Abstract
Background
We previously reported on a Swedish patient with Behçet’s disease (BD) who was an ultra-rapid metaboliser of drugs catalysed by CYP2C9. Was this extreme metabolism caused by the disease?
Aim
This study aims to compare the genotype/phenotype of CYP2C9 in patients with BD and healthy subjects. As the occurrence of BD is high in Turkey, all subjects were recruited from this country.
Methods
Genotyping of CYP2C9 was performed using standard PCR-RFLP and allele-specific PCR methods. Phenotyping of CYP2C9 was performed by administration of a 50-mg single oral dose of losartan and by calculating the urinary metabolic ratio (MR) of probe drug to its metabolite E-3174. Quantitation was performed by HPLC.
Results
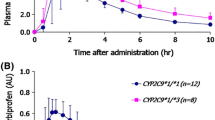
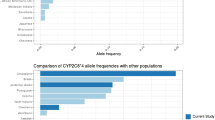
The frequency of CYP2C9*2 and *3 was not significantly different between the Behçet’s disease patients (12.5 and 8.7 %) and the healthy subjects (8.9 and 8.2 %). The geometric mean losartan MR was higher in the 52 patients (1.75) than in the 96 healthy subjects (1.02) (p = 0.002; t-test). Within the genotypes *1/*1, there was a significant difference of MR between patients and healthy subjects (P = 0.006). All but three of the Behçet’s disease patients were treated with colchicine. In nine subsequent patients, we found no significant effect of 2 weeks of treatment with colchicine on the CYP2C9 MR.
Conclusion
Contrary to expectation, the CYP2C9 activity was lower in Turkish BD patients compared to healthy subjects. As this seems not to be due to colchicine treatment, our hypothesis is that inflammation related to BD might have caused the down-regulation of the CYP2C9 activity due to immune cytokine reactions. The ultra-rapid metabolism of CYP2C9 substrate drugs in the Swedish patient was not due to her BD.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Helldén A, Bergman U, Hellgren KE, Masquelier M, Remahl IN, Odar-Cederlöf I, Ramsjö M, Bertilsson L (2010) Fluconazole-induced intoxication with phenytoin in a patient with ultra-high activity of CYP2C9. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 66(8):791–795
Hatta FH, Teh LK, Helldén A, Hellgren KE, Roh HK, Salleh MZ, Aklillu E, Bertilsson L (2012) Search for the molecular basis of ultra-rapid CYP2C9-catalysed metabolism: relationship between SNP IVS8-109A > T and the losartan metabolism phenotype in Swedes. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 68(7):1033–1042
Kaya TI (2012) Genetics of Behçet’s disease. Patho Res Int 2012, Article ID 912589, 6 pages doi:10.1155/2012/912589
Mizuki N, Meguro A, Ota M, Ohno S, Shiota T, Kawagoe T, Ito N, Kera J, Okada E, Yatsu K, Song YW, Lee EB, Kitaichi N, Namba K, Horie Y, Takeno M, Sugita S, Mochizuki M, Bahram S, Ishigatsubo Y, Inoko H (2010) Genome-wide association studies identify IL23R-IL12RB2 and IL10 as Behçet’s disease susceptibility loci. Nat Genet 42(8):703–706
Mahr A, Belarbi L, Wechsler B, Jeanneret D, Dhote R, Fain O, Lhote F, Ramanoelina J, Coste J, Guillevin L (2008) Population-based prevalence study of Behçet’s disease: differences by ethnic origin and low variation by age at immigration. Arthritis Rheum 58(12):3951–3959
Keino H, Okada AA (2007) Behçet’s disease: global epidemiology of an old silk road disease. Br J Ophthalmol 91(12):1573–1574
Türsen Ü (2012) Pathophysiology of the Behçet’s disease. Patholog Res Int Published online 2011 October 1. doi: 10.1155/2012/493015
Mizushima Y, Matsumura N, Shimizu T, Fukushima B, Mimura Y, Saito K, Sugiura S (1977) Colchicine in Behçet’s disease. Lancet 2:1037
Haim S, Friedman-Birnbaum R (1977) Colchicine in Behçet’s disease. Harefuah 93:399–400
