaluation of the lower face is important in patients applied for rhinoplasty. In this study, we aimed to describe the values of lower face anthropometric measurements in Turkish patients who applied for rhinoplasty and to compare these values with measurements of individuals who are pleased with their nasal appearance.
Methods
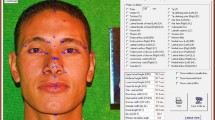
A Turkish population of 252 rhinoplasty-negative individuals and 171 rhinoplasty patients were included in this study as the control and rhinoplasty groups. Using the preoperative photographs of the facial profile, seven vertical measurements were taken and seven indices were used to determine the relationships between measurements of the lower face.
Results
In the rhinoplasty group, most vertical profile measurements were greater in males. The only variables with no gender differences were lower and upper vermilion heights. Only variables with a significant difference between two groups were upper lip vermilion height in females and upper lip height in males.
Conclusions
This study provides objective reference material for the evaluation of the lower face when planning for rhinoplasty. Besides, the differences found between two groups emphasize the importance of the nasolabial region when planning for rhinoplasty.
Level of Evidence: Level II, diagnostic study.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Rhodes G (2006) The evolutionary psychology of facial beauty. Annu Rev Psychol 57:199–226
Cellerino A (2003) Psychobiology of facial attractiveness. J Endocrinol Invest 26:45–48
Zaidel DW, Cohen JA (2005) The face, beauty, and symmetry: perceiving asymmetry in beautiful faces. Int J Neurosci 115:1165–1173
Tessier P, Farkas LGMI (1987) Anthropometric facial proportions in medicine. Charles C Thomas, Springfield
Edler R, Agarwal P, Wertheim D et al (2006) The use of anthropometric proportion indices in the measurement of facial attractiveness. Eur J Orthod 28:274–281
Stucker FJ Jr (1982) Management of the scoliotic nose. Laryngoscope 92:128–134
Vuyk HD (2000) A review of practical guidelines for correction of the deviated, asymmetric nose. Rhinology 38:72–78
Farkas LG, Kolar JC, Munro IR (1986) Geography of the nose: a morphometric study. Aesthetic Plast Surg 10:191–223
Choe KS, Yalamanchili HR, Litner JA et al (2006) The Korean American woman’s nose: an in-depth nasal photogrammatic analysis. Arch Facial Plast Surg 8:319–323
Gunter JP, Rohrich RJ (1988) Management of the deviated nose. The importance of septal reconstruction. Clin Plast Surg 15:43–55
Falces E, Wesser D, Gorney M (1970) Cosmetic surgery of the non-Caucasian nose. Plast Reconstr Surg 45:317–325
Le TT, Farkas LG, Ngim RC et al (2002) Proportionality in Asian and North American Caucasian faces using neoclassical facial canons as criteria. Aesthetic Plast Surg 26:64–69
Posen JM (1967) A longitudinal study of the growth of the nose. Am J Orthod 53:746–756
Vegter F, Hage JJ (2000) Clinical anthropometry and canons of the face in historical perspective. Plast Reconstr Surg 106:1090–1096
Farkas LG, Katic MJ, Forrest CR et al (2005) International anthropometric study of facial morphology in various ethnic groups/races. J Craniofac Surg 16:615–646
Douglas TS (2004) Image processing for craniofacial landmark identification and measurement: a review of photogrammetry and cephalometry. Comput Med Imaging Graph 28:401–409
Tuncel U, Turan A, Kostakoglu N (2013) Digital anthropometric shape analysis of 110 rhinoplasty patients in the Black Sea Region in Turkey. J Craniomaxillofac Surg 41:98–102
Mishima K, Mori Y, Yamada T et al (2002) Anthropometric analysis of the nose in the Japanese. Cells Tissues Organs 170:198–206
Porter JP, Olson KL (2003) Analysis of the African American female nose. Plast Reconstr Surg 111:620–626, discussion 627–628
Dong Y, Zhao Y, Bai S et al (2010) Three-dimensional anthropometric analysis of the Chinese nose. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg 63:1832–1839
Choi JY, Park JH, Javidnia H et al (2013) Effect of various facial angles and measurements on the ideal position of the nasal tip in the Asian patient population. JAMA Facial Plast Surg 15:417–421
Jayaratne YS, Deutsch CK, Zwahlen RA (2014) Nasal morphology of the Chinese: three-dimensional reference values for rhinoplasty. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 150:956–961
Anic-Milosevic S, Mestrovic S, Prlic A et al (2010) Proportions in the upper lip-lower lip-chin area of the lower face as determined by photogrammetric method. J Craniomaxillofac Surg 38:90–95
Bishara SE, Jorgensen GJ, Jakobsen JR (1995a) Changes in facial dimensions assessed from lateral and frontal photographs. Part I—methodology. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop 108:389–393
Bishara SE, Jorgensen GJ, Jakobsen JR (1995b) Changes in facial dimensions assessed from lateral and frontal photographs. Part II—results and conclusions. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop 108:489–499
Farkas LG, Katic MJ, Hreczko TA et al (1984) Anthropometric proportions in the upper lip-lower lip-chin area of the lower face in young white adults. Am J Orthod 86:52–60
Park YC, Burstone CJ (1986) Soft-tissue profile—fallacies of hard-tissue standards in treatment planning. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop 90:52–62
Yuen SW, Hiranaka DK (1989) A photographic study of the facial profiles of southern Chinese adolescents. Quintessence Int 20:665–676
Fernandez-Riveiro P, Suarez-Quintanilla D, Smyth-Chamosa E et al (2002) Linear photogrammetric analysis of the soft tissue facial profile. Am J Orthod Dentofac Orthop 122:59–66
Arnett GW, Bergman RT (1993) Facial keys to orthodontic diagnosis and treatment planning—part II. Am J Orthod Dentofac Orthop 103:395–411
Legan HL, Burstone CJ (1980) Soft tissue cephalometric analysis for orthognathic surgery. J Oral Surg 38:744–751
Ethical standards
This work was approved by decision number 13/36 dated 03.02.2013 by the Başkent University Clinical Study Ethical Committee (project; KA 13:61) and therefore carried out in compliance with the Declaration of Helsinski.
Conflict of interest
Ozan L. Abbas, Ayla Kürkçüoğlu, Can Pelin, Ayşe Canan Yazıcı declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Patients consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Abbas, O.L., Kürkçüoğlu, A., Pelin, C. et al. Anthropometric measurement and analysis of the lower face in Turkish rhinoplasty patients. Eur J Plast Surg 38, 449–458 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00238-015-1135-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00238-015-1135-9