Abstract
Purpose
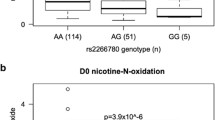
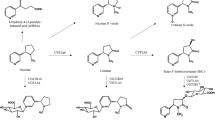
We investigated the role of genetic, physiological, environmental, and epigenetic factors in regulating CYP2A6 expression and nicotine metabolism.
Methods
Human livers (n = 67) were genotyped for CYP2A6 alleles and assessed for nicotine metabolism and CYP2A6 expression (mRNA and protein). In addition, a subset of livers (n = 18), human cryopreserved hepatocytes (n = 2), and HepG2 cells were used for DNA methylation analyses.
Results
Liver samples with variant CYP2A6 alleles had significantly lower CYP2A6 protein expression, nicotine C-oxidation activity, and affinity for nicotine. Female livers had significantly higher CYP2A6 protein and mRNA expression compared to male livers. Livers exposed to dexamethasone and phenobarbital had higher CYP2A6 expression and activity, however the difference was not statistically significant. Age and DNA methylation status of the CpG island and a regulatory site were not associated with altered CYP2A6.
Conclusions
We identified genotype, gender, and exposure to inducers as sources of variation in CYP2A6 expression and activity, but much variation remains to be accounted for.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Pelkonen O, Rautio A, Raunio H, Pasanen M (2000) CYP2A6: a human coumarin 7-hydroxylase. Toxicology 144(1–3):139–147. doi:S0300483X99002000 [pii]
Benowitz NL (2009) Pharmacology of nicotine: addiction, smoking-induced disease, and therapeutics. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 49:57–71. doi:10.1146/annurev.pharmtox.48.113006.094742
Ho MK, Tyndale RF (2007) Overview of the pharmacogenomics of cigarette smoking. Pharmacogenomics J 7(2):81–98. doi:6500436 [pii] 10.1038/sj.tpj.6500436
Benowitz NL, Jacob P 3rd (1994) Metabolism of nicotine to cotinine studied by a dual stable isotope method. Clin Pharmacol Ther 56(5):483–493
Messina ES, Tyndale RF, Sellers EM (1997) A major role for CYP2A6 in nicotine C-oxidation by human liver microsomes. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 282(3):1608–1614
Nakajima M, Yamamoto T, Nunoya K, Yokoi T, Nagashima K, Inoue K, Funae Y, Shimada N, Kamataki T, Kuroiwa Y (1996) Role of human cytochrome P4502A6 in C-oxidation of nicotine. Drug Metab Dispos 24(11):1212–1217
Nakajima M, Fukami T, Yamanaka H, Higashi E, Sakai H, Yoshida R, Kwon JT, McLeod HL, Yokoi T (2006) Comprehensive evaluation of variability in nicotine metabolism and CYP2A6 polymorphic alleles in four ethnic populations. Clin Pharmacol Ther 80(3):282–297. doi:S0009-9236(06)00204-9 [pii] 10.1016/j.clpt.2006.05.012
Shimada T, Yamazaki H, Mimura M, Inui Y, Guengerich FP (1994) Interindividual variations in human liver cytochrome P-450 enzymes involved in the oxidation of drugs, carcinogens and toxic chemicals: studies with liver microsomes of 30 Japanese and 30 Caucasians. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 270(1):414–423
Rodriguez-Antona C, Donato MT, Pareja E, Gomez-Lechon MJ, Castell JV (2001) Cytochrome P-450 mRNA expression in human liver and its relationship with enzyme activity. Arch Biochem Biophys 393(2):308–315. doi:10.1006/abbi.2001.2499 S0003986101924993 [pii]
Mwenifumbo JC, Al Koudsi N, Ho MK, Zhou Q, Hoffmann EB, Sellers EM, Tyndale RF (2008) Novel and established CYP2A6 alleles impair in vivo nicotine metabolism in a population of Black African descent. Hum Mutat 29(5):679–688. doi:10.1002/humu.20698
Haberl M, Anwald B, Klein K, Weil R, Fuss C, Gepdiremen A, Zanger UM, Meyer UA, Wojnowski L (2005) Three haplotypes associated with CYP2A6 phenotypes in Caucasians. Pharmacogenet Genomics 15(9):609–624. doi:01213011-200509000-00002 [pii]
Kiyotani K, Yamazaki H, Fujieda M, Iwano S, Matsumura K, Satarug S, Ujjin P, Shimada T, Guengerich FP, Parkinson A, Honda G, Nakagawa K, Ishizaki T, Kamataki T (2003) Decreased coumarin 7-hydroxylase activities and CYP2A6 expression levels in humans caused by genetic polymorphism in CYP2A6 promoter region (CYP2A6*9). Pharmacogenetics 13(11):689–695. doi:10.1097/01.fpc.0000054136.14659.be
Fukami T, Nakajima M, Higashi E, Yamanaka H, Sakai H, McLeod HL, Yokoi T (2005) Characterization of novel CYP2A6 polymorphic alleles (CYP2A6*18 and CYP2A6*19) that affect enzymatic activity. Drug Metab Dispos 33(8):1202–1210. doi:dmd.105.004994 [pii] 10.1124/dmd.105.004994
