Abstract
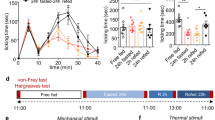
The amygdala has been demonstrated to contribute to pain-related behavior and food preference. Here, the effect of pain on food preference and food-matched visual-cue memory, in the presence or absence of a basolateral amygdala (BLA) lesion, has been evaluated using a novel innovative apparatus and protocol. Forty adult male Wistar rats were randomly divided into five groups (n = 8) as follows: control, pain, ibuprofen + pain, BLA lesion, BLA lesion + pain groups. Bilateral lesions of the BLA were produced by passing a current of 1.5 mA for 7 s. Pain was induced on the right hind paw of the rats by sub-plantar injection of 50 μl of 2.5% formalin. The animals were encountered with four different meals including wholemeal, wholemeal + sugar, white flour, and biscuit. Each test session consisted of six trials with inter-trial intervals of 15 min. The number of visits to each meal zone and port, the amount of time spent in each food zone and port, traveled distance in each food zone, food consumption per each visit and the total food consumption were recorded. The control group showed a high biscuit preference and low white flour preference. Rats suffering BLA lesion and rats in the BLA lesion + pain group exhibited a shifted preference curve. They had a bias toward eating wholemeal + sugar rather than white flour and biscuit. This group also showed an impaired spatial memory. In conclusion, our findings suggest that the BLA may be involved in pain-induced food preference and food-matched visual-cue memory.








Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and material
The data and materials for all experiments are available upon request from the corresponding author and will be made available in a data repository prior to the publication.
References
Álvarez EO, Ruarte MB (2004) Glutamic acid and histamine-sensitive neurons in the ventral hippocampus and the basolateral amygdala of the rat: functional interaction on memory and learning processes. Behav Brain Res 152:209–219
Amorim D, David-Pereira A, Pertovaara A, Almeida A, Pinto-Ribeiro F (2014) Amitriptyline reverses hyperalgesia and improves associated mood-like disorders in a model of experimental monoarthritis. Behav Brain Res 265:12–21
Anseloni VC, Weng H-R, Terayama R et al (2002) Age-dependency of analgesia elicited by intraoral sucrose in acute and persistent pain models. Pain 97:93–103
Baile C, Martin F, Forbes J, Webb R, Kingsbury W (1974) Intrahypothalamic injections of prostaglandins and prostaglandin antogonists and feeding in sheep. J Dairy Sci 57:81–88
Barnett S, Spencer MM (1953) Experiments on the food preferences of wild rats (Rattus norvegicus Berkenhout). Epidemiol Infect 51:16–34
Becker S, Gandhi W, Schweinhardt P (2012) Cerebral interactions of pain and reward and their relevance for chronic pain. Neurosci Lett 520:182–187
Benemei S, Nicoletti P, Capone JG, Geppetti P (2009) CGRP receptors in the control of pain and inflammation. Curr Opin Pharmacol 9:9–14
Benoit SC, Davis JF, Davidson T (2010) Learned and cognitive controls of food intake. Brain Res 1350:71–76
Bodnar RJ (2004) Endogenous opioids and feeding behavior: a 30-year historical perspective. Peptides 25:697–725
Borsini F, Rolls E (1984) Role of noradrenaline and serotonin in the basolateral region of the amygdala in food preferences and learned taste aversions in the rat. Physiol Behav 33:37–43
Box BM, Mogenson G (1975) Alterations in ingestive behaviors after bilateral lesions of the amygdala in the rat. Physiol Behav 15:679–688
