Abstract
Objective
The aim of this study was to assess the efficacy and safety of a single intravenous (i.v.) bolus of dexketoprofen trometamol compared with an i.v. infusion of dipyrone in patients with moderate to severe pain due to renal colic.
Methods
A total of 308 patients with renal colic and visual analog scale (VAS) score ≥40 mm participated in a multicenter, randomized, double blind, double-dummy, parallel, and active-controlled study and were randomized to dexketoprofen 25 mg (n = 101), dexketoprofen 50 mg (n = 104), and dipyrone 2 g (n = 103).
Results
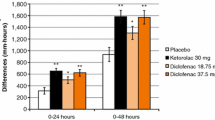
Mean [± standard deviation (SD)] total pain relief (TOTPAR) scores were similar in the dexketoprofen 50 mg (15.3 ± 8.6) and dipyrone (15.5 ± 8.6) and slighly higher than in dexketoprofen 25 mg (13.5 ± 8.6), although significant differences were not achieved. In the same way, patients in the dexketoprofen 50 mg and dipyrone groups showed higher scores in the sum of pain intensity differences (SPID) and the sum of analogue pain intensity differences (SAPID) than patients in the dexketoprofen 25 mg group, reaching statistical significance in comparison with dexketoprofen 25 mg and dipyrone for SPID and SAPID (p < 0.05). The time–effect course for pain intensity differences and pain relief showed significantly higher values for both doses of dexketoprofen during the first 30 min after drug administration (p < 0.05). Dexketoprofen 50 mg and dipyrone groups had 66% and 70%, respectively, of patients with at least 50% of maximum obtainable TOTPAR in comparison with 56% in the dexketoprofen 25 mg group. The study medications were well tolerated.
Conclusions
Dexketoprofen 50 mg administered as a single i.v. bolus was effective for the relief of moderate to severe pain in patients with renal colic, with a good safety profile and efficacy similar to i.v. dipyrone 2 g. Dexketoprofen produced analgesia that was faster in onset.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bagán JV, López Arranz JS, Valencia E, Santamaria J, Eguidazu I, Horas M, Forns M, Zapata A, Artigas R, Mauleon D (1998) Clinical comparison of dexketoprofen trometamol and dipyrone in postoperative dental pain. J Clin Pharmacol 38(Suppl 18):55–64
Beltrán J, Martín Mola E, Figueroa M, Granados J, Sanmarti R, Artigas R, Torres F, Forns M, Mauleon D (1998) Comparison of dexketoprofen trometamol and ketoprofen in the treatment of osteoarthritis of the knee. J Clin Pharmacol 38(Suppl 18):74–80
Bergus GR (1996) Pain relief for renal colic. J Fam Pract 43:438–440
Capriati A, Mas M, Bertolotti M et al (2002) Dexketoprofen trometamol im injection in acute low back pain. International Association for the Study of Pain. 10th World Congress on Pain, August 17–22, San Diego, CA, 1590–P108
Collaborative Group of the Spanish Society of Clinical Pharmacology (1991) Comparative study of the efficacy of dipyrone, diclofenac sodium and pethidine in acute renal colic. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 40:543–546
Cordell WH, Wright SW, Wolfson AB, Timerding BL, Maneatis TJ, Lewis RH, Bynum L, Nelson DR (1996) Comparison of intravenous ketorolac, meperidine, and both (balanced analgesia) for renal colic. Ann Emerg Med 28:151–158
Davenport K, Timoney AG, Keeley FX (2005) Conventional and alternative methods for providing analgesia in renal colic. BJU Int 95:297–300
Debré M, Zapata A, Bertolotti M et al (2002) The analgesic efficacy of dexketoprofen troetamol i.v. in renal colic: a double blind, randomised, active controlled trial versus ketorpofen. International Association for the Study of Pain. 10th World Congress on Pain, August 17–22, San Diego, CA, 1590–P138
Edwards JE, Meseguer F, Faura C, Moore RA, McQuay HJ (2004) Single dose dipyrone for acute renal colic pain. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 4:CD003867
Ezcurdia M, Cartejoso FJ, Lanzón R, Ugalde FJ, Herruzo A, Artigas R, Fernandez F, Torres F, Mauleon D (1998) Comparison of the efficacy and tolerability of dexketoprofen and ketoprofen in the treatment of primary dysmenorrhea. J Clin Pharmacol 38(Suppl 18):65–73
Gay C, Planas E, Donado M, Martínez JM, Artigas R, Torres F, Mauleón D, Carganico G (1996) Analgesic effect of low doses of dexketoprofen in the dental pain model: a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Clin Drug Invest 11:320–330
Hanna MH, Elliott KM, Stuart-Taylor ME, Roberts DR, Buggy D, Arthurs GJ (2003) Comparative study of analgesic efficacy and morphine-sparing effect of intramuscular dexketoprofen trometamol with ketoprofen or placebo after major orthopaedic surgery. Br J Clin Pharmacol 55:126–133
Heid J, Jage J (2002) The treatment of pain in urology. BJU Int 90:126–133
Holdgate A, Pollock T (2004) Systematic review of the relative efficacy of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and opioids in the treatment of acute renal colic. BMJ 328:1401
Jimenez-Martinez E, Gasco-Garcia C, Arrieta-Blanco JJ, Gomez del Torno J, Bartolome Villar B (2004) Study of the analgesic efficacy of Dexketoprofen Trometamol 25 mg. vs. Ibuprofen 600 mg. after their administration in patients subjected to oral surgery. Oral Med 9:143–148
