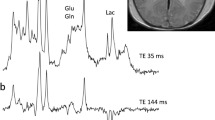
Abstract
Proton MRS of the brain provides the ability to gather direct information regarding the metabolic status of the brain at the time of MRI. Although selective vulnerability of brain tissue may yield distinct imaging patterns in neurometabolic disorders, it is not uncommon for the brain MRI to be normal, nonspecific, or show ambiguous abnormalities among several possible diagnoses, metabolic, or otherwise. This review highlights childhood neurometabolic diseases in which 1H MRS may show diagnostic or suggestive metabolic profiles without complicated acquisition or postprocessing techniques.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barkovich AJ, Patay Z (2012) Metabolic, toxic, and inflammatory brain disorders. In: Barkovich AJ, Raybaud C (eds) Pediatric neuroimaging, 5th edn. Lippincott, Williams, & Wilkins, Philadelphia
Karimzadeh P, Jafari N, Nejad Biglari H, Rahimian E, Ahmadabadi F et al (2014) The clinical features and diagnosis of Canavan’s disease: a case series of iranian patients. Iran J Child Neurol 8(4):66–71
Janson CG, McPhee SW, Francis J, Shera D, Assadi M et al (2006) Natural history of Canavan disease revealed by proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy (1H-MRS) and diffusion-weighted MRI. Neuropediatrics 37(4):209–221
Rossi A, Biancheri R (2013) Magnetic resonance spectroscopy in metabolic disorders. Neuroimaging Clin N Am 23(3):425–448
Blüml S, Panigrahy A (2013) MR spectroscopy of pediatric brain disorders. Springer-Verlag, New York
Whitehead MT, Gropman AL (2018) Other metabolic syndromes. In: Lewis J, Keshari K (eds) Imaging and Metabolism. Springer, Cham
Kingsley PB, Shah TC, Woldenberg R (2006) Identification of diffuse and focal brain lesions by clinical magnetic resonance spectroscopy. NMR Biomed 19(4):435–462
Poretti A, Blaser SI, Lequin MH, Fatemi A, Meoded A, Northington FJ et al (2013) Neonatal neuroimaging findings in inborn errors of metabolism. J Magn Reson Imaging 37(2):294–312
Patay Z, Blaser SI, Poretti A, Huisman TA (2015) Neurometabolic diseases of childhood. Pediatr Radiol 45(Suppl 3):S473–S484
Gordon N (2001) Canavan disease: a review of recent developments. Eur J Paediatr Neurol 5(2):65–69
De Bernardo G, Giordano M, Sordino D, Buono S (2015) Early diagnosis of Canavan syndrome: how can we get there? BMJ Case Rep bcr2014208755.
Varho T, Komu M, Sonninen P, Holopainen I, Nyman S, Manner T et al (1999) A new metabolite contributing to N-acetyl signal in 1H MRS of the brain in Salla disease. Neurology 52(8):1668–1672
Assadi M, Janson C, Wang DJ, Goldfarb O, Suri N, Bilaniuk L, Leone P (2010) Lithium citrate reduces excessive intra-cerebral N-acetyl aspartate in Canavan disease. Eur J Paediatr Neurol 14(4):354–359
Barkhof F, van der Knaap MS (2009) Unraveling pathology in juvenile Alexander disease: serial quantitative MR imaging and spectroscopy of white matter. Neuroradiology 51(10):669–675
van der Knaap MS, Naidu S, Breiter SN, Blaser S, Stroink H et al (2001) Alexander disease: diagnosis with MR imaging. Am J Neuroradiol 22:541–552
Davison JE, Davies NP, English MW, Philip S, MacPherson LKR et al (2011) Magnetic resonance spectroscopy in the diagnostic evaluation of brainstem lesions in Alexander disease. J Child Neurol 26(3):356–360
Brockmann K, Dechent P, Meins M, Haupt M, Sperner J, Stephani U et al (2003) Cerebral proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy in infantile Alexander disease. J Neurol 250(3):300–306
Whitehead MT, Fricke ST, Gropman AL (2015) Structural brain defects. Clin Perinatol 42(2):337–361 ix
Huisman TA, Thiel T, Steinmann B, Zeilinger G, Martin E (2002) Proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy of the brain of a neonate with nonketotic hyperglycinemia: in vivo-in vitro (ex vivo) correlation. Eur Radiol 12:858–861
Stence NV, Fenton LZ, Levek C, Tong S, Coughlin CR 2nd, Hennermann JB et al (2019) Brain imaging in classic nonketotic hyperglycinemia: quantitative analysis and relation to phenotype. J Inherit Metab Dis 42(3):438–450
