Abstract.
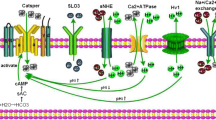
It has been shown previously that the antifertility agents Lonidamine and its analogue AF2785, [1-(2,4-dichlorobenzyl)-indazole-3-acrylic acid] are potent inhibitors of the cAMP-activated chloride channel (CFTR) in rat epididymal cells. In this study, we further characterized the blocking actions of these two compounds and compared them with the known chloride channel blocker diphenylamine-2-carboxylate (DPC). Results show that the order of potency in blocking the cAMP-activated current is AF2785 > Lonidamine > DPC. All three compounds shared similar blocking characteristics. Firstly, their blockade of the current exhibited voltage dependence; all three agents blocked the current more markedly at negative than at positive membrane potentials. Secondly, they blocked the channels from the outside of the cell. Thirdly, their blocking efficacies were maximal at low extracellular pH. Lastly, the time course of the block by AF2785 and DPC appeared to be more rapid than that of Lonidamine. It is hoped that further studies with other indazole compounds will add knowledge to the physiology and pharmacology of CFTR in the epididymis. Such information will be of great importance to our quest for novel male contraceptives.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 8 February 2000/Revised: 25 September 2000
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gong, X., Wong, P. Characterization of Lonidamine and AF2785 Blockade of the Cyclic AMP-Activated Chloride Current in Rat Epididymal Cells. J. Membrane Biol. 178, 225–233 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1007/s002320010030
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s002320010030