Abstract
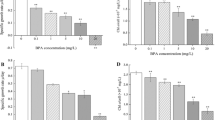
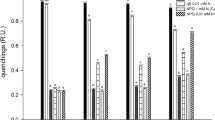
Cylindrotheca closterium is a common marine diatom living in intertidal environments where it can be present both in the water column and on sediments, depending on the tidal regime. In the present work this diatom was employed to investigate the responses to desiccation and to increase in PAR and UVB intensity, as occurs during emersion. Under these circumstances, the production of active oxygen species (AOS) may be enhanced resulting in an oxidative stress. Stress responses in this species were measured by exposing it to normal (30) and double salinity (60), supplying light of low or high intensity for 12 h, in the latter case either without or with moderate dose rates of UVB. Pulse amplitude modulated fluorometry was used to measure Chl a autofluorescence (F0), an index of photosynthetic efficiency of PSII (Fv/Fm) and the relative electron transfer rate (rETR). The oxidative stress was evaluated by analysing GSH pools and SOD activity. It was observed that at double salinity and under low light, intracellular pools of reduced glutathione (GSH) were higher than under the two conditions of high light without and with UVB at both salinities. The antioxidative defence activity of superoxide dismutase (SOD) was far higher under hypersaline conditions. The oxidative damage was evaluated as protein and lipid damage. The results showed that it expressed itself mainly through protein peroxidation: at normal salinity relative protein carbonyl content was (a) twice as high as in cells grown at double salinity, and (b) three times as high under UVB. Total unsaturated lipid contents doubled under hypersalinity conditions. The lipid peroxidation marker malondialdehyde showed the strongest response to low light and UVB at salinity value of 60. Lipid peroxide content was significantly higher at salinity of 60 compared to normal salinity and was the highest under low light and high light with UVB. The simulated emersion condition of the diatom seems to lead to the establishment of a balance between damage and repair, expressed mainly as (a) oxidative protein damage at normal salinity, in particular due to UV radiation, (b) sufficient protection by SOD activity mainly under hypersaline conditions.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allakhverdiev SI, Nishitaka Y, Suzuki I, Tasaka Y, Murata N (1999) Genetic engineering of the unsaturation of fatty acids in membrane lipids alters the tolerance of Synechocystis to salt stress. Plant Biol, Proc Natl Acad USA 26:5862–5867
Al-Medhi AB, Shuman H, Fisher AB (1997) Oxidant generation with K+ -induced depolarization in the isolated perfused lung. Free Radic Biol Med 23:47–56
Asada K, Takahashi M (1987) Production and scavenging of active oxygen in photosynthesis. In: Kyle DJ, Osmond CB, Arntzen CJ (eds) Photoinhibition. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 227–287
Barranguet C, Kromkamp J (2000) Estimating primary production rates from photosynthetic electron transport in estuarine microphytobenthos. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 204:39–52
Beardall J, Quigg A, Raven JA (2003) Oxygen consumption: photorespiration and chlororespiration. In: Larkum AWD, Duglas SE, Raven JA (eds) Photosynthesis in algae. Kluwer, Dordrecht, pp 157–181
Beardall J, Raven JA (2004) The potential effects of global climate change on microbial photosynthesis, growth and ecology. Phycologia 43:26–40
Boscolo PRS, Menossi M, Jorge RA (2003) Aluminium-induced oxidative stress in maize. Phytochemistry 62:181–189
Bradford M (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantification of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 180:136–139
De Brouwer JFC, Wolfstein K, Stal LJ (2002) Physical characterization and diel dynamics of different fractions of extracellular polysaccharides in an axenic culture of a benthic diatom. Eur J Phycol 37:37–44
Dix TA, Aikens J (1993) Mechanisms and biological relevance of lipid peroxidation initiation. Chem Res Toxicol 6:2–18
Foyer CH, Noctor G (2000) Tansley review No. 112. Oxygen processing in photosynthesis: regulation and signalling. New Phytol 146:359–388
Gigon A, Matos AR, Laffray D, Zuily-Fodil Y, Pham-Thi AT (2004) Effect of drought stress on lipid metabolism in the leaves of Arabidopsis thaliana (ecotype Columbia). Ann Bot 94:345–351
Girotti AW (1998) Lipid hydroperoxide generation, turnover and effector action in biological systems. J Lipid Res 30:1529–1539
Hermes-Lima M, Willimore WG, Storey KB (1995) Quantification of lipid Peroxidation in tissue extracts based on Fe(III)Xilenol orange complex formation. Free Radic Biol Med 19:271–280
Ishii N, Goto S, Hartman PS (2002) Protein oxidation during aging of the nematode Caeonorhabditis elegans. Free Radic Biol Med 33:1021–1025
Iturbe-Ormaetxe I, Escuredo PR, Arrese-Igor C, Becana M (1998) Oxidative damage in Pea plants exposed to water deficit or paraquat. Plant Physiol 116:173–181
Izard J, Limberger RJ (2003) Rapid screening method for quantitation of bacterial cell lipids from whole cells. J Microbiol Meth 55:411–418
Juneau P, Popovic R (1999) Evidence for the rapid phytotoxicity and environmental stress evaluation using the PAM fluorometric method: importance and future application. Ecotoxicology 8:449–455