Bushnell M, Case L, Ceko M et al (2015) Effect of environment on the long-term consequences of chronic pain. Pain 156:S42
Choi KW, Somers TJ, Babyak MA, Sikkema KJ, Blumenthal JA, Keefe FJ (2014) The relationship between pain and eating among overweight and obese individuals with osteoarthritis: an ecological momentary study. Pain Res Manag 19:e159–e163
Cooper SJ, Turkish S (1989) Effects of naltrexone on food preference and concurrent behavioral responses in food-deprived rats. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 33:17–20
de la Puente B, Romero-Alejo E, Vela JM, Merlos M, Zamanillo D, Portillo-Salido E (2015) Changes in saccharin preference behavior as a primary outcome to evaluate pain and analgesia in acetic acid-induced visceral pain in mice. J Pain Res 8:663
Desgranges B, Ramirez-Amaya V, Ricaño-Cornejo I, Lévy F, Ferreira G (2010) Flavor preference learning increases olfactory and gustatory convergence onto single neurons in the basolateral amygdala but not in the insular cortex in rats. PLoS ONE 5:e10097
Drewnowski A, Mennella JA, Johnson SL, Bellisle F (2012) Sweetness and food preference. J Nutr 142:1142S-1148S
Dueñas M, Ojeda B, Salazar A, Mico JA, Failde I (2016) A review of chronic pain impact on patients, their social environment and the health care system. J Pain Res 9:457
Garzón J, Sánchez-Blázquez P, Höllt V, Lee N, Loh H (1983) Endogenous opioid peptides: comparative evaluation of their receptor affinities in the mouse brain. Life Sci 33:291–294
Gehlert D (1999) Role of hypothalamic neuropeptide Y in feeding and obesity. Neuropeptides 33:329–338
Gosnell B, Levine A (2009) Reward systems and food intake: role of opioids. Int J obes 33:54–58
Han JS, Adwanikar H, Li Z, Ji G, Neugebauer V (2010) Facilitation of synaptic transmission and pain responses by CGRP in the amygdala of normal rats. Mol Pain. https://doi.org/10.1186/1744-8069-6-10
Harrison D, Bueno M, Yamada J, Adams-Webber T, Stevens B (2010) Analgesic effects of sweet-tasting solutions for infants: current state of equipoise. Pediatrics 126:894–902
Hökfelt T, Brumovsky P, Shi T, Pedrazzini T, Villar M (2007) NPY and pain as seen from the histochemical side. Peptides 28:365–372
Inglis I, Shepherd D, Smith P, Haynes P, Bull D, Cowan D, Whitehead D (1996) Foraging behaviour of wild rats (Rattus norvegicus) towards new foods and bait containers. Appl Anim Behav Sci 47:175–190
Inui-Yamamoto C, Yamamoto T, Ueda K, Nakatsuka M, Kumabe S, Inui T, Iwai Y (2017) Taste preference changes throughout different life stages in male rats. PLoS ONE 12:e0181650
Ishizuka T, Sako N, Murotani T, Morimoto A, Yamatodani A, Ohura K (2010) The effect of hardness of food on amygdalar histamine release in rats. Brain Res 1313:97–102
Ji G, Neugebauer V (2009) Hemispheric lateralization of pain processing by amygdala neurons. J Neurophysiol 102:2253–2264
Ji G, Sun H, Fu Y, Li Z, Pais-Vieira M, Galhardo V, Neugebauer V (2010) Cognitive impairment in pain through amygdala-driven prefrontal cortical deactivation. J Neurosci 30:5451–5464
Jung AP, Curtis TS, Turner MJ, Lightfoot JT (2010) Physical activity and food consumption in high-and low-active inbred mouse strains. Med Sci Sports Exerc 42:1826
Kakeda T, Ogino Y, Moriya F, Saito S (2010) Sweet taste-induced analgesia: an fMRI study. NeuroReport 21:427–431
Kapitzke D, Vetter I, Cabot PJ (2005) Endogenous opioid analgesia in peripheral tissues and the clinical implications for pain control. Ther clin risk manage 1:279
Kawabata A (2011) Prostaglandin E2 and pain—an update. Biol Pharm Bull 34:1170–1173
