Abstract
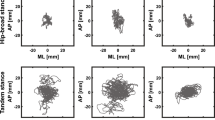
The aim of the present study was to evaluate the effects of mental fatigue (MF) induced by a 90-min continuous demanding cognitive task on balance control. Twenty healthy young participants were recruited. They had to perform three postural tasks (on a stable support with eyes open, with eyes closed and on a wobble board) while standing on a force platform before and after watching a documentary in a control condition or carrying out a prolonged continuous demanding cognitive task (AX-continuous performance test—AX-CPT) in a MF condition. Results showed that performing the AX-CPT generated MF since participants felt a higher subjective workload from the NASA Task Load Index after the AX-CPT than after viewing the documentary. Both the AX-CPT and the viewing of the documentary impaired balance control, mainly by affecting postural regulatory mechanisms which evolved towards a less automatic and less complex regulation mode with an increased participation of cognitive resources. MF generated by the AX-CPT affected balance control by compromising the attentional processing, while the deleterious influence of watching a documentary on postural control could stem from an adverse effect of prolonged sitting on balance control during subsequent standing.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baker R, Coenen P, Howie E, Williamson A, Straker L (2018) The short term musculoskeletal and cognitive effects of prolonged sitting during office computer work. Int J Environ Res Public Health. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph15081678
Blons E, Arsac LM, Gilfriche P et al (2019) Alterations in heart–brain interactions under mild stress during a cognitive task are reflected in entropy of heart rate dynamics. Sci Rep 9(1):18190. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-54547-7
Boksem MAS, Tops M (2008) Mental fatigue: costs and benefits. Brain Res Rev 59:125–139
Boksem MAS, Meijman TF, Lorist MM (2005) Effects of mental fatigue on attention: an ERP study. Cogn Brain Res 25:107–116
Bonnet CT (2016) Advantages and disadvantages of stiffness instructions when studying postural control. Gait Posture 46:208–210
Cherng RJ, Lee HY, Su FC (2003) Frequency spectral characteristics of standing balance in children and young adults. Med Eng Phys 25:509–515
Cug M, Wikstrom EA (2014) Learning effects associated with the least stable level of the Biodex® stability system during dual and single limb stance. J Sports Sci Med 13:387–392
Deschamps T, Magnard J, Cornu C (2013) Postural control as a function of time-of-day: influence of a prior strenuous running exercise or demanding sustained-attention task. J Neuroeng Rehabil 10:26. https://doi.org/10.1186/1743-0003-10-26
Dolan KJ, Green A (2006) Lumbar spine reposition sense: the effect of a ‘slouched’ posture. Man Ther 11(3):202–207
Doumas M, Morsanyi K, Young WR (2018) Cognitively and socially induced stress affects postural control. Exp Brain Res 236(1):305–314
Fothergill A, Linfield M (2007) Earth [Motion picture]. BBC Worldwide
Franco C, Fleury A, Diot B, Vuillerme N (2018) Applying entropy to human center of foot pressure data to assess attention investment in balance control. Conf Proc IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc 2018:5586–5589. https://doi.org/10.1109/EMBC.2018.8513533
Hart SG, Staveland LE (1988) Development of NASA-TLX (Task Load Index): results of empirical and theoretical research. In: Hancock PA, Meshkati N (eds) Human mental workload. North-Holland, Amsterdam, pp 139–183
Howarth SJ, Glisic D, Lee JG, Beach TA (2013) Does prolonged seated deskwork alter the lumbar flexion relaxation phenomenon? J Electromyogr Kinesiol 23(3):587–593
Ivanenko YP, Solopova IA, Levik YS (2000) The direction of postural instability affects postural reactions to ankle muscle vibration in humans. Neurosci Lett 292(2):103–106
Kastelic K, Voglar M, Šarabon N (2018) Acute effect of full time office work in real environment on postural actions and lumbar range of motion. J Electromyogr Kinesiol 43:82–87
Lajoie Y, Teasdale N, Bard C, Fleury M (1993) Attentional demands for static and dynamic equilibrium. Exp Brain Res 97:139–144
Le Mansec Y, Pageaux B, Nordez A, Dorel S, Jubeau M (2017) Mental fatigue alters the speed and the accuracy of the ball in table tennis. J Sports Sci 36(23):2751–2759
Maincent A, Martin R, Van Box Som D (2005) Evaluation de la charge de travail d’opérateurs d’un système complexe à risques, le cas du pilotage d’une centrale nucléaire. Cahiers de la MRSH no spécial, pp 345–365
Marcora SM, Staiano W, Manning V (2009) Mental fatigue impairs physical performance in humans. J Appl Physiol 106:857–864
