Abstract
Introduction
The objective of this study was to evaluate the effect of apolipoprotein E (APOE) epsilon 4 allele on regional cerebral perfusion (rCBF) changes using arterial spin labeling (ASL) magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) in subjects who are carriers or noncarriers of this risk factor for Alzheimer disease (AD).
Methods
Twenty-five subjects with AD, 25 with amnestic mild cognitive impairment (MCI) and 25 cognitively normal (CN) subjects underwent isotropic volumetric T1-weighted imaging and pulsed ASL MRI. All subjects were divided into carrier or noncarriers of the epsilon4 allele. Voxel-based statistical analyses were performed among groups on rCBF by ANOVA tests. In each subject group, we also evaluated the rCBF change between carrier and noncarrier groups.
Results
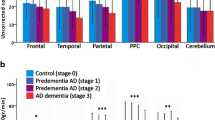
rCBF was significantly reduced in AD subjects compared to other subjects. In CN and AD subjects, rCBF in the carrier group was significantly reduced in several areas of the brain compared with that of the noncarrier group. In the carrier group, rCBF was significantly increased in the right parahippocampal gyrus, the bilateral cingulate gyri and the right posterior cingulate on the MCI group in addition to the right superior frontal gyrus in the AD group.
Conclusion
rCBF in the CN and AD groups were significantly reduced in the subjects with the carriers of the epsilon4 allele, which is a risk factor for Alzheimer’s disease. In addition, rCBF in the MCI group was significantly increased in subjects who were carriers. Therefore, rCBF can be used as a biomarker to show disease progression in areas of the brain of MCI subjects.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Good CD, Scahill RI, Fox NC, Ashburner J, Friston KJ, Chan D, Crum WR, Rossor MN, Frackowiak RS (2002) Automatic differentiation of anatomical patterns in the human brain: validation with studies of degenerative dementias. NeuroImage 17(1):29–46
Karas GB, Burton EJ, Rombouts SA, van Schijndel RA, O’Brien JT, Scheltens P, McKeith IG, Williams D, Ballard C, Barkhof F (2003) A comprehensive study of gray matter loss in patients with Alzheimer’s disease using optimized voxel-based morphometry. NeuroImage 18(4):895–907
Busatto GF, Diniz BS, Zanetti MV (2008) Voxel-based morphometry in Alzheimer’s disease. Expert Rev Neurother 8(11):1691–1702
Jellinger KA (2006) Alzheimer 100—highlights in the history of Alzheimer research. J Neural Transm 113(11):1603–1623
Small GW, Bookheimer SY, Thompson PM, Cole GM, Huang SC, Kepe V, Barrio JR (2008) Current and future uses of neuroimaging for cognitively impaired patients. Lancet Neurol 7(2):161–172
Petersen RC, Doody R, Kurz A, Mohs RC, Morris JC, Rabins PV, Ritchie K, Rossor M, Thal L, Winblad B (2001) Current concepts in mild cognitive impairment. Arch Neurol 58(12):1985–1992
Lopez OL, Jagust WJ, DeKosky ST, Becker JT, Fitzpatrick A, Dulberg C, Breitner J, Lyketsos C, Jones B, Kawas C, Carlson M, Kuller LH (2003) Prevalence and classification of mild cognitive impairment in the cardiovascular health study cognition study: part 1. Arch Neurol 60(10):1385–1389
Chua TC, Wen W, Slavin MJ, Sachdev PS (2008) Diffusion tensor imaging in mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer’s disease: a review. Curr Opin Neurol 21(1):83–92
Dai W, Lopez OL, Carmichael OT, Becker JT, Kuller LH, Gach HM (2009) Mild cognitive impairment and alzheimer disease: patterns of altered cerebral blood flow at MR imaging. Radiology 250(3):856–866
Stahl R, Dietrich O, Teipel SJ, Hampel H, Reiser MF, Schoenberg SO (2007) White matter damage in Alzheimer disease and mild cognitive impairment: assessment with diffusion-tensor MR imaging and parallel imaging techniques. Radiology 243(2):483–492