Heindel W, Kugel H, Roth B (1993) Noninvasive detection of increased glycine content by proton MR spectroscopy in the brains of two infants with nonketotic hyperglycinemia. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 14(3):629–635
Jan W, Zimmerman RA, Wang ZJ, Berry GT, Kaplan PB, Kaye EM (2003) MR diffusion imaging and MR spectroscopy of maple syrup urine disease during acute metabolic decompensation. Neuroradiology 45(6):393–399
Sener RN (2007) Maple syrup urine disease: diffusion MRI, and proton MR spectroscopy findings. Comput Med Imaging Graph 31(2):106–110
Gropman A (2010) Brain imaging in urea cycle disorders. Mol Genet Metab 100(Suppl 1):S20–S30
Sen K, Anderson AA, Whitehead MT, Gropman AL (2021) Review of multi-modal imaging in urea cycle disorders: the old, the new, the borrowed, and the blue. Front Neurol 12:632307
Pacheco-Colón I, Fricke S, VanMeter J, Gropman AL (2014) Advances in urea cycle neuroimaging: proceedings from the 4th International Symposium on urea cycle disorders, Barcelona, Spain. Mol Genet Metab 113(1-2):118–126
Sen K, Whitehead MT, Gropman AL (2020) Multimodal imaging in urea cycle-related neurological disease - what can imaging after hyperammonemia teach us? Transl Sci Rare Dis 5(1-2):87–95
Gunz AC, Choong K, Potter M, Miller E (2013) MRI findings and neurodevelopmental outcomes in neonates with urea-cycle defects. Int Med Case Rep J 6:41–48
Bireley WR, Van Hove JL, Gallagher RC, Fenton LZ (2012) Urea cycle disorders: brain MRI and neurological outcome. Pediatr Radiol 42(4):455–462
Sijens PE, Reijngoud DJ, Soorani-Lunsing RJ, Oudkerk M, van Spronsen FJ (2006) Cerebral 1H MR spectroscopy showing elevation of brain guanidinoacetate in argininosuccinate lyase deficiency. Mol Genet Metab 88(1):100–102
Güngör S, Akinci A, Firat AK, Tabel Y, Alkan Y (2008) Neuroimaging findings in hyperargininemia. J Neuroimaging 18(4):457–462
Fourati H, Ellouze E, Ahmadi M, Chaari D, Kamoun F, Hsairi I et al (2016) MRI features in 17 patients with l2 hydroxyglutaric aciduria. Eur J Radiol Open 3:245–250
Goffette SM, Duprez TP, Nassogne MCL, Vincent MFA, Jacobs C, Sindic CJ (2006) l-2-Hydroxyglutaric aciduria: clinical, genetic, and brain MRI characteristics in two adult sisters. Eur J Neurol 13(5):499–504
Reddy N, Calloni SF, Vernon HJ, Boltshauser E, Huisman TAGM, Soares BP (2018) Neuroimaging findings of organic acidemias and aminoacidopathies. Radiographics 38(3):912–931
Lorek AK, Penrice JM, Cady EB, Leonard JV, Wyatt JS, IIes RA et al (1996) Cerebral energy metabolism in isovaleric acidaemia. Arch Dis Child Fetal Neonatal Ed 74(3):F211–F213
Takahashi Y, Sukegawa K, Aoki M, Ito A, Suzuki K, Sakaguchi H et al (2001) Evaluation of accumulated mucopolysaccharides in the brain of patients with mucopolysaccharidoses by (1)H-magnetic resonance spectroscopy before and after bone marrow transplantation. Pediatr Res 49(3):349–355
Martin P, Hagberg GE, Schultz T, Harzer K, Klose U, Bender B, et al (2020) T2-pseudonormalization and microstructural characterization in advanced stages of late-infantile metachromatic leukodystrophy. Clin Neuroradiol [Epub ahead of print]
Kruse B, Hanefeld F, Christen HJ, Bruhn H, Michaelis T, Hänicke W et al (1993) Alterations of brain metabolites in metachromatic leukodystrophy as detected by localized proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy in vivo. J Neurol 241(2):68–74
Martin A, Sevin C, Lazarus C, Bellesme C, Aubourg P, Adamsbaum C (2012) Toward a better understanding of brain lesions during metachromatic leukodystrophy evolution. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 33(9):1731–1739
van Rappard DF, Klauser A, Steenweg ME, Boelens JJ, Bugiani M, van der Knaap MS et al (2018) Quantitative MR spectroscopic imaging in metachromatic leukodystrophy: value for prognosis and treatment. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 89(1):105–111