Dvorak Z, Modrianský M, Pichard-Garcia L, Balaguer P, Vilarem MJ, Ulrichová J, Maurel P, Pascussi JM (2003) Colchicine down-regulates cytochrome P450 2B6, 2C8, 2C9, and 3A4 in human hepatocytes by affecting their glucocorticoid receptor-mediated regulation. Mol Pharmacol 64:160–169
Babaoglu MO, Yasar U, Sandberg M, Eliasson E, Dahl ML, Kayaalp SO, Bozkurt A (2004) CYP2C9 genetic variants and losartan oxidation in a Turkish population. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 60(5):337–342
Tursen U, Tamer L, Api H, Yildirim H, Baz K, İkizoglu G, Atik U (2007) Cytochrome P450 polymorphisms in patients with Behçet’s disease. Int J Dermatol 46:153–156
Liang L, Wang H, Peng XY, Zhao M (2011) The changes of Th lymphocyte subsets in patients with Behçet disease. Zhonghua Yan Ke Za Zhi 47(5):393–397
Renton KW (2004) Cytochrome P450 regulation and drug biotransformation during inflammation and infection. Curr Drug Metab 5:235–243
Aitken AE, Richardson TA, Morgan ET (2006) Regulation of drug-metabolizing enzymes and transporters in inflammation. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 46:123–149
Aitken AE, Morgan ET (2007) Gene-specific effects of inflammatory cytokines on cytochrome P450 2C, 2B6 and 3A4 mRNA levels in human hepatocytes. Drug Metab Dispos 35(9):1687–1693
Yasar U, Sain-Guven G, Yardimci Y, Kilicarslan A, Babaoglu MO, Bozkurt A (2011) Effect of atorvastatin on CYP2C9 metabolic activity as measured by the formation rate of losartan metabolite in hypercholesterolaemic patients. Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol 109(2):73–77
Barrett JC, Fry B, Maller J, Daly MJ (2005) Haploview: analysis and visualization of LD and haplotype maps. Bioinformatics 21(2):263–265
Akman-Demir G, Tüzün E, Içöz S, Yeşilot N, Yentür SP, Kürtüncü M, Mutlu M, Saruhan-Direskeneli G (2008) Interleukin-6 in neuro-Behçet’s disease: association with disease subsets and long-term outcome. Cytokine 44:373–376
Shimizu J, Yoshikawa H, Takada E, Hirotsu C, Suzuki N (2011) Unbalanced helper T-cell function in Behçet’s disease. Inflamm Regenet 31:296–301
Knüpfer H, Schmidt R, Stanitz D, Brauckhoff M, Schönfelder M, Preiss R (2004) CYP2C and IL-6 expression in breast cancer. Breast 13:28–34
Shah RR, Smith RL (2015) Inflammation-induced phenoconversion of polymorphic drug metabolizing enzymes: a hypothesis with implications for personalized medicine. Drug Metab Dispos 43:400–410
Daneshtalab N, Lewanczuk RZ, Russell AS, Jamali F (2006) Drug–disease interactions: losartan effect is not downregulated by rheumatoid arthritis. J Clin Pharmacol 46:1344–1355
Dreisbach AW, Japa S, Gebrekal AB, Mowry SE, Lertora JJ, Kamath BL, Rettie AE (2003) Cytochrome P4502C9 activity in end-stage renal disease. Clin Pharmacol Ther 73:475–477
Limdi MA, Crowley MR, Beasley TM, Limdi NA, Allon M (2013) Influence of kidney function on risk of hemorrhage among patients taking warfarin: a cohort study. Am J Kidney Dis 61:354–357
Limdi NA, Limdi MA, Cavallari L, Anderson AM, Crowley MR, Baird MF, Allon M, Beasley TM (2010) Warfarin dosing in patients with impaired kidney function. Am J Kidney Dis 56:823–831
Langmann T, Schmitz G (2006) Loss of detoxification in inflammatory bowel disease. Nat Clin Pract Gastroenterol Hepatol 3:358–359
Acknowledgments
Support wasgranted by Hacettepe University Scientific Research Projects Coordination Unit (HU.09.D06.101.005).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Mustafa Tugrul Goktaş and Fazleen Hatta contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Goktaş, M.T., Hatta, F., Karaca, O. et al. Lower CYP2C9 activity in Turkish patients with Behçet’s disease compared to healthy subjects: a down-regulation due to inflammation?. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 71, 1223–1228 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00228-015-1899-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00228-015-1899-7