Kemble ED, Levine MS, Gregoire K, Koepp K, Thomas TT (1972) Reactivity to saccharin and quinine solutions following amygdaloid or septal lesions in rats. Behav Biol 7:503–512
Kemble ED, Schwartzbaum J (1969) Reactivity to taste properties of solutions following amygdaloid lesions. Physiol Behav 4:981–985
Kim SF (2012) Animal models of eating disorders. Neuroscience 211:2–12
Kolesnikov Y, Cristea M, Oksman G, Torosjan A, Wilson R (2004) Evaluation of the tail formalin test in mice as a new model to assess local analgesic effects. Brain Res 1029:217–223
Kooshki R, Abbasnejad M, Esmaeili-Mahani S, Raoof M (2017) The modulatory role of orexin 1 receptor in CA1 on orofacial pain-induced learning and memory deficits in rats. Basic Clin Neurosci 8:213
Korz V, Frey JU (2005) Bidirectional modulation of hippocampal long-term potentiation under stress and no-stress conditions in basolateral amygdala-lesioned and intact rats. J Neurosci 25:7393–7400
Kracke GR, Uthoff KA, Tobias JD (2005) Sugar solution analgesia: the effects of glucose on expressed mu opioid receptors. Anesth Analg 101:64–68
Laviano A, Di Lazzaro L, Koverech A (2018) Changes in eating behavior, taste and food preferences and the effects of gastrointestinal hormones. Clin Nutr Exp 20:65–70
Lee MC, Ploner M, Wiech K et al (2013) Amygdala activity contributes to the dissociative effect of cannabis on pain perception. PAIN® 154:124–134
Li N, Liang J, Fang C-Y, Han H-R, Ma M-S, Zhang G-X (2008) Involvement of CGRP and CGRPl receptor in nociception in the basolateral nucleus of amygdala of rats. Neurosci Lett 443:184–187
Li Z, Wang J, Chen L, Zhang M, Wan Y (2013) Basolateral amygdala lesion inhibits the development of pain chronicity in neuropathic pain rats. PLoS ONE 8:e70921
Lyte JM (2018) Eating for 3.8 × 1013: examining the impact of diet and nutrition on the microbiota-gut-brain axis through the lens of microbial endocrinology. Front Endocrinol. https://doi.org/10.3389/fendo.2018.00796
Maren S (1999) Neurotoxic basolateral amygdala lesions impair learning and memory but not the performance of conditional fear in rats. J Neurosci 19:8696–8703
Martire SI, Holmes N, Westbrook RF, Morris MJ (2013) Altered feeding patterns in rats exposed to a palatable cafeteria diet: increased snacking and its implications for development of obesity. PLoS ONE 8:e60407
Nesa L, Munira S, Mollika S, Islam M (2014) Evaluation of analgesic, anti-inflammatory and CNS depressant activities of methanolic extract of Lawsonia inermis barks in mice. Avicenna J Phytomed 4:287
Neugebauer V (2015) Amygdala pain mechanisms. Pain control. Springer, Berlin, pp 261–284
Neugebauer V, Galhardo V, Maione S, Mackey SC (2009) Forebrain pain mechanisms. Brain Res Rev 60:226–242
Nuseir KQ, Alzoubi KH, Alhusban A, Bawaane A, Al-Azzani M, Khabour OF (2017) Sucrose and naltrexone prevent increased pain sensitivity and impaired long-term memory induced by repetitive neonatal noxious stimulation: role of BDNF and β-endorphin. Physiol Behav 179:213–219
Paré D (2003) Role of the basolateral amygdala in memory consolidation. Prog Neurobiol 70:409–420
Parent AJ, Beaudet N, Beaudry H et al (2012) Increased anxiety-like behaviors in rats experiencing chronic inflammatory pain. Behav Brain Res 229:160–167
Passani MB, Blandina P, Torrealba F (2011) The histamine H3 receptor and eating behavior. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 336:24–29
Raoul S, Leduc D, Vegas T et al (2007) Deep brain stimulation electrodes used for staged lesion within the basal ganglia: experimental studies for parameter validation. J Neurosurg 107:1027–1035
