Abstract
Introduction
The aim of our study was to evaluate the safety and efficacy of intra-arterial (IA) thrombolysis using recombinant tissue plasminogen activator (rt-PA) in patients with acute stroke due to occlusion in the anterior or posterior circulation.
Methods
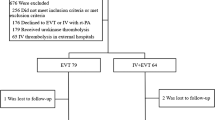
We retrospectively analyzed the clinical and radiological data of 88 consecutive patients with acute ischemic stroke who underwent emergency cerebral angiography for the purpose of subsequent IA thrombolysis. The neurological deficit on admission and discharge was graded using the National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale (NIHSS) score. Baseline computer tomography (CT) scans were examined for any signs indicative of cerebral ischemia. The angiographic findings were classified according to the Thrombolysis in Myocardial Infarction (TIMI) score for myocardial infarction. Follow-up CT scans were examined for hemorrhagic complication.
Results
Of the 88 patients who underwent IA thrombolysis, 63 presented with complete or partial arterial occlusion in the suspected perfusion area. In these 63 patients, the median NIHSS score dropped from 15 points on admission to 10 points at discharge. The recanalization rate was 52.6% for partial and complete reperfusion. In-hospital mortality was 20.6% (9.1% for carotid, 44.4% for basilar territory occlusion). Intracerebral bleeding (ICB) occurred in 38.6% of the patients with occlusion in the anterior circulation, resulting in these patients presenting a worse clinical outcome than those without ICB. Only minor extracranial bleedings occurred in 20.6% of patients. Patients with ICB had a significantly higher frequency of ischemic signs on the baseline CT scan.
Conclusion
Occlusion of a cerebral artery is present in about 75% of the patients eligible for thrombolytic therapy. Intra-arterial thrombolysis using rt-PA in patients with acute ischemic stroke can achieve re-vascularization, although ICB remains the major risk factor affecting its efficacy.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
The National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke rt-PA Stroke Study Group (1995) Tissue plasminogen activator for acute ischemic stroke. N Engl J Med 333:1581–1587
del Zoppo GJ, Higashida RT, Furlan AJ, Pessin MS, Rowley HA, Gent M, the PROACT Investigators (1998) PROACT: a phase II randomized trial of recombinant pro-urokinase by direct arterial delivery in acute middle cerebral artery stroke. Stroke 29:4–11
Furlan A, Higashida R, Wechsler L, Gent M, Rowley H, Kase C, Pessin M, Ahuja A, Gallahan F, Clark WM, Silver F, Rivera F, for the PROACT Investigators (1999) Intra-arterial prourokinase for acute ischemic stroke the PROACT II study: a randomized controlled trial. JAMA 282:2003–2011
Higashida RT, Furlan AJ (2003) Trial design and reporting standards for intra-arterial cerebral thrombolysis for acute ischemic stroke. Stroke 34:e109–e137
Mielke O, Wardlaw J, Liu M (2004) Thrombolysis (different doses, routes of administration and agents) for acute ischaemic stroke. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 18:CD000514
Williams LS, Yilmaz EY, Lopez-Yunez AM (2000) Retrospective assessment of initial stroke severity with the NIH stroke scale. Stroke 31:858–886
Bourekas EC, Slivka AP, Shah R, Tarr RW, Sunshine J, Suarez JI (2004) Intaarterial thrombolytic therapy within 3 hours of the onset of stroke. Neurosurgery 54:39–46
Zaidat OO, Suarez JI, Sunshine JL, Tarr RW, Alexander MJ, Smith TP, Enterline DS, Selman WR, Landis DM (2005) Thrombolytic therapy of acute ischemic stroke: correlation of angiographic recanalization with clinical outcome. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 26:880–884