Martin K, Meeusen R, Thompson KG, Keegan R, Rattray B (2018) Mental fatigue impairs endurance performance: a physiological explanation. Sports Med 48(9):2041–2051
Pageaux B, Lepers R (2018) The effects of mental fatigue on sport-related performance. Prog Brain Res 240:291–315
Pageaux B, Marcora SM, Lepers R (2013) Prolonged mental exertion does not alter neuromuscular function of the knee extensors. Med Sci Sports Exerc 45:2254–2264
Paillard T (2017) Plasticity of the postural function to sport and/or motor experience. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 72:129–152
Paillard T, Noé F, Bru N, Couderc M, Debove L (2016) The impact of time of day on the gait and balance control of Alzheimer's patients. Chronobiol Int 33(2):161–168
Pallant J (2007) SPSS survival manual: a step by step guide to data analysis using SPSS for Windows. Berkshire, England
Palluel E, Nougier V, Olivier I (2010) Postural control and attentional demand during adolescence. Brain Res 1358:151–159
Pires FO, Silva-Júnior FL, Brietzke C, Franco-Alvarenga PE, Pinheiro FA, de França NM, Teixeira S, Meireles Santos T (2018) Mental fatigue alters cortical activation and psychological responses, impairing performance in a distance-based cycling Trial. Front Physiol 9:227. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphys.2018.00227
R Core Team (2016) R: a language and environment for statistical computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria. https://www.R-project.org/. Accessed 24 June 2018
Ramdani S, Seigle B, Lagarde J, Bouchara F, Bernard PL (2009) On the use of sample entropy to analyze human postural sway data. Med Eng Phys 31(8):1023–1031
Razon S, Basevitch I, Land W, Thompson B, Tenenbaum G (2009) Perception of exertion and attention allocation as a function of visual and auditory conditions. Psychol Sport Exerc 10:636–643
Reinert SS, Kinney AL, Jackson K, Diestelkamp W, Bigelow K (2017) Age stratification and sample entropy analysis enhance the limits of stability tests for older adults. J Appl Biomech 33(6):419–423
Roerdink M, Hlavackova P, Vuillerme N (2011) Effects of plantar-flexor muscle fatigue on the magnitude and regularity of center-of-pressure fluctuations. Exp Brain Res 212(3):471–476
Rozand V, Lebon F, Papaxanthis C, Lepers R (2015) Effect of mental fatigue on speed-accuracy trade-off. Neuroscience 297:219–230
Schweimer J, Hauber W (2006) Dopamine D1 receptors in the anterior cingulate cortex regulate effort-based decision making. Learn Mem 13(6):777–782
Smith MR, Marcora SM, Coutts AJ (2015) Mental fatigue impairs intermittent running performance. Med Sci Sports Exerc 47:1682–1690
Smith MR, Thompson C, Marcora SM, Skorski S, Meyer T, Coutts AJ (2018) Mental fatigue and soccer: current knowledge and future directions. Sports Med 48(7):1525–1532
Smith MR, Chai R, Nguyen HT, Marcora SM, Coutts AJ (2019) Comparing the effects of three cognitive tasks on indicators of mental fatigue. J Psychol 153(8):759–783
Triglav J, Howe E, Cheema J, Dube B, Fenske MJ, Strzalkowski N, Bent L (2019) Physiological and cognitive measures during prolonged sitting: comparisons between a standard and multi-axial office chair. Appl Ergon 78:176–183
Vaillancourt DE, Newell KM (2002) Changing complexity in human behavior and physiology through aging and disease. Neurobiol Aging 23:1–11
Van der Linden D, Massar SAA, Schellekens AFA, Ellenbroek BA, Verkes RJ (2006) Disrupted sensorimotor gating due to mental fatigue: preliminary evidence. Int J Psychophysiol 62:168–174
Van Cutsem J, Marcora S, De Pauw K, Bailey S, Meeusen R, Roelands B (2017) The effects of mental fatigue on physical performance: a systematic review. Sports Med 47(8):1569–1588
Acknowledgements
The authors thank all the subjects for their cooperation.
Funding
This research did not receive any specific grant from funding agencies in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization: BH, FN, HC; methodology: BH, FN, HC; data curation: BH; formal analysis: BH, BT; software: BT; writing-original draft preparation: BH; writing-review and editing: FN, TP, HC; supervision: FN, TP.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Additional information
Communicated by Winston D. Byblow.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hachard, B., Noé, F., Ceyte, H. et al. Balance control is impaired by mental fatigue due to the fulfilment of a continuous cognitive task or by the watching of a documentary. Exp Brain Res 238, 861–868 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00221-020-05758-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00221-020-05758-2