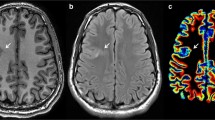
Abstract
Purpose
To figure out the spectra features of malformations of cortical development (MCDs) and the differences between MCDs subcategories.
Methods
Twenty patients and 18 controls were studied. The patients included two subcategories: disorders of migration (DOM) and postmigration (DOPM). Spectra of patients were acquired from both the lesion and the normal-appearing contralateral side (NACS), and they were compared to those of the controls obtained from the frontal lobe.
Results
Compared to the controls, a decreased NAA (P = 0.002) was identified in MCDs. After dividing the MCDs into the DOM and DOPM, we found that NAA reduction was only notable in the DOM (P = 0.007). Moreover, Ins and Cr of the DOPM were higher than those of the controls (P = 0.017 and 0.013) and the DOM (P = 0.027 and 0.001). Compared to the NACS, a decreased NAA (P = 0.042) and an increased Ins (P = 0.039) were identified in the lesion of MCDs. After dividing the MCDs into the DOM and DOPM, we found no significant differences in the DOM, but Ins, Cr, and Glx of the lesion were higher than those of the NACS (P = 0.007, 0.005 and 0.047) in the DOPM. In addition, we found that Cr and Glx correlated positively to the seizure frequency (P = 0.003 and 0.016).
Conclusion
Decreased NAA was the prominent abnormality confirmed in MCDs. Spectra of different MCDs subcategories were different: the DOM was characterized by decreased NAA, while the DOPM was characterized by increased Ins.





Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and material
Not applicable.
Code availability
Not applicable.
References
Battal B, Ince S, Akgun V, Kocaoglu M, Ozcan E, Tasar M (2015) Malformations of cortical development: 3T magnetic resonance imaging features. World J Radiol 7(10):329–335. https://doi.org/10.4329/wjr.v7.i10.329
Barkovich AJ, Kuzniecky RI, Jackson GD, Guerrini R, Dobyns WB (2005) A developmental and genetic classification for malformations of cortical development. Neurology 65(12):1873–1887. https://doi.org/10.1212/01.wnl.0000183747.05269.2d
Barkovich AJ, Guerrini R, Kuzniecky RI, Jackson GD, Dobyns WB (2012) A developmental and genetic classification for malformations of cortical development: update 2012. Brain 135(5):1348–1369. https://doi.org/10.1093/brain/aws019
Celi Santos A (2011) Malformations of cortical development: current concepts and advanced neuroimaging review. Arq Neuropsiquiatr 69(1):130–138. https://doi.org/10.1590/s0004-282x2011000100024
Leite CC, Lucato LT, Sato JR, Valente KD, Otaduy MCG (2007) Multivoxel proton MR spectroscopy in malformations of cortical development. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 28(6):1071–1075; discussion 1076-7. https://doi.org/10.3174/ajnr.A0511
Li LM, Cendes F, Bastos AC, Andermann F, Dubeau F, Arnold DL (1998) Neuronal metabolic dysfunction in patients with cortical developmental malformations: a proton magnetic resonance spectroscopic imaging study. Neurology 50(3):755–759. https://doi.org/10.1212/wnl.50.3.755
Munakata M, Haginoya K, Soga T, Yokoyama H, Noguchi R, Nagasaka T, Murata T, Higano S, Takahashi S, Iinuma K (2003) Metabolic properties of band heterotopia differ from those of other cortical dysplasias: a proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy study. Epilepsia 44(3):366–371. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1528-1157.2003.33901.x
Marsh L, Lim KO, Sullivan EV, Lane B, Spielman D (1996) Proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy of a gray matter heterotopia. Neurology 47(6):1571–1574. https://doi.org/10.1212/wnl.47.6.1571
Simone IL, Federico F, Tortorella C, De Blasi R, Bellomo R, Lucivero V et al (1999) Metabolic changes in neuronal migration disorders: evaluation by combined MRI and proton MR spectroscopy. Epilepsia 40(7):872–879. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1528-1157.1999.tb00793.x
Woermann FG, McLean MA, Bartlett PA, Barker GJ, Duncan JS (2001) Quantitative short echo time proton magnetic resonance spectroscopic imaging study of malformations of cortical development causing epilepsy. Brain 124(Pt 2):427–436. https://doi.org/10.1093/brain/124.2.427
Simister RJ, McLean MA, Barker GJ, Duncan JS (2007) Proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy of malformations of cortical development causing epilepsy. Epilepsy Res 74:107–115. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eplepsyres.2007.02.002
Widdess-Walsh P, Diehl B, Najm I (2006) Neuroimaging of focal cortical dysplasia. J Neuroimaging 16(3):185–196. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1552-6569.2006.00025.x
Tschampa HJ, Urbach H, Traber F, Sprinkart AM, Greschus S, Malter MP (2015) Proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy in focal cortical dysplasia at 3T. Seizure 32:23–29. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seizure.2015.08.008
Mueller SG, Laxer KD, Barakos JA, Cashdollar N, Flenniken DL, Vermathen P (2005) Metabolic characteristics of cortical malformations causing epilepsy. J Neurol 252(9):1082–1092. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-005-0819-7
Guerrini R, Dobyns WB (2014) Malformations of cortical development: clinical features and genetic causes. Lancet Neurol 13(7):710–726. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1474-4422(14)70040-7
Kaminaga T, Kobayashi M, Abe T (2001) Proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy in disturbances of cortical development. Neuroradiology 43(7):575–580. https://doi.org/10.1007/s002340100548
Kuzniecky R, Hetherington H, Pan J, Hugg J, Palmer C, Gilliam F, Faught E, Morawetz R (1997) Proton spectroscopic imaging at 4.1 tesla in patients with malformations of cortical development and epilepsy. Neurology 48(4):1018–1024. https://doi.org/10.1212/wnl.48.4.1018