Luckhaus C, Flub MO, Wittsack HJ, Grass-Kapanke B, Janner M, Khalili-Amiri R, Friedrich W, Supprian T, Gaebel W, Modder U, Cohnen M (2008) Detection of changed regional cerebral blood flow in mild cognitive impairment and early Alzheimer’s dementia by perfusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging. NeuroImage 40(2):495–503
Asllani I, Habeck C, Scarmeas N, Borogovac A, Brown TR, Stern Y (2008) Multivariate and univariate analysis of continuous arterial spin labeling perfusion MRI in Alzheimer’s disease. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 28(4):725–736
Johnson NA, Jahng GH, Weiner MW, Miller BL, Chui HC, Jagust WJ, Gorno-Tempini ML, Schuff N (2005) Pattern of cerebral hypoperfusion in Alzheimer disease and mild cognitive impairment measured with arterial spin-labeling MR imaging: initial experience. Radiology 234(3):851–859
Bradley KM, O’Sullivan VT, Soper ND, Nagy Z, King EM, Smith AD, Shepstone BJ (2002) Cerebral perfusion SPET correlated with Braak pathological stage in Alzheimer’s disease. Brain 125(Pt 8):1772–1781
Chetelat G, Desgranges B, de la Sayette V, Viader F, Eustache F, Baron JC (2003) Mild cognitive impairment: Can FDG-PET predict who is to rapidly convert to Alzheimer’s disease? Neurology 60(8):1374–1377
Drzezga A, Riemenschneider M, Strassner B, Grimmer T, Peller M, Knoll A, Wagenpfeil S, Minoshima S, Schwaiger M, Kurz A (2005) Cerebral glucose metabolism in patients with AD and different APOE genotypes. Neurology 64(1):102–107
Mevel K, Desgranges B, Baron JC, Landeau B, De la Sayette V, Viader F, Eustache F, Chetelat G (2007) Detecting hippocampal hypometabolism in mild cognitive impairment using automatic voxel-based approaches. NeuroImage 37(1):18–25
Corder EH, Saunders AM, Strittmatter WJ, Schmechel DE, Gaskell PC, Small GW, Roses AD, Haines JL, Pericak-Vance MA (1993) Gene dose of apolipoprotein E type 4 allele and the risk of Alzheimer’s disease in late onset families. Science 261(5123):921–923
Hyman BT, Gomez-Isla T, West H, Briggs M, Chung H, Growdon JH, Rebeck GW (1996) Clinical and neuropathological correlates of apolipoprotein E genotype in Alzheimer’s disease. Window on molecular epidemiology. Ann N Y Acad Sci 777:158–165
Deary IJ, Whiteman MC, Pattie A, Starr JM, Hayward C, Wright AF, Carothers A, Whalley LJ (2002) Cognitive change and the APOE epsilon 4 allele. Nature 418(6901):932
Nicoll JA, Savva GM, Stewart J, Matthews FE, Brayne C, Ince P (2011) Association between APOE genotype, neuropathology and dementia in the older population of England and Wales. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol 37(3):285–294
Vemuri P, Wiste HJ, Weigand SD, Knopman DS, Shaw LM, Trojanowski JQ, Aisen PS, Weiner M, Petersen RC, Jack CR Jr (2010) Effect of apolipoprotein E on biomarkers of amyloid load and neuronal pathology in Alzheimer disease. Ann Neurol 67(3):308–316
Filippini N, Rao A, Wetten S, Gibson RA, Borrie M, Guzman D, Kertesz A, Loy-English I, Williams J, Nichols T, Whitcher B, Matthews PM (2009) Anatomically-distinct genetic associations of APOE epsilon4 allele load with regional cortical atrophy in Alzheimer’s disease. NeuroImage 44(3):724–728
Liu Y, Paajanen T, Westman E, Wahlund LO, Simmons A, Tunnard C, Sobow T, Proitsi P, Powell J, Mecocci P, Tsolaki M, Vellas B, Muehlboeck S, Evans A, Spenger C, Lovestone S, Soininen H (2010) Effect of APOE epsilon4 allele on cortical thicknesses and volumes: the AddNeuroMed study. J Alzheimers Dis 21(3):947–966
Tanaka S, Kawamata J, Shimohama S, Akaki H, Akiguchi I, Kimura J, Ueda K (1998) Inferior temporal lobe atrophy and APOE genotypes in Alzheimer’s disease. X-ray computed tomography, magnetic resonance imaging and Xe-133 SPECT studies. Dement Geriatr Cogn Disord 9(2):90–98