Klatt P, Lamas S (2000) Regulation of protein function by S-glutathione in response to oxidative and nitrosative stress. Eur J Biochem 267:4928–4944
Knight JA, Shauna A, Rawle JM (1972) Chemical basis of the sulfo-phospho-vanillin method for estimating total serum lipids. Clin Chem 18:199–203
Krieger-Liszkay A (2004) Singlet oxygen production in photosynthesis. J Exp Bot 56(411):337–346
Kromkamp J, Peene J (1999) Estimation of phytoplankton photosynthesis and nutrient limitation in the Eastern Scheldt estuary using variable fluorescence. Aquat Ecol 33:101–104
Lavorel J, Etienne AL (1977) In vivo chlorophyll fluorescence. In: Barber J (ed) Primary processes of photosynthesis, vol II. Elsevier/North-Holland Biomedical Press, Amsterdam, pp 203–268
Levine RL, Garland D, Oliver CN, Amici A, Climent I, Lenz AG, Ahn B, Shaltiel S, Stadtman ER (1990) Determination of carbonyl content in oxidatively modified proteins. Methods Enzymol 186:464–478
Little C (2000) The biology of soft shores and estuaries. Oxford University Press, New York
Lyndsay MA, Giembycz MA (1997) Signal transduction and activation of the NADPH oxidase in eosinophils. Mem Inst Osvaldo Cruz 2:115–123
Mallick N, Mohn FH (2000) Reactive oxygen species: response of algal cells. J Plant Physiol 157:183–193
Masojidek J, Grobberlaar JU, Pechar L, Koblizek M (2001) Photosystem II electron transport rates and oxygen production in natural waterblooms of freshwater cyanobacteria during a diel cycle. J Plankton Res 23:57–66
McCord JM, Fridovich I (1969) Superoxide Dismutase: an enzymatic reaction for erythrocuprein (hemocuprein). J Biol Chem 244:6049–6055
Monteiro De Paula F, Pham-Thi AT, Vieira Da Silva J, Justin AM, Demandre C, Mazliak P (1990) Effects of water stress on the molecular species composition of polar lipids from Vigna unguiculata L. leaves. Plant Sci 66:185–193
Neale PJ (2000) Spectral weighting functions for quantifying effects of UV radiation in marine ecosystems. In: De Mora SJ, Demers S, Vernet M (eds) The effects of UV radiation in the marine environment. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, pp 72–100
Peletier H, Gieskes WWC, Buma AGJ (1996) Ultraviolet-B radiation resistance of benthic diatoms isolated from tidal flats in the Dutch Wadden Sea. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 135:163–168
Platt T, Gallegos CL, Harrison WG (1980) Photoinibition of photosynthesis in natural assemblages of marine phytoplankton. J Mar Res 38:687–701
Raven JA, Beardall J (2003) CO2 acquisition mechanisms of algae: carbon dioxide diffusion and carbon dioxide concentrated mechanisms. In: Larkum AW, Douglas SE, Raven JA (eds) Photosynthesis in algae. Kluwer, The Netherlands, pp 225–244
Rijstenbil JW (2001) Effects of periodic, low UVA radiation on cell characteristics and oxidative stress in the marine planktonic diatom Dytilum brightwellii. Eur J Phycol 36:1–8
Rijstenbil JW (2002) Assessment of oxidative stress in the planktonic diatom Thalassiosira pseudonana in response to UVA and UVB radiation. J Plankton Res 24:1277–1288
Rijstenbil JW (2003) Effects of UVB radiation and salt stress on growth, pigments and antioxidative defence of the marine diatom Cylindrotheca closterium. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 254:37–48
Rijstenbil JW (2005) UV- and salinity-induced oxidative effects in the marine diatom Cylindrotheca closterium during simulated emersion. Mar Biol 147:1063–1073
Rijstenbil JW, Gerringa LJA (2002) Interactions of algal ligands, metal complexation and availability and cell responses of the diatom Ditylum brightwellii with a gradual increase in copper. Aquat Toxicol 56:115–131
Rijstenbil JW, Wijnholds JA (1996) HPLC analyses of nonprotein thiols in planktonic diatoms: pool size, redox state and response to copper and cadmium exposure. Mar Biol 127:45–54
Rodriguez-Vargas S, Sanchez-Garcia A, Martinez-Rivas JM, Prieto JA, Randez-Gil F (2007) Fluidization of membrane lipids enhances the tolerance of Saccharomyces cerevisiae to freezing and salt stress. Appl Environ Microbiol 73:110–116
Sigaud-Kutner TCS, Pinto E, Neto AMP, Colepicolo P (2005) Changes in antioxidant enzyme activities, malondialdehyde, and glutathione contents in the dinoflagellate Lingulodinium polyedrum (Dinophyceae) grown in batch cultures. Phycol Res 53:209–214
Smirnoff N (1993) Transley review n. 52. The role of active oxygen in the response of plants to water deficit and dessication. New Phytol 125:27–58
Underwood GJC, Kromkamp JC (1999) Primary production by phytoplankton and microphytobenthos in estuaries. Adv Ecol Res 29:93–152
Withers K, Tunnel JW (1998) Identification of tidal flat alterations and identification of effects on biological productivity of these habitats within the coastal bend. Corpus Christi Bay National Estuary Program, publication CCBNEP 26
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Anita Wijnholds and Tanja Moerdijk for their help with the analyses.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by R. Cattaneo-Vietti.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Roncarati, F., Rijstenbil, J.W. & Pistocchi, R. Photosynthetic performance, oxidative damage and antioxidants in Cylindrotheca closterium in response to high irradiance, UVB radiation and salinity. Mar Biol 153, 965–973 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00227-007-0868-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00227-007-0868-9