Sener RN (2003) Metachromatic leukodystrophy. Diffusion MR imaging and proton MR spectroscopy. Acta Radiol 44(4):440–443
Dali C, Hanson LG, Barton NW, Fogh J, Nair N, Lund AM (2010) Brain N-acetylaspartate levels correlate with motor function in metachromatic leukodystrophy. Neurology 75(21):1896–1903
Morana G, Biancheri R, Dirocco M, Filocamo M, Marazzi MG, Pessagno A, Rossi A (2009) Enhancing cranial nerves and cauda equina: an emerging magnetic resonance imaging pattern in metachromatic leukodystrophy and krabbe disease. Neuropediatrics 40(6):291–294
Avenarius DF, Svendsen JS, Malm D (2011) Proton nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopic detection of oligomannosidic n glycans in alpha-mannosidosis: a method of monitoring treatment. J Inherit Metab Dis 34(5):1023–1027
Danielsen ER, Lund AM, Thomsen C (2013) Cerebral magnetic resonance spectroscopy demonstrates long-term effect of bone marrow transplantation in α-mannosidosis. JIMD Rep 11:49–52
Majovska J, Nestrasil I, Paulson A, Jurickova K, Hlavata A, Lund T et al (2020) White matter alteration and cerebellar atrophy are hallmarks of brain MRI in alpha-mannosidosis. Mol Genet Metab S1096-7192(20):30253–30255
Mamourian AC, Hopkin JR, Chawla S, Poptani H (2010) Characteristic MR spectroscopy in fucosidosis: in vitro investigation. Pediatr Radiol 40(8):1446–1449
Ediz SS, Aralasmak A, Yilmaz TF, Toprak H, Yesil G, Alkan A (2016) MRI and MRS findings in fucosidosis; a rare lysosomal storage disease. Brain Dev 38(4):435–438
Oner AY, Cansu A, Akpek S, Serdaroglu A (2007) Fucosidosis: MRI and MRS findings. Pediatr Radiol 37(10):1050–1052
Wilken B, Dechent P, Hanefeld F, Frahm J (2008) Proton MRS of a child with Sandhoff disease reveals elevated brain hexosamine. Eur J Paediatr Neurol 12(1):56–60
Kumar D, Ramanathan S, Khanna M, Palaniappan Y (2014) Bithalamic T2 hypointensity: a diagnostic clue for Sandhoff's disease. Neurol India 62(4):481–482
Mascalchi M, Montomoli M, Guerrini R (2018) Neuroimaging in mitochondrial disorders. Essays Biochem 62(3):409–421
Lunsing RJ, Strating K, de Koning TJ, Sijens PE (2017) Diagnostic value of MRS-quantified brain tissue lactate level in identifying children with mitochondrial disorders. Eur Radiol 27(3):976–984
Helman G, Caldovic L, Whitehead MT, Simons C, Brockmann K, Edvardson S et al (2016) Magnetic resonance imaging spectrum of succinate dehydrogenase- related infantile leukoencephalopathy. Ann Neurol 79(3):379–386
Karimzadeh P, Keramatipour M, Karamzade A, Pourbakhtyaran E (2020) Succinate dehydrogenase deficiency: a treatable neurometabolic disorder. Iran J Child Neurol 14(4):111–116
Brockmann K, Bjornstad A, Dechent P, Korenke CG, Smeitink J, Trijbels JM et al (2002) Succinate in dystrophic white matter: a proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy finding characteristic for complex II deficiency. Ann Neurol 52(1):38–46
Rubio-Gozalbo ME, Heerschap A, Trijbels JM, De Meirleir L, Thijssen HO, Smeitink JA (1999) Proton MR spectroscopy in a child with pyruvate dehydrogenase complex deficiency. Magn Reson Imaging 17(6):939–944
Zand DJ, Simon EM, Pulitzer SB, Wang DJ, Wang ZJ, Rorke LB et al (2003) In vivo pyruvate detected by MR spectroscopy in neonatal pyruvate dehydrogenase deficiency. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 24(7):1471–1474
Barnerias C, Saudubray JM, Touati G, De Lonlay P, Dulac O, Ponsot G et al (2010) Pyruvate dehydrogenase complex deficiency: four neurological phenotypes with differing pathogenesis. Dev Med Child Neurol 52(2):e1–e9
Staps P, Rizzo WB, Vaz FM, Bugiani M, Giera M, Heijs B et al (2020) Disturbed brain ether lipid metabolism and histology in Sjögren-Larsson syndrome. J Inherit Metab Dis 43(6):1265–1278
Miyanomae Y, Ochi M, Yoshioka H, Takaya K, Kizaki Z, Inoue F et al (1995) Cerebral MRI and spectroscopy in Sjögren-Larsson syndrome: case report. Neuroradiology 37(3):225–228
Mano T, Ono J, Kaminaga T, Imai K, Sakurai K, Harada K et al (1999) Proton MR spectroscopy of Sjögren-Larsson’s syndrome. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 20(9):1671–1673
