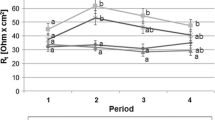
Abstract
Heat stable (STa) enterotoxin from E. coli reduced fluid absorption in vivo in the perfused jejunum of the anaesthetized rat in Krebs-phosphate buffer containing lactate and glucose (nutrient buffer), in glucose saline and in glucose free saline. Bicarbonate ion enhanced fluid absorption of 98 ± 7 (6) μl/cm/h was very significantly (P < 0.0001) reduced by STa to 19 ± 4 (6) μl/cm/h, but net secretion was not found. When impermeant MES substituted for bicarbonate ion, net fluid absorption of 29 ± 3 (6) μl/cm/h was less (P < 0.01) than the values for phosphate buffer and bicarbonate buffer. With STa in MES buffer, fluid absorption of 3 ± 2 (6) μl/cm/h was less than (P < 0.001) that in the absence of STa and not significantly different from zero net fluid absorption. E. coli STa did not cause net fluid secretion in vivo under any of the above circumstances. Neither bumetanide nor NPPB when co-perfused with STa restored the rate of fluid absorption. In experiments with zero sodium ion-containing perfusates, STa further reduced fluid absorption modestly by 20 μl/cm/h. Perfusion of ethyl-isopropyl-amiloride (EIPA) with STa in zero sodium ion buffers prevented the small increment in fluid entry into the lumen caused by STa, indicating that the STa effect was attributable to residual sodium ion and fluid uptake that zero sodium-ion perfusates did not eradicate. These experiments, using a technique that directly measures mass transport of fluid into and out of the in vivo proximal jejunum, do not support the concept that E. coli STa acts by stimulating a secretory response.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barrett K.E. 1991. Immune-related intestinal chloride secretion III. Acute and chronic effects of human mast cell mediators on chloride secretion by a human colonic epithelial cell line. J. Immunology 147:959–964
Barrett K.E., Keely S.J. 2000. Chloride secretion by the intestinal epithelium: Molecular basis and regulatory aspects. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 62:535–572
Beubler E., Badhri P., Schirgi-Degen A. 1992. 5-HT receptor antagonists and heat-stable Escherichia coli enterotoxin-induced effects in the rat. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 219:445–450
BMDP. 1981. Biomedical Programmes manual. UCLA Press, University of California.
Bradford M.M. 1976. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal. Biochem. 72:247–254
Chao A.C., de Sauvage F.J., Dong Y.-J., Wagner J.A. Goeddel D.V., Gardner P. 1994. Activation of intestinal CFTR Cl− channel by heat-stable enterotoxin and guanylin via cAMP dependent protein. EMBO J. 13:1065–1072
Charney A.N., Dansky H.M. 1990. Additive effects of ileal secretagogues in the rat. Gastroenterology, 98:881–887
Cohen M.B., Nogueira J., Laney Jr. D.W., Conti T.R. 1992. The jejunal secretory response to Escherichia coli heat-stable enterotoxin is prolonged in malnourished rats. Pediatric Res. 31:228–233
Cruickshank S.F., Baxter L.M., Drummond R.M. 2003. The Cl− channel blocker niflumic acid releases Ca2+ from an intracellular store in rat pulmonary artery smooth muscle cells. Brit. J. Pharmacol. 140:1442–1450
Cuthbert A.W., Hickman M.E., MacVinish L.J., Evans M.J., Colledge W.H., Ratcliffe R., Seale P.W., Humphrey P.P.A. 1994. Chloride secretion in response to guanylin in colonic epithelia from normal and transgenic cystic fibrosis mice. Brit. J. Pharmacol. 112:31–36
Eklund S., Jodal M., Lundgren O. 1985. The enteric nervous system participates in the secretory response to the heat stable enterotoxins of Escherichia coli in rats and cats. Neuroscience 14:673–681
Farack U.M., Asher A., Elsenhans B., Schuette-Lückenga B., Gerzer R. 2000. Effect of loperamide on mucosal guanylyl cyclase activity in rat jejunum following Escherichia coli heat-stable toxin-induced fluid accumulation. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 86:78–82