Reid LD (1985) Endogenous opioid peptides and regulation of drinking and feeding. Am J Clin Nutr 42:1099–1132
Rolls BJ, Rolls ET (1973a) Effects of lesions in the basolateral amygdala on fluid intake in the rat. J Comp Physiol Psychol 83:240
Rolls ET, Rolls BJ (1973b) Altered food preferences after lesions in the basolateral region of the amygdala in the rat. J Comp Physiol Psychol 83:248
Schou WS, Ashina S, Amin FM, Goadsby PJ, Ashina M (2017) Calcitonin gene-related peptide and pain: a systematic review. J Headache Pain 18:34
Segawa T, Miyakoshi N, Kasukawa Y, Aonuma H, Tsuchie H, Shimada Y (2013) Analgesic effects of minodronate on formalin-induced acute inflammatory pain in rats. Biomed Res 34:137–141
Siegel A, Joyner K, Smith G (1987) Amygdaloid-lesion decrease sham feeding of sucrose. International journal of obesity, vol 11. Stockton Press Houndmills, Basingstoke, pp 22–22
Skoubis P, Lam H, Shoblock J, Narayanan S, Maidment N (2005) Endogenous enkephalins, not endorphins, modulate basal hedonic state in mice. Eur J Neurosci 21:1379–1384
Small DM, Apkarian AV (2006) Increased taste intensity perception exhibited by patients with chronic back pain. Pain 120:124–130
Smeester BA, Lee J-H, Beitz AJ (2017) Influence of social interaction on nociceptive-induced changes in locomotor activity in a mouse model of acute inflammatory pain: use of novel thermal assays. Brain Res Bull 134:47–54
Smeets PA, Charbonnier L, van Meer F, van der Laan LN, Spetter MS (2012) Food-induced brain responses and eating behaviour. Proc Nutr Soc 71:511–520
Solway B, Bose SC, Corder G, Donahue RR, Taylor BK (2011) Tonic inhibition of chronic pain by neuropeptide Y. Proc Natl Acad Sci 108:7224–7229
Tamaddonfard E, Khalilzadeh E, Hamzeh-Gooshchi N, Seiednejhad-Yamchi S (2008) Central effect of histamine in a rat model of acute trigeminal pain. Pharmacol Rep 60:219
Thompson JM, Neugebauer V (2017) Amygdala plasticity and pain. Pain research & management 2017
Wang Y, Fontanini A, Katz DB (2006) Temporary basolateral amygdala lesions disrupt acquisition of socially transmitted food preferences in rats. Learn Mem 13:794–800
Wassum K, Ostlund S, Maidment N, Balleine B (2009) Distinct opioid circuits determine the palatability and the desirability of rewarding events. Proc Natl Acad Sci 106:12512–12517
Yamamoto T, Ueji K (2011) Brain mechanisms of flavor learning. Front Syst Neurosci 5:76
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by funds from Shahid Bahonar University of Kerman.
Funding
This study was financially supported by Shahid Bahonar University of Kerman, Kerman, Iran (Grant number: 98.6).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study. MA designed the study protocol. MZ collected the data. SEM carried out the statistical analyses. MA and VS and MR drafted the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
There is no conflict of interest to declare.
Ethical approval
All experiments were executed in accordance with the guidelines on ethical standards for investigation in animals in Shahid Bahonar University of Kerman, Kerman, Iran (IR.UK.VETMED.REC.1398.018).
Additional information
Communicated by Sreedharan Sajikumar.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zamyad, M., Abbasnejad, M., Esmaeili-Mahani, S. et al. Pain influences food preference and food-related memory by activating the basolateral amygdala in rats. Exp Brain Res 239, 79–93 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00221-020-05961-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00221-020-05961-1