Tachibana Y, Aida N, Enomoto K, Iai M, Kurosawa K (2012) A case of Sjogren-Larsson syndrome with minimal MR imaging findings facilitated by proton spectroscopy. Pediatr Radiol 42:380–382
Van Mieghem F, Van Goethem JW, Parizel PM, van den Hauwe L, Cras P, De Meirleire J, De Schepper AM (1997) MR of the brain in Sjögren-Larsson syndrome. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 18(8):1561–1563
Pirgon O, Aydin K, Atabek ME (2006) Proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy findings and clinical effects of montelukast sodium in a case with Sjögren-Larsson syndrome. J Child Neurol 21(12):1092–1095
Abdel-Hamid MS, Issa MY, Elbendary HM, Abdel-Ghafar SF, Rafaat K, Hosny H (2019) Phenotypic and mutational spectrum of thirty-five patients with Sjögren-Larsson syndrome: identification of eleven novel ALDH3A2 mutations and founder effects. J Hum Genet 64(9):859–865
Huigen MC, van der Graaf M, Morava E, Dassel AC, van Steensel MA, Seyger MM et al (2015) Cerebral lipid accumulation in Chanarin-Dorfman syndrome. Mol Genet Metab 114(1):51–54
Roomets E, Lundbom N, Pihko H, Heikkinen S, Tyni T (2006) Lipids detected by brain MRS during coma caused by carnitine palmitoyltransferase 1 deficiency. Neurology 67(8):1516–1517
Ferreira CR, Silber MH, Chang T, Murnick JG, Kirmse B (2016) Cerebral lipid accumulation detected by MRS in a child with carnitine palmitoyltransferase 2 deficiency: a case report and review of the literature on genetic etiologies of lipid peaks on MRS. JIMD Rep 28:69–74
Dorum S, Güney Varal I, Gorukmez O, Dogan P, Ekici A (2019) A novel mutation leading to the lethal form of carnitine palmitoyltransferase type-2 deficiency. J Pediatr Endocrinol Metab 32(7):781–783
Elpeleg ON, Hammerman C, Saada A, Shaag A, Golzand E, Hochner-Celnikier D et al (2001) Antenatal presentation of carnitine palmitoyltransferase II deficiency. Am J Med Genet 102(2):183–187
Dorninger F, Forss-Petter S, Berger J (2017) From peroxisomal disorders to common neurodegenerative diseases—the role of ether phospholipids in the nervous system. FEBS Lett 591(18):2761–2788
Groenendaal F, Bianchi MC, Battini R, Tosetti M, Boldrini A, de Vries LS et al (2001) Proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy (1H-MRS) of the cerebrum in two young infants with Zellweger syndrome. Neuropediatrics 32(1):23–27
Rosewich H, Dechent P, Krause C, Ohlenbusch A, Brockmann K, Gärtner J (2016) Diagnostic and prognostic value of in vivo proton MR spectroscopy for Zellweger syndrome spectrum patients. J Inherit Metab Dis 39(6):869–876
Stockler-Ipsiroglu S, Apatean D, Battini R, DeBrosse S, Dessoffy K, Edvardson S et al (2015) Arginine:glycine amidinotransferase (AGAT) deficiency: clinical features and long term outcomes in 16 patients diagnoses worldwide. Mol Genet Metab 116(4):252–259
Stockler-Ipsiroglu S, van Karnebeek C, Longo N, Korenke GC, Mercimek-Mahmutoglu S, Marquart I et al (2014) Guanidinoacetate methyltransferase (GAMT) deficiency: outcomes in 48 individuals and recommendations for diagnosis, treatment and monitoring. Mol Genet Metab 111(1):16–25
Dunbar M, Jaggumantri S, Sargent M, Stockler-Ipsiroglu S, van Karnebeek CD (2014) et al. Treatment of X-linked creatine transporter (SLC6A8) deficiency: systematic review of the literature and three new cases. Mol Genet Metab 112(4):259–274
Mercimek-Mahmutoglu S, Tucker T, Casey B (2011) Phenotypic heterogeneity in two siblings with 3-methylglutaconic aciduria type I caused by a novel intragenic deletion. Mol Genet Metab 104(3):410–413
Eriguchi M, Mizuta H, Kurohara K, Kosugi M, Yakushiji Y, Okada R et al (2006) 3-methylglutaconic aciduria type I causes leukoencephalopathy of adult onset. Neurology 67(10):1895–1896
Wortmann SB, Kremer BH, Graham A, Willemsen MA, Loupatty FJ, Hogg SL et al (2010) 3-Methylglutaconic aciduria type I redefined: a syndrome with late-onset leukoencephalopathy. Neurology 75(12):1079–1083