Fasano A., Uzzau S., Fiore C., Margaretten K. 1997. The enterotoxic effect of zona occludens toxin on rabbit small intestine involves the paracellular pathway. Gastroenterology 112:839–846
Fedorak R.N., Alien S.L. 1989. Effect of somatostatin analog (SMS 201–995) on in vivo intestinal fluid transport in rats. A limited systemic effect. Dig. Dis. Sci. 34:567–572
Feng Y., Wente S.R., Majerus P.W. (2001) Overexpression of the inositol phosphatase SopB in human 293 cells stimulates cellular chloride influx and inhibits nuclear mRNA export. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 98:875–879
Field M. 1971. Intestinal secretion: effect of cyclic AMP and its role in cholera. New Engl. J. Med. 284:1137–1143
Field M., Fromm D., McColl I. 1971 Ion transport in rabbit ileal mucosa. I. Na and Cl fluxes and short-circuit current. Amer. J. Physiol. 220:1388–1396
Field M., Graf Jr. L.H., Laird W.J., Smith P.L. (1978) Heat-stable enterotoxin of Escherichia coli: In vitro effects on guanylate cyclase activity, cyclic GMP concentration, and ion transport in small intestine. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 75:2800–2804
Fiske C.H., Subbarow Y. 1925. The colorimetric determination of phosphorus. J. Biol. Chem. 66:375–400
Flagella M., Clarke L.L., Miller M.L., Erway L.C., Gianella R.A., Andringa A., Gawenis L.R., Kramer J., Duffy J.J., Doetschman T., Lorenz J.N., Yamoah E.N., Cardell E.L., Shull G.E. 1999. Mice lacking the basolateral Na-K-2Cl cotransporter have impaired epithelial chloride secretion and are profoundly deaf. J. Biol. Chem. 274:26946–26955
Forrester R.L., Wataji L.J., Silverman D.A., Pierre K.J. 1976. Enzymatic method for the determination of CO2 in serum. Clin. Chem. 22:243–245
Forte L.R., Eber S.L., Turner J.T., Freeman R.H., Fok K.F., Currie M.G. 1993. Guanylin stimulation of Cl− secretion in human intestinal T84 cells via cyclic guanosine monophosphate. J. Clin. Invest. 91:2423–2428
Goldstein J.L., Sahi J., Bhuva M., Layden T.J., Rao M.C. 1994. Escherichia coli heat-stable enterotoxin-mediated colonic Cl− secretion is absent in cystic fibrosis. Gastroenterology 107:950–956
Guandalini S., Rao M.C., Smith P.L., Field M. 1982. cGMP modulation of ileal ion transport: in vitro effects of Escherichia coli heat-stable e. Am. J. Physiol. 243:G36–G41
Guba M., Kuhn M., Forssmann W.G., Classen M., Gregor M., Seidler U. 1996. Guanylin strongly stimulates rat duodenal HCO3− secretion: proposed mechanism and comparison with other secretagogues. Gastroenterology 111:1558–1568
Guerrant R.L., Hughes J.M., Chang B., Robertson D.C., Murad F. 1980. Activation of intestinal guanylate cyclase by heat stable enterotoxin of Escherichia coli: studies of tissue specificity, potential receptors, and intermediates. J. Infect. Diseases 142:220–228
Hamilton D.L., Johnson M.R., Roe W.E., Nielsen N.O. 1978. Effects of intraluminal glucose on intestinal secretion induced by heat stable and heat labile Escherichia coli enterotoxin, cholera toxin and theophylline. Canad J. Comp. Med. 42:89–95
Hamilton D.L., Roe W.E., Nielsen N.O. 1977. Effects of heat-stable and heat labile Escherichia coli enterotoxins, cholera toxin and theophylline on unidirectional sodium and chloride fluxes in the proximal and distal jejunum of weanling swine. Can. J. Comp. Med. 41:306–317
Hamilton R.S. 1966. A direct photometric method for chloride in biological fluids employing mercuric thiocyanate and perchloric acid. Clin. Chem. 12:1–8
Hindle W., Code C.F. 1962. Some differences between duodenal and ileal sorption. Amer. J. Physiol. 203:215–220
Hohorst H.J. 1957. Enzymatic determination of L (+) lactic acid. Biochem. Z. 328:509–521
Hubel K.A. 1973. Effect of luminal sodium concentration on bicarbonate absorption in rat jejunum. J. Clin. Invest. 52:3172–3179