Lewandowski CA, Frankel M, Tomsick TA, Broderick J, Frey J, Clark W, Starkman S, Grotta J, Spilker J, Khoury J, Brott T, the EMS Bridging Trial Investigators (1999) Combined intravenous and intra-arterial r-TPA versus intra-arterial therapy of acute ischemic stroke, emergency management of stroke (EMS) bridging trial. Stroke 30:2598–2605
Clark WM, Wissman S, Albers GW, Jhamandas JH, Madden KP, Hamilton S (1999) Recombinant tissue-type plasminogen activator (Alteplase) for ischemic stroke 3 to 5 hours after symptom onset. The ATLANTIS study: a randomized controlled trial. Alteplase thrombolysis for acute noninterventional therapy in ischemic stroke. JAMA 282:2019–2026
Grotta JC, Burgin WS, El-Mitwalli A, Long M, Campbell M, Morgenstern LB, Malkoff M, Alexandrov AV (2001) Intravenous tissue-type plasminogen activator therapy for ischemic stroke: houston experience 1996 to 2000. Arch Neurol 58:2009–2013
Katzan IL, Furlan AJ, Lloyd LE, Frank JI, Harper DL, Hinchey JA, Hammel JP, Qu A, Sila CA (2000) Use of tissue-type plasminogen activator for acute ischemic stroke: the cleveland area experience. JAMA 283:1151–1158
Schellinger PD, Fiebach JB, Mohr A, Ringleb PA, Jansen O, Hacke W (2001) Thrombolytic therapy for ischemic stroke – a review. Part II – intra-arterial thrombolysis, vertebrobasilar stroke, phase IV trials, and stroke imaging. Crit Care Med 29(9):1819–1825
Lindsberg PJ, Soinne L, Tatlisumak T, Roine RO, Kallela M, Happola O, Kaste M (2004) Long-term outcome after intravenous thrombolysis of basilar artery occlusion. JAMA 292:1862–1866
Brandt T (2002) Diagnosis and thrombolytic therapy of acute basilar artery occlusion: a review. Clin Exp Hypertens 24:611–622
Lindsberg PJ, Mattle HP (2006) Therapy of basilar artery occlusion, a systematic analysis comparing intra-arterial and intravenous thrombolysis. Stroke 37:922–928
Jahan R, Duckwiler GR, Kidwell CS, Sayre JW, Gobin YP, Villablanca JP, Saver J, Starkman S, Martin N, Vinuela F (1999) Intraarterial thrombolysis for treatment of acute stroke: experience in 26 patients with long-term follow-up. Am J Neuroradiol 20:1291–1299
Edwards MT, Murphy MM, Geraghty JJ, Wulf JA, Konzen JP (1999) Intra-arterial cerebral thrombolysis for acute ischemic stroke in a community hospital. Am J Neuroradiol 20:1682–1687
Arnold M, Schroth G, Nedeltchev K, Loher T, Remonda L, Stepper F, Sturzenegger M, Mattle HP (2002) Intra-arterial thrombolysis in 100 patients with acute stroke due to middle cerebral artery occlusion. Stroke 33:1828–1833
Wardlaw JM, Mielke O (2005) Early signs of brain infarction at CT: observer reliability and outcome after thrombolytic treatment-systematic review. Radiology 235:444–453
von Kummer R, Hacke W (2002) “Early ischemic signs” haben eine prädiktive Aussage für den Erfolg und Komplikationsrate der systemischen Thrombolyse. Akt Neurol 29:511–512
Hamman GF, Röther J (2002) “Early ischemic signs” haben keine prädiktive Aussage für den Erfolg und Komplikationsrate der systemischen Thrombolyse. Akt Neurol 29:513–515
Keris V, Rudnicka S, Vorona V, Enina G, Tilgale B, Fricbergs J (2001) Combined intraarterial/intravenous thrombolysis for acute ischemic stroke. Am J Neuroradiol 22:352–358
Brandt T, von Kummer R, Müller-Küppers M, Hacke W (1996) Thrombolytic therapy of acute basilar artery occlusion: variables affecting recanalization and outcome. Stroke 27:875–881
Wijdicks EFM, Nichols DA, Thielen KR, Fulgham JR, Brown RD Jr, Meissner I, Meyer F, Piepgras DG (1997) Intra-arterial thrombolysis in acute basilar artery thromboembolism: the initial Mayo clinic experience. Mayo Clnic Proc 72:1005–1013
Cross DT III, Moran CJ, Akins PT, Angtuaco EE, Diringer MN (1997) Relationship between clot location and outcome after basilar artery thrombolysis. Am J Neuroradiol 18:1221–1228