Christiansen P, Henriksen O, Stubgaard M, Gideon P, Larsson HB (1993) In vivo quantification of brain metabolites by 1H-MRS using water as an internal standard. Magn Reson Imaging 11(1):107–118. https://doi.org/10.1016/0730-725x(93)90418-d
Petroff OA, Pleban LA, Spencer DD (1995) Symbiosis between in vivo and in vitro NMR spectroscopy: the creatine, N-acetylaspartate, glutamate, and GABA content of the epileptic human brain. Magn Reson Imaging 13(8):1197–1211. https://doi.org/10.1016/0730-725x(95)02033-p
Pouwels PJ, Brockmann K, Kruse B, Wilken B, Wick M, Hanefeld F et al (1999) Regional age dependence of human brain metabolites from infancy to adulthood as detected by quantitative localized proton MRS. Pediatr Res 46(4):474–485. https://doi.org/10.1203/00006450-199910000-00019
Castillo M, Kwock L, Mukherji SK (1996) Clinical applications of proton MR spectroscopy. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 17(1):1–15
Andrade CS, Leite Cda C (2011) Malformations of cortical development: current concepts and advanced neuroimaging review. Arq Neuropsiquiatr 69(1):130–138. https://doi.org/10.1590/s0004-282x2011000100024
Cross JH (2003) Functional neuroimaging of malformations of cortical development. Epileptic Disord 5(Suppl 2):S73–S80
Madan N, Grant PE (2009) New directions in clinical imaging of cortical dysplasias. Epilepsia 50(Suppl 9):9–18. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1528-1167.2009.02292.x
Woermann FG, McLean MA, Bartlett PA, Barker GJ, Duncan JS (1999) Short echo time single-voxel 1H magnetic resonance spectroscopy in magnetic resonance imaging-negative temporal lobe epilepsy: different biochemical profile compared with hippocampal sclerosis. Ann Neurol 45(3):369–376. https://doi.org/10.1002/1531-8249(199903)45:3<369::aid-ana13>3.0.co;2-q
Simister RJ, McLean MA, Barker GJ, Duncan JS (2003) Proton MRS reveals frontal lobe metabolite abnormalities in idiopathic generalized epilepsy. Neurology 61(7):897–902. https://doi.org/10.1212/01.wnl.0000086903.69738.dc
Leventer RJ, Guerrini R, Dobyns WB (2008) Malformations of cortical development and epilepsy. Dialogues Clin Neurosci 10(1):47–62. https://doi.org/10.31887/DCNS.2008.10.1/rjleventer
Juric-Sekhar G, Hevner RF (2019) Malformations of cerebral cortex development: molecules and mechanisms. Annu Rev Pathol 14:293–318. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-pathmechdis-012418-012927
Hannan AJ, Servotte S, Katsnelson A, Sisodiya S, Blakemore C, Squier M, Molnár Z (1999) Characterization of nodular neuronal heterotopia in children. Brain 122(Pt 2):219–238. https://doi.org/10.1093/brain/122.2.219
Chevassus-Au-Louis N, Represa A (1999) The right neuron at the wrong place: biology of heterotopic neurons in cortical neuronal migration disorders, with special reference to associated pathologies. Cell Mol Life Sci 55(10):1206–1215. https://doi.org/10.1007/s000180050367
Baraban SC, Wenzel HJ, Hochman DW, Schwartzkroin PA (2000) Characterization of heterotopic cell clusters in the hippocampus of rats exposed to methylazoxymethanol in utero. Epilepsy Res 39(2):87–102. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0920-1211(99)00104-7
Luhmann HJ (2016) Models of cortical malformation—Chemical and physical. J Neurosci Methods 260:62–72. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jneumeth.2015.03.034
Bourdillon P, Rheims S, Catenoix H, Montavont A, Ostrowsky-Coste K, Isnard J, Guénot M (2019) Malformations of cortical development: new surgical advances. Rev Neurol (Paris) 175(3):183–188. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neurol.2019.01.392
Baker EH, Basso G, Barker PB, Smith MA, Bonekamp D, Horská A (2008) Regional apparent metabolite concentrations in young adult brain measured by (1)H MR spectroscopy at 3 tesla. J Magn Reson Imaging 27(3):489–499. https://doi.org/10.1002/jmri.21285
Haga KK, Khor YP, Farrall A, Wardlaw JM (2009) A systematic review of brain metabolite changes, measured with 1H magnetic resonance spectroscopy, in healthy aging. Neurobiol Aging 30(3):353–363. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2007.07.005
Petroff OA, Mattson RH, Rothman DL (2000) Proton MRS: GABA and glutamate. Adv Neurol 83:261–271
Garcia M, Huppertz HJ, Ziyeh S, Buechert M, Schumacher M, Mader I (2009) Valproate-induced metabolic changes in patients with epilepsy: assessment with H-MRS. Epilepsia 50(3):486–492. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1528-1167.2008.01801.x
Funding
This work was supported by the Sichuan Provincial Foundation of Science and Technology (grant numbers 2019YFS0428 and 2013SZ0047) and the Foundation of the National Research Center of Geriatrics (grant number Z2018A07).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Ethical approval
Institutional Review Board approval was obtained for this study. All procedures performed in this study were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional research committee and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki Declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed consent
All subjects or their guardians gave their written informed consent to be enrolled in this study before the MRI examination.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tan, Q., Liu, W., Wan, X. et al. Quantitative 1H-MRS reveals metabolic difference between subcategories of malformations of cortical development. Neuroradiology 63, 1539–1548 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-021-02694-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-021-02694-y