Labrecque M, Dostaler LP, Rousselle R, Nguyen T, Poirier S (1994) Efficacy of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs in the treatment of acute renal colic. A meta-analysis. Arch Intern Med 154:1381–1387
Larkin GL, Peacock WF 4th, Pearl SM, Blair GA, D’Amico F (1999) Efficacy of ketorolac tromethamine versus meperidine in the ED treatment of acute renal colic. Am J Emerg Med 17:6–19
Mauleón D, Artigas R, García ML, Carganico G (1996) Preclinical and clinical development of dexketoprofen trometamol. Drugs 52(Suppl 5):24–46
McGurk M, Robinson P, Rajayogeswaran V, De Luca M, Casini A, Artigas R, Munoz G, Mauleon D (1998) Clinical comparison of dexketoprofen trometamol, ketoprofen, and placebo in postoperative dental pain. J Clin Pharmacol 38(Suppl 18):46–54
Miralles F, Zapata A, Mas A et al (2002) Morphine sparing effect of dexketoprofen trometamol when used in the treatment of postoperative pain after major abdominal surgery. International Association for the Study of Pain. 10th World Congress on Pain, August 17–22, San Diego, CA, 952–P222
Muriel C, Ortiz P, the Cooperative Study Group (1993) Efficacy of two different intramuscular doses of dipyrone in acute renal colic. Meth Find Exp Clin Pharmacol 15:465–469
Muriel-Villoria C, Zungri-Telo E, Díaz-Curiel M, Fernández-Guerrero M, Moreno J, Puerta J, Ortiz P (1995) Comparison of the onset and duration of the analgesic effect of dipyrone, 1 or 2 g, by the intramuscular or intravenous route, in acute renal colic. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 48:103–107
Ready LB, Brown CR, Stahlgren LH, Egan KJ, Ross B, Wild L, Moodie JE, Jones SF, Tommeraasen M, Trierwieler M (1994) Evaluation of intravenous ketorolac administered by bolus or infusion for treatment of postoperative pain. A double-blind, placebo-controlled, multicenter study. Anesthesiology 80:1277–1286
Rodriguez MJ, Contreras D, Gálvez R, Castro A, Camba MA, Busquets C, Herrera J (2003) Double-blind evaluation of short-term analgesic efficacy of orally administered dexketoprofen trometamol and ketorolac in bone cancer pain. Pain 104:103–110
Sánchez-Carpena J, Sesma-Sánchez J, Sánchez-Juan C, Tomás-Vecina S, García-Alonso D, Rico-Salvadó J, Forns M, Mas M, Paredes I, Artigas R, the Dexketoprofen Renal Colic Study Group (2003) Comparison of dexketoprofen trometamol and dipyrone in the treatment of renal colic. Clin Drug Invest 23:139–152
Stankov G, Schmieder G, Zerle G, Schinzel S, Brune K (1994) Double-blind study with dipyrone versus tramadol and butylscopolamine in acute renal colic pain. World J Urol 12:155–161
Teichman JM (2004) Clinical practice. Acute renal colic from ureteral calculus. N Engl J Med 350:684–693
Tramer MR, Williams JE, Carroll D, Wiffen PJ, Moore RA, McQuay HJ (1998) Comparing analgesic efficacy of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs given by different routes in acute and chronic pain: a qualitative systematic review. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand 42:71–79
Van Laecke E, Oosterlinck W (1994) Physiopathology of renal colic and the therapeutic consequences. Acta Urol Belg 62:15–18
Acknowledgments
This study was financially supported by a grant from the Menarini Group. The authors have no conflicts of interest directly relevant to the content of this study. The authors thank Marta Pulido MD for editing the manuscript and editorial assistance, and Silvia Garrido for the technical support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Consortia
Corresponding author
Additional information
Dexketoprofen Renal Colic Study Group: S. Tomás Vecina, Hospital Mútua de Terrassa, Barcelona; Ma L. Recuero Sánchez, Hospital del Insalud de Mérida, Badajoz; R. Bugarín González, Hospital Clínico Universitario, Santiago de Compostela, E. Gene Tous, Corporació Sanitària Parc Taulí, Sabadell, Barcelona; JA. Mota Gracia, Hospital Rafael Méndez, Murcia; A. Román Jasanada, Hospital General Universitario de Guadalajara, Guadalajara; Sonia González, Fundación Hospital Alcorcón, Alcorcón, Madrid; D. García Alonso, Consorci Sanitari de Terrassa, Terrassa, Barcelona; L García González, Consorci Sanitari Integral, Hospital General de l’Hospitalet de Llobregat, Barcelona; J. Sánchez Carpena, Hospital Universitario Dr. Peset, Valencia; M. Mariné Blanco, Hospital de El Escorial, El Escorial, Madrid; F, Roqueta Egea, Fundació Althaia — Xarxa Assistencial de Manresa, Manresa, Barcelona; J. A. Serrano Martínez, Hospital General Universitario Morales Messeguer, Murcia; G. Ferrán Martínez, Hospital General de Castellón, Castellón; A. Martín Joven, Policlínica de Vigo, S.A, Pontevedra; M.L. Mosteiro Álvarez, Hospital de Montecelo, Pontevedra; and F. Domínguez Hervella, Complejo Hospitalario Cristal Piñor, Ourense.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sánchez-Carpena, J., Domínguez-Hervella, F., García, I. et al. Comparison of intravenous dexketoprofen and dipyrone in acute renal colic. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 63, 751–760 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00228-007-0322-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00228-007-0322-4