Benowitz NL, Lessov-Schlaggar CN, Swan GE, Jacob P 3rd (2006) Female sex and oral contraceptive use accelerate nicotine metabolism. Clin Pharmacol Ther 79(5):480–488. doi:S0009-9236(06)00033-6 [pii] 10.1016/j.clpt.2006.01.008
Molander L, Hansson A, Lunell E (2001) Pharmacokinetics of nicotine in healthy elderly people. Clin Pharmacol Ther 69(1):57–65. doi:S0009-9236(01)99195-7 [pii] 10.1067/mcp. 2001.113181
Ho M, Mwenifumbo J, Al Koudsi N, Okuyemi K, Ahluwalia J, Benowitz N, Tyndale R (2009) Association of nicotine metabolite ratio and CYP2A6 genotype with smoking cessation treatment in African-American light smokers. Clin Pharmacol Ther. doi:clpt200919 [pii] 10.1038/clpt.2009.19
Hukkanen J, Jacob P 3rd, Benowitz NL (2006) Effect of grapefruit juice on cytochrome P450 2A6 and nicotine renal clearance. Clin Pharmacol Ther 80(5):522–530. doi:S0009-9236(06)00329-8 [pii] 10.1016/j.clpt.2006.08.006
Maurice M, Emiliani S, Dalet-Beluche I, Derancourt J, Lange R (1991) Isolation and characterization of a cytochrome P450 of the IIA subfamily from human liver microsomes. Eur J Biochem 200(2):511–517
Gomez A, Ingelman-Sundberg M (2009) Pharmacoepigenetics: its role in interindividual differences in drug response. Clin Pharmacol Ther 85(4):426–430. doi:clpt20092 [pii] 10.1038/clpt.2009.2
Schumacher A, Petronis A (2006) Epigenetics of complex diseases: from general theory to laboratory experiments. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol 310:81–115
Ingelman-Sundberg M, Sim SC, Gomez A, Rodriguez-Antona C (2007) Influence of cytochrome P450 polymorphisms on drug therapies: pharmacogenetic, pharmacoepigenetic and clinical aspects. Pharmacol Ther 116(3):496–526. doi:S0163-7258(07)00201-X [pii] 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2007.09.004
Ling G, Wei Y, Ding X (2007) Transcriptional regulation of human CYP2A13 expression in the respiratory tract by CCAAT/enhancer binding protein and epigenetic modulation. Mol Pharmacol 71(3):807–816. doi:mol.106.031104 [pii] 10.1124/mol.106.031104
Campbell ME, Grant DM, Inaba T, Kalow W (1987) Biotransformation of caffeine, paraxanthine, theophylline, and theobromine by polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon-inducible cytochrome(s) P-450 in human liver microsomes. Drug Metab Dispos 15(2):237–249
Meier PJ, Mueller HK, Dick B, Meyer UA (1983) Hepatic monooxygenase activities in subjects with a genetic defect in drug oxidation. Gastroenterology 85(3):682–692. doi:S0016508583002176 [pii]
Pearce RE, McIntyre CJ, Madan A, Sanzgiri U, Draper AJ, Bullock PL, Cook DC, Burton LA, Latham J, Nevins C, Parkinson A (1996) Effects of freezing, thawing, and storing human liver microsomes on cytochrome P450 activity. Arch Biochem Biophys 331(2):145–169. doi:S0003-9861(96)90294-5 [pii] 10.1006/abbi.1996.0294
Yamazaki H, Inoue K, Turvy CG, Guengerich FP, Shimada T (1997) Effects of freezing, thawing, and storage of human liver samples on the microsomal contents and activities of cytochrome P450 enzymes. Drug Metab Dispos 25(2):168–174
Schoedel KA, Hoffmann EB, Rao Y, Sellers EM, Tyndale RF (2004) Ethnic variation in CYP2A6 and association of genetically slow nicotine metabolism and smoking in adult Caucasians. Pharmacogenetics 14(9):615–626. doi:00008571-200409000-00006 [pii]
Al Koudsi N, Ahluwalia JS, Lin SK, Sellers EM, Tyndale RF (2009) A novel CYP2A6 allele (CYP2A6(*)35) resulting in an amino-acid substitution (Asn438Tyr) is associated with lower CYP2A6 activity in vivo. Pharmacogenomics J. doi:tpj200911 [pii] 10.1038/tpj.2009.11
Al Koudsi N, Mwenifumbo JC, Sellers EM, Benowitz NL, Swan GE, Tyndale RF (2006) Characterization of the novel CYP2A6*21 allele using in vivo nicotine kinetics. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 62(6):481–484. doi:10.1007/s00228-006-0113-3
Itoh M, Nakajima M, Higashi E, Yoshida R, Nagata K, Yamazoe Y, Yokoi T (2006) Induction of human CYP2A6 is mediated by the pregnane X receptor with peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma coactivator 1alpha. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 319(2):693–702. doi:jpet.106.107573 [pii] 10.1124/jpet.106.107573
