Abstract
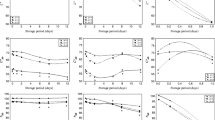
The colour parameters (CIE L*a*b*) of black locust (Robinia pseudoacacia L.) wood meals extracted with seven solvents and heated under saturate vapour at 120°C are measured and the UV–vis spectrum analysis of dioxane extractives is performed to investigate the influence of extraction and thermal treatment on wood discolouration. The results show that extractions with polar solvents such as water, ethanol and dioxane can cause substantial decrease of b* but have little effect on a* and that extractions with less or non-polar solvents such as chloroform, ether and hexane can hardly influence both a* and b*. Extractions with ethanol and dioxane can also increase the optical reflection (L*) and arise a higher ΔE change than that with less or non-polar solvents. Heat treatment has much more influence on colour parameters than extractions do. After heat treatment, the lightness index of all the samples declines but a* value increases. The discolouration during thermal treatment is mainly due to the existence of polar extractives. Tannins, flavonoids and hydroxyanthraquinones are found in the dioxane extractives. The heated dioxane extractives have an obvious absorption between 400 and 600 nm. The condensation of the tannin molecules and the oxidation of the hydroxyl groups in flavonol molecules make up the potential reason of the formation of new colour substances during heat treatment. The elimination of the dioxane extractives can effectively reduce the extent of thermally induced discolouration.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bekhta P, Niemz P (2003) Effect of high temperature on the change in color, dimensional stability and mechanical properties of spruce wood. Holzforschung 57:539–546
Burtin P, Jay-Allemand C, Charpentier J-P, Janin G (1998) Natural wood colouring process in Juglans sp. (J. nigra, J. regia and hybrid J. nigra 23 × J. regia) depends on the native phenolic compounds accumulated in the transition zone between sapwood and heartwood. Trees Struct Funct 12:258–264
Charrier B, Haluk JP, Metche M (1995) Characterization of European Oakwood constituents acting in the brown discolouration during kiln drying. Holzforschung 49:168–172
Christie RM (2001) Colour chemistry. Royal Society of Chemistry, Cambridge, p 27
Esteves B, Marques AV, Domingos I, Pereira H (2008) Heat-induced colour changes of pine (Pinus pinaster) and eucalypt (Eucalyptus globulus) wood. Wood Sci Technol 42:369–384
Gao J (2003a) Phytochemistry, 1st edn. Science Press, Beijing, pp 176–180
Gao J (2003b) Phytochemistry, 1st edn. Science Press, Beijing, pp 201–202
Hiltunen E, Alvila L, Pakkanen TT (2006a) Characterization of Brauns’ lignin from fresh and vacuum dried birch (Betula pendula) wood. Wood Sci Technol 40:575–584
Hiltunen E, Pakkanen TT, Alvila L (2006b) Phenolic compounds in silver birch (Betula pendula Roth) wood. Holzforschung 60:519–527
Kreber B, Fernandez M, McDonald AG (1998) Migration of kiln brown stain precursors during the drying of radiata pine sapwood. Holzforschung 52:441–446
Legocki A, Bothe H, Puhler A (1997) Biological fixation of nitrogen for ecology and sustainable agriculture. Springer, Berlin, pp 215–216
Luostarinen K (2006) Relationship of selected cell characteristics and colour of silver birch wood after two different drying processes. Wood Mater Sci Eng 1:21–28
Luostarinen K, Möttönen V (2004) Effects of log storage and drying on birch (Betula pendula) wood proanthocyanidin concentration and discoloration. J Wood Sci 50:151–156
Magel E, Jay-Allemand C, Ziegler H (1994) Formation of heartwood substances in the stemwood of Robinia pseudoacacia L. II. Distribution of nonstructural carbohydrates and wood extractives across the trunk. Trees Struct Funct 8:165–171
Mitsui K, Takada H, Sugiyama M, Hasegawa R (2001) Changes in the properties of light-irradiated wood with heat treatment, part 1. Effect of treatment conditions on the change in color. Holzforschung 55:601–605
Nuopponen M, Vuorinen T, Jamsa S, Viitaniemi P (2004) Thermal modifications in softwood studied by FT-IR and UV resonance Raman spectroscopies. J Wood Chem Technol 24:13–26
Oltean L, Teischinger A, Hansmann C (2008) Wood surface discolouration due to simulated indoor sunlight exposure. Holz Roh Werkst 66:51–56
Sehlstedt-Persson M (2003) Colour responses to heat-treatment of extractives and sap from pine and spruce. In: 8th International IUFRO wood drying conference, Brasov Romania, 24–29 August 2003, pp 459–464
Sivonen H, Maunu SL, Sundholm F, Jämsä S, Viitaniemi P (2002) Magnetic resonance studies of thermally modified wood. Holzforschung 56:648–654
Sundqvist B, Morén T (2002) The influence of wood polymers and extractives on wood colour induced by hydrothermal treatment. Holz Roh Werkst 60:375–376
Tjeerdsma BF, Boonstra M, Pizzi A, Tekeley P, Militz H (1998) Characterisation of thermally modified wood: molecular reasons for wood performance improvement. Holz Roh- Werkst 56:149–153
Wikberg H, Maunu SL (2004) Characterisation of thermally modified hard- and softwoods by 13C CPMAS NMR. Carbohydr Polym 58:461–466
Acknowledgments
Thanks are owed to the financial support from National Natural Science Foundation of China for this research (serial number of the project: 30671633).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fan, Y., Gao, J. & Chen, Y. Colour responses of black locust (Robinia pseudoacacia L.) to solvent extraction and heat treatment. Wood Sci Technol 44, 667–678 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00226-009-0289-7
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00226-009-0289-7