Hogh P, Knudsen GM, Kjaer KH, Jorgensen OS, Paulson OB, Waldemar G (2001) Single photon emission computed tomography and apolipoprotein E in Alzheimer’s disease: impact of the epsilon4 allele on regional cerebral blood flow. J Geriatr Psychiatry Neurol 14(1):42–51
Kang Y, Na DL (eds) (2003) Seoul neuropsychological screening battery (SNSB). Human Brain Research & Consulting, Incheon
Petersen RC, Smith GE, Waring SC, Ivnik RJ, Tangalos EG, Kokmen E (1999) Mild cognitive impairment: clinical characterization and outcome. Arch Neurol 56(3):303–308
Criteria for the clinical diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease. Excerpts from the NINCDS-ADRDA Work Group report (1985). J Am Geriatr Soc 33 (1):2–3
Golay X, Petersen ET, Hui F (2005) Pulsed star labeling of arterial regions (PULSAR): a robust regional perfusion technique for high field imaging. Magn Reson Med 53(1):15–21
Wang Z, Aguirre GK, Rao H, Wang J, Fernandez-Seara MA, Childress AR, Detre JA (2008) Empirical optimization of ASL data analysis using an ASL data processing toolbox: ASLtbx. Magn Reson Imaging 26(2):261–269
Du AT, Jahng GH, Hayasaka S, Kramer JH, Rosen HJ, Gorno-Tempini ML, Rankin KP, Miller BL, Weiner MW, Schuff N (2006) Hypoperfusion in frontotemporal dementia and Alzheimer disease by arterial spin labeling MRI. Neurology 67(7):1215–1220
Leenders KL, Perani D, Lammertsma AA, Heather JD, Buckingham P, Healy MJ, Gibbs JM, Wise RJ, Hatazawa J, Herold S et al (1990) Cerebral blood flow, blood volume and oxygen utilization. Normal values and effect of age. Brain 113(Pt 1):27–47
Kim MJ, Jahng GH, Lee HY, Kim SM, Ryu CW, Shin WC, Lee SY (2010) Development of a Korean standard structural brain template in cognitive normals and patients with mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer’s disease. J Korean Soc Magn Reson Med 14:103–114
Jagust W, Thisted R, Devous MD Sr, Van Heertum R, Mayberg H, Jobst K, Smith AD, Borys N (2001) SPECT perfusion imaging in the diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease: a clinical-pathologic study. Neurology 56(7):950–956
Mielke R, Kessler J, Szelies B, Herholz K, Wienhard K, Heiss WD (1998) Normal and pathological aging—findings of positron-emission-tomography. J Neural Transm 105(8–9):821–837
Sakamoto S, Matsuda H, Asada T, Ohnishi T, Nakano S, Kanetaka H, Takasaki M (2003) Apolipoprotein E genotype and early Alzheimer’s disease: a longitudinal SPECT study. J Neuroimaging 13(2):113–123
Alsop DC, Casement M, de Bazelaire C, Fong T, Press DZ (2008) Hippocampal hyperperfusion in Alzheimer’s disease. NeuroImage 42(4):1267–1274
Luckhaus C, Cohnen M, Flubeta MO, Janner M, Grass-Kapanke B, Teipel SJ, Grothe M, Hampel H, Peters O, Kornhuber J, Maier W, Supprian T, Gaebel W, Modder U, Wittsack HJ (2010) The relation of regional cerebral perfusion and atrophy in mild cognitive impairment (MCI) and early Alzheimer’s dementia. Psychiatry Res 183(1):44–51
Hayasaka S, Du AT, Duarte A, Kornak J, Jahng GH, Weiner MW, Schuff N (2006) A non-parametric approach for co-analysis of multi-modal brain imaging data: application to Alzheimer’s disease. NeuroImage 30(3):768–779
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by a grant of the Korean Health Technology R&D Project, Ministry for Health, Welfare & Family Affairs, Republic of Korea (A092125).
Conflict of interest
We declare that we have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, S.M., Kim, M.J., Rhee, H.Y. et al. Regional cerebral perfusion in patients with Alzheimer’s disease and mild cognitive impairment: effect of APOE Epsilon4 allele. Neuroradiology 55, 25–34 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-012-1077-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-012-1077-x