Bock C, Reither S, Mikeska T, Paulsen M, Walter J, Lengauer T (2005) BiQ Analyzer: visualization and quality control for DNA methylation data from bisulfite sequencing. Bioinformatics 21(21):4067–4068. doi:bti652 [pii] 10.1093/bioinformatics/bti652
Yamano S, Tatsuno J, Gonzalez FJ (1990) The CYP2A3 gene product catalyzes coumarin 7-hydroxylation in human liver microsomes. Biochemistry 29(5):1322–1329
Oscarson M, McLellan RA, Asp V, Ledesma M, Bernal Ruiz ML, Sinues B, Rautio A, Ingelman-Sundberg M (2002) Characterization of a novel CYP2A7/CYP2A6 hybrid allele (CYP2A6*12) that causes reduced CYP2A6 activity. Hum Mutat 20(4):275–283. doi:10.1002/humu.10126
Pitarque M, von Richter O, Oke B, Berkkan H, Oscarson M, Ingelman-Sundberg M (2001) Identification of a single nucleotide polymorphism in the TATA box of the CYP2A6 gene: impairment of its promoter activity. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 284(2):455–460. doi:10.1006/bbrc.2001.4990 S0006-291X(01)94990-3 [pii]
Hukkanen J, Jacob P 3rd, Benowitz NL (2005) Metabolism and disposition kinetics of nicotine. Pharmacol Rev 57(1):79–115. doi:57/1/79 [pii] 10.1124/pr.57.1.3
Higashi E, Fukami T, Itoh M, Kyo S, Inoue M, Yokoi T, Nakajima M (2007) Human CYP2A6 is induced by estrogen via estrogen receptor. Drug Metab Dispos 35(10):1935–1941. doi:dmd.107.016568 [pii] 10.1124/dmd.107.016568
Parkinson A, Mudra DR, Johnson C, Dwyer A, Carroll KM (2004) The effects of gender, age, ethnicity, and liver cirrhosis on cytochrome P450 enzyme activity in human liver microsomes and inducibility in cultured human hepatocytes. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 199(3):193–209. doi:10.1016/j.taap.2004.01.010 S0041008X04000638 [pii]
Kinirons MT, O'Mahony MS (2004) Drug metabolism and ageing. Br J Clin Pharmacol 57(5):540–544. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2125.2004.02096.x BCP2096 [pii]
Wortham M, Czerwinski M, He L, Parkinson A, Wan YJ (2007) Expression of constitutive androstane receptor, hepatic nuclear factor 4 alpha, and P450 oxidoreductase genes determines interindividual variability in basal expression and activity of a broad scope of xenobiotic metabolism genes in the human liver. Drug Metab Dispos 35(9):1700–1710. doi:dmd.107.016436 [pii] 10.1124/dmd.107.016436
Yamazaki H, Inoue K, Hashimoto M, Shimada T (1999) Roles of CYP2A6 and CYP2B6 in nicotine C-oxidation by human liver microsomes. Arch Toxicol 73(2):65–70
Hart SN, Wang S, Nakamoto K, Wesselman C, Li Y, Zhong XB (2008) Genetic polymorphisms in cytochrome P450 oxidoreductase influence microsomal P450-catalyzed drug metabolism. Pharmacogenet Genomics 18(1):11–24. doi:10.1097/FPC.0b013e3282f2f121 01213011-200801000-00002 [pii]
Dannenberg LO, Edenberg HJ (2006) Epigenetics of gene expression in human hepatoma cells: expression profiling the response to inhibition of DNA methylation and histone deacetylation. BMC Genomics 7:181. doi:1471-2164-7-181 [pii] 10.1186/1471-2164-7-181
Kerkel K, Spadola A, Yuan E, Kosek J, Jiang L, Hod E, Li K, Murty VV, Schupf N, Vilain E, Morris M, Haghighi F, Tycko B (2008) Genomic surveys by methylation-sensitive SNP analysis identify sequence-dependent allele-specific DNA methylation. Nat Genet 40(7):904–908. doi:ng.174 [pii] 10.1038/ng.174
Acknowledgments
We thank Bin Zhao, Qian Zhou, Fariba Baghai Wadji, Sharon Miksys, Linda Liu, and Amandeep Mann for their technical assistance and Dr. Arturas Petronis for his valuable input in planning and analyzing the epigenetic experiments. This work was supported by the Centre for Addiction and Mental Health and Canadian Institutes for Health Research (CIHR) MOP86471. N.K. receives funding from CIHR-Strategic Training Program in Tobacco Use in Special Populations (TUSP) and Ontario Graduate Scholarship program (OGS). R.F.T. holds a Canada Research Chair in Pharmacogenetics.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Al Koudsi, N., Hoffmann, E.B., Assadzadeh, A. et al. Hepatic CYP2A6 levels and nicotine metabolism: impact of genetic, physiological, environmental, and epigenetic factors. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 66, 239–251 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00228-009-0762-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00228-009-0762-0