Humphreys M.H., Earley L.E. 1971. The mechanism of decreased intestinal sodium and water absorption after acute volume expansion in the rat. J. Clin. Invest. 50:2355–2367
Huott P.A., Liu W., McRoberts J.A., Giannella R.A., Dharmsathaphorn K. 1988. Mechanism of action of Escherichia coli heat stable enterotoxin in a human colonic cell line. J. Clin. Invest. 82:514–523
Ieda H., Naruse S., Kitigawa M., Ishiguro H., Hayakawa T. 1999. Effects of guanylin and uroguanylin on rat jejunal fluid and electrolyte transport: comparison with heat-stable enterotoxin. Regulatory Peptides 79:165–171
Jodal M., Lundgren O., Naftalin R.J. 1987. Changes in vivo in rat ileal fluid uptake and mucosal volume induced by changes in the tonicity of the luminal perfusion fluid. J. Physiol. 391:P29
Klipstein F.A., Engert R.F. 1978. Reversal of jejunal water secretion by glucose in rats exposed to coliform enterotoxins. Gastroenterology, 75:255–262
Krebs H.A., Henseleit K. 1932. Untersuchungen über die Harnstoffbildung im Tierkörper. Hoppe-Seyler’s Z. Physiol. Chemie 210:33–66
Kuhn M., Adermann K., Jähne J., Forssmann W.G., Rechkemmer G. 1994. Segmental differences in the effects of guanylin and Escherichia coli heat-stable enterotoxin on Cl− secretion in human gut. J. Physiol. 479:433–440
Lee J.S. 1977. Epithelial cell extrusion during fluid transport in canine small intestine. Amer. J. Physiol. 232:E408–E414
Lucas M.L. 2005. Amendments to the theory underlying Ussing chamber data of chloride ion secretion after bacterial enterotoxin exposure. J. Theor. Biol. 234:21–37
Lucas M.L., Cannon M.J. 1983. Measurement of sodium ion concentration in the unstirred layer of rat small intestine by polymer Na+-sensitive electrodes. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 730:41–48
McEwan G.T.A., Lucas M.L. 1990. The effect of E. coli STa enterotoxin on the absorption of weakly dissociable drugs from rat proximal jejunum in vivo. Brit. J. Pharmacol. 101:937–943
Miller D.L., Schedl H.P. 1970. Total recovery studies of nonabsorbable indicators in the rat small intestine. Gastroenterology 58:40–46
Moreau A. 1868. Ueber die Folgen der Durchschneidung der Darmnerven. Zentralbl. Med. Wissenschaft 14:209–211
Mourad F.H., Nassar C.F. 2000. Effect of vasoactive intestinal polypeptide (VIP) antagonism on rat jejunal fluid and electrolyte secretion induced by cholera and Escherichia coli enterotoxin. Gut 47:382–386
Nataro J.P., Kaper J.B. 1998. Diarrheagenic Escherichia coli. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 11:142–201
Nobles M., Diener M., Rummel W. 1991. Segment-specific effects of the heat-stable enterotoxin of E. coli on electrolyte transport in the rat colon. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 202:201–211
Nzegwu H.C., Levin R.J. 1994. Fluid hypersecretion induced by enterotoxin STa in nutritionally deprived rats: jejunal and ileal dynamics in vivo. Exp. Physiol. 79:547–560
Orlowski J. 1993. Heterologous expression and functional properties of amiloride high affinity (NHE-1) and low affinity (NHE-3) isoforms of the rat Na/H exchanger. J. Biol. Chem. 268:16369–16377
Pappenheimer J.R., Reiss K.Z. 1987. Contribution of solvent drag through intracellular junctions to absorption of nutrients by the small intestine of the rat. J. Membrane Biology 100:123–136
Raabo E., Terkildsen T.C. 1960. On the enzymatic determination of blood glucose. Scand. J. Clin. Lab. Invest. 12:402–409
Rolfe V., Levin R.J. 1994. Enterotoxin Escherichia coli STa activates a nitric oxide-dependent myenteric plexus secretory reflex in the rat ileum. J. Physiol. 475:531–537
Rolston D.D.K., Mathan V.I. 1992. Effect of base precursors on water and electrolyte transport during oral hydration solution perfusion in secreting rat intestine. Dig. Dis. Sci. 37:47–52