Ortigoza-Escobar JD, Serrano M, Molero M, Oyarzabal A, Rebollo M, Muchart J et al (2014) Thiamine transporter-2 deficiency: outcome and treatment monitoring. Orphanet J Rare Dis 9:92
Ferreira CR, Whitehead MT, Leon E (2017) Biotin-thiamine responsive basal ganglia disease: Identification of a pyruvate peak on brain spectroscopy, novel mutation in SLC19A3, and calculation of prevalence based on allele frequencies from aggregated next-generation sequencing data. Am J Med Genet A 173(6):1502–1513
Fassone E, Wedatilake Y, DeVile CJ, Chong WK, Carr LJ, Rahman S (2013) Treatable Leigh-like encephalopathy presenting in adolescence. BMJ Case Rep 2013:200838
Welsink-Karssies MM, Ferdinandusse S, Geurtsen GJ, Hollak CEM, Huidekoper HH, Janssen MCH et al (2020) Deep phenotyping classical galactosemia: clinical outcomes and biochemical markers. Brain Commun 2(1):fcaa006
Otaduy MC, Leite CC, Lacerda MT, Costa MO, Arita F, Prado E, Rosemberg S (2006) Proton MR spectroscopy and imaging of a galactosemic patient before and after dietary treatment. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 27(1):204–207
Wang ZJ, Berry GT, Dreha SF, Zhao H, Segal S, Zimmerman RA (2001) Proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy of brain metabolites in galactosemia. Ann Neurol 50(2):266–269
Berry GT, Hunter JV, Wang Z, Dreha S, Mazur A, Brooks DG et al (2001) In vivo evidence of brain galactitol accumulation in an infant with galactosemia and encephalopathy. J Pediatr 138(2):260–262
Harting I, Boy N, Heringer J, Seitz A, Bendszus M, Pouwels PJ et al (2015) (1)H-MRS in glutaric aciduria type 1: impact of biochemical phenotype and age on the cerebral accumulation of neurotoxic metabolites. J Inherit Metab Dis 38(5):829–838
Alfadhel M, Nashabat M, Alrifai MT, Alshaalan H, Al Mutairi F, Al-Shahrani SA et al (2018) Further delineation of the phenotypic spectrum of ISCA2 defect: a report of ten new cases. Eur J Paediatr Neurol 22(1):46–55
Simons C, Griffin LB, Helman G, Golas G, Pizzino A, Bloom M et al (2015) Loss-of-function alanyl-tRNA synthetase mutations cause an autosomal-recessive early-onset epileptic encephalopathy with persistent myelination defect. Am J Hum Genet 96(4):675–681
Zulfiqar M, Lin DD, Van der Graaf M, Barker PB, Fahrner JA, Marie S et al (2013) Novel proton MR spectroscopy findings in adenylosuccinate lyase deficiency. J Magn Reson Imaging 37(4):974–980
Takanashi J, Inoue K, Tomita M, Kurihara A, Morita F, Ikehira H, Tanada S et al (2002) Brain N-acetylaspartate is elevated in Pelizaeus-Merzbacher disease with PLP1 duplication. Neurology 58(2):237–241
Availability of data and material
None (NA, review article).
Code availability
None (NA)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Dr. Whitehead conceived the idea, designed the layout, performed a literature search, wrote the initial draft and revised all subsequent versions, and provided and annotated figures.
Dr. Lai performed a literature search and added to and edited all versions of the manuscript after the first draft.
Dr. Bluml performed a literature search, added to and edited all versions of the manuscript after the first draft, and provided and annotated figures.
The first draft of the manuscript was written by Matthew Whitehead, MD, and all the authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All the authors read and approved the final manuscript
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
NA (review article)
Consent to participate
NA (review article)
Consent for publication
NA (review article)
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
This article is the follow-up to https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-022-02917-w
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Whitehead, M.T., Lai, L.M. & Blüml, S. Clinical 1H MRS in childhood neurometabolic diseases — part 2: MRS signatures. Neuroradiology 64, 1111–1126 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-022-02918-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-022-02918-9