Cross DT III, Derdeyn CP, Moran CJ (2001) Bleeding complications after basilar artery fibrinolysis with tissue plasminogen activator. Am J Neuroradiol 22:521–525
Arnold M, Nedeltchev K, Remonda L, Fischer U, Brekenfeld C, Keserue B, Schroth G, Mattle HP (2005) Recanalisation of middle cerebral artery occlusion after intra-arterial thrombolysis: different recanalisation grading systems and clinical functional outcome. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 76:1373–1376
Cross DT III, Moran CJ, Akins PT, Angtuaco EE, Derdeyn CP, Diringer MN (1998) Collateral circulation and outcome after basilar artery thrombolysis. Am J Neuroradiol 19:1557–1563
von Kummer R, Bourquain H, Bastianello S, Bozzao L, Manelfe C, Meier D, Hacke W, for the European Cooperative Acute Stroke Study II Group (2001) Early prediction of irreversible brain damage after ischemic stroke by computed tomography. Radiology 219:95–100
Burnett WC, Nesbit GM (2001) Intra-arterial thrombolysis for acute ischemic stroke. Eur Radiol 11:626–634
The NINDS t-PA Stroke Study Group (1997) Intracerebral hemorrhage after intravenous t-PA therapy for ischemic stroke. Stroke 28:2109–2118
Albers GW, Clark WM, Madden KP, Hamilton SA (2002) ATLANTIS trial: results for patients treated within 3 hours of stroke onset. Stroke 33:493–496
Hacke W, Kaste M, Fieschi C, Toni D, Lesaffre E, von Kummer R, Boysen G, Bluhmki E, Höxter G, Mahagne M-H, Hennerici M, for the ECASS Study Group (1995) Intravenous thrombolysis with recombinant tissue plasminogen activator for acute hemispheric stroke. The European Cooperative Acute Stroke Study. JAMA 274:1017–1025
Hacke W, Kaste M, Fieschi C, von Kummer R, Davalos A, Meier D, Larrue V, Bluhmki E, Davis S, Donnan G, Schneider D, Diez-Tejedor E, Trouillas P, for the second European-Australasian Acute Stroke Study Investigators (1998) Randomised double-blind placebo-controlled trial of thrombolytic therapy with intravenous alteplase in acute ischaemic stroke (ECASS II). Lancet 352:1245–1251
Larrue V, von Kummer R, del Zoppo G, Bluhmki E (1997) Hemorrhagic transformation in acute ischemic stroke: potential contributing factors in the european cooperative acute stroke study. Stroke 28:957–960
Trouillas P, Nighoghossian N, Derex L, Adeleine P, Honnorat J, Neuschwander P, Riche G, Getenet JC, Li W, Froment JC, Turjman F, Malicier D, Fournier G, Gabry AL, Ledoux X, Berthezene Y, Ffrench P, Dechavanne M (1998) Thrombolysis with intravenous rtPA in a series of 100 cases of acute carotid territory stroke: determination of etiological, topographic, and radiological outcome factors. Stroke 29:2529–2540
Derex L, Hermier M, Adeleine P, Pialat JB, Wiart M, Berthezene Y, Philippeau F, Honnorat J, Froment JC, Trouillas P, Nighoghossian N (2005) Clinical and imaging predictors of intracerebral haemorrhage in stroke patients treated with intravenous tissue plasminogen activator. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 76:70–75
Chiu D, Krieger D, Villar-Cordova C, Kasner SE, Morgenstern LB, Bratina PL, Yatsu FM, Grotta JC (1998) Intravenous tissue plasminogen activator for acute ischemic stroke: feasibility, safety, and efficacy in the first year of clinical practice. Stroke 29:18–22
Jaillard A, Cornu C, Durieux A, Moulin T, Boutitie F, Lees K, Hommel M (1999) Hemorrhagic transformation in acute ischemic stroke: The MAST-E study. Stroke 30:1326–1332
Conflict of interest statement
We declare that we have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tountopoulou, A., Ahl, B., Weissenborn, K. et al. Intra-arterial thrombolysis using rt-PA in patients with acute stroke due to vessel occlusion of anterior and/or posterior cerebral circulation. Neuroradiology 50, 75–83 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-007-0306-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-007-0306-1