Schanker L.S., Tocco D.J., Brodie B.B., Hogben C.A.M. 1958. Absorption of drugs from the rat small intestine. J. Pharmaceut. Exp. Therapeutics 123:81–88
Schulz S., Lopez M.J., Kuhn M., Garbers D.L. 1997. Disruption of the guanyl cyclase-C gene leads to a paradoxical phenotype of viable but heat stable enterotoxin-resistant mice. J. Clin. Invest. 100:1590–1595
See N.A., Bass P. 1993. Glucose-induced ion secretion in rat jejunum-a mucosal reflex that requires integration by the myenteric plexus. J. Auton. Nerv. System 42:33–40
Sheerin H.E., Field M. 1977. Ileal mucosal cyclic AMP and Cl secretion: serosal vs. mucosal addition of cholera toxin. Amer. J. Physiol. 232:E210–E215
Solomon A.K. 1964. Validity of tracer measurements of fluxes in kidney tubules and other three compartment systems. In: Snell F.M., Noell W.K., Eds, Transcellular membrane potentials and ionic fluxes. Chapter IV. Gordon & Breach, New York, London
Sladen G.E., Harries J.T. 1972. Studies on the effects of unconjugated dihydroxy bile salts on rat small intestinal function in vivo. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 288:443–456
Sund R.B. 1975. The effect of dodecylsulphate upon net sodium and water transport from tied jejunal loops in anaesthetized rats. Acta Pharmacol. Toxicol. 37:282–296
Tantisira M.H., Jodal M., Lundgren O. 1990. Further studies of the changes in alkaline secretion, transepithelial potential difference and net fluid transport induced by the heat-stable enterotoxin of Escherichia coli (STa) in the rat jejunum in vivo. Acta Physiol. Scand. 140:557–565
Teitelbaum D.H., Sonnino R.E., Dunaway D.J., Stellin G., Harmel R.P. 1993. Rat jejunal absorptive function after intestinal transplantation. Effects of extrinsic denervation. Digest. Dis. Sci 38:1099–1104
Thiagarajah J.R., Broadbent E., Hsieh E., Verkman A.S. 2004. Prevention of toxin-induced intestinal ion and fluid secretion by a small-molecule CFTR inhibitor. Gastroenterology 126:511–519
Turvill J.L., Kasapidis P., Farthing M.J.G. 1999. The sigma ligand, igmesine, inhibits cholera toxin and Escherichia coli enterotoxin induced jejunal secretion in the rat. Gut 45:564–569
Vaandrager A.B., Bot A.G.M., Ruth P., Pfeifer A., Hofmann F., De Jonge H.R. 2000. Differential role of cyclic GMP-dependent protein kinase II in ion transport in murine small intestine and colon. Gastroenterology 118:108–114
Volant K., Grishina O., Descroix-Vagne M., Pansu D. 1997. Guanylin-, heat-stable enterotoxin of Escherichia coli- and vasoactive intestinal polypeptide-induced water and ion secretion in the rat intestine in vivo. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 328:217–227
Winne D., Görig H. 1982. Appearance of 14C-polyethylene glycol 4000 in intestinal venous blood: influence of osmolarity and laxatives, effect on net water flux determination. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg’s Arch. Pharmakol. 321:149–156
Young A., Levin R.J. 1990. Diarrhoea of famine and malnutrition: investigations using a rat model. 1 Jejunal hypersecretion induced by starvation. Gut 31:43–53
Young A., Levin R.J. 1992. Intestinal hypersecretion of the refed starved rat: a model for alimentary diarrhea. Gut 33:1050–1056
Acknowledgement
The authors are grateful to the late Dr. Oliver Holmes and to the late Dr. A.V. Edwards for their advice and interest in the topic. My (MLL) thanks are offered to the Royal Society of London and to Astra-Haessle for providing research funding.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lucas, M., Thom, M., Bradley, J. et al. Escherichia coli Heat Stable (STa) Enterotoxin and the Upper Small Intestine: Lack of Evidence in Vivo for Net Fluid Secretion. J Membrane Biol 206, 29–42 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00232-005-0771-6
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00232-005-0771-6