Abstract
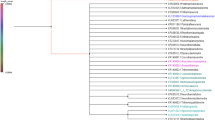
Allozyme electrophoresis was used to compare the genetic divergence of global populations of Mugil cephalus Linnaeus, 1758 and two congeneric [M.␣curema Cuvier & Valenciennes, 1836; M. gyrans (Jordan & Gilbert, 1885)] and two more distantly related [Liza ramada (Risso, 1826); Xenomugil thoburni (Jordan & Starks, 1896)] species on the basis of 18 enzyme loci. The amount of genetic divergence among the species examined is in agreement with their present systematic status, the differences being larger among non-congeneric species than among species of the same genus. Intraspecific genetic distances in M. cephalus (average Nei's D= 0.154), although higher than those reported for conspecific populations of fish, appear to be small when compared to the interspecific values among mugilid species (0.821 ≤ Nei's D ≤ 1.744). Phylogenetic trees obtained by genetic distance methods and discrete character parsimony analysis were of similar topology, except for the relationships within the genus Mugil and for the arrangement of M. cephalus populations.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 7 April 1997 / Accepted: 4 February 1998
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rossi, A., Capula, M., Crosetti, D. et al. Genetic divergence and phylogenetic inferences in five species of Mugilidae (Pisces: Perciformes). Marine Biology 131, 213–218 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1007/s002